比特币源码情景分析之启动初始化
源码情景分析系列写到这里,大家可能会有疑惑,标准套路不是一开始就讲启动初始化的嘛,为啥现在才姗姗来迟.其实我一开始也是从main函数入手开始一步一步看下去,但是发现,只能看个大概,没什么感觉(当然,这一步我推荐也是要走的,只不过只需要初略的看完即可,然后就应该带有目的的去看具体模块)。于是就以具体情境需求出发,带有问题有针对性的去看具体代码,比如P2SH究竟是什么(有了script相关的博文)? SPV支持如何实现的(有了spv, bloom filter的相关文章)?区块是如何sync下来的,别人挖到新区块后本节点是如何拿到区块内容的(有了前面的message相关的文章)。然后探索这几个问题的时候,一部分初始化的内容其实也已经接触到了,比如脚本执行线程初始化,消息处理线程初始化, 网络事件监听线程初始化。所以接下来就是走下整个启动初始化以更了解更多细节。
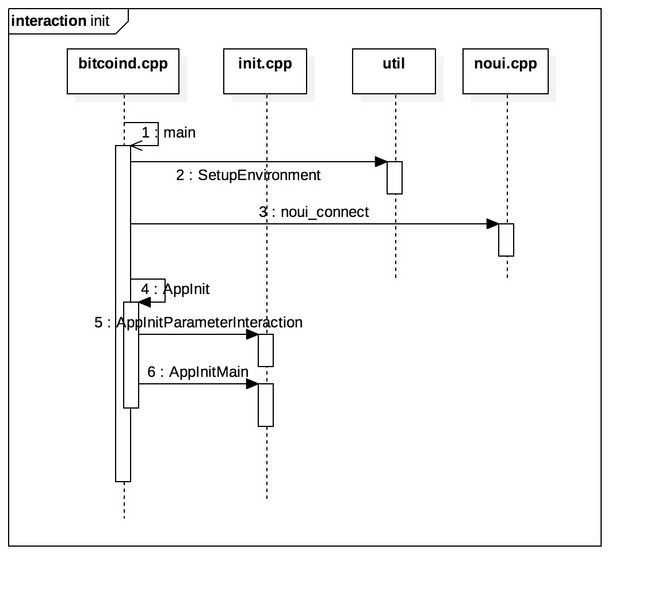
哪个才是真正的main函数
我们知道c++可执行程序的入口是main函数,由于bitcoin包含了各种测试程序,所以整个源码有多个main函数的,不过通过看文件名即可大概猜出bitcoind.cpp的main函数才是真正core的入口.
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//这个函数基本没做什么有用的事
SetupEnvironment
();
// Connect bitcoind signal handlers
// 初始化signal handlers
// signal handlers是什么呢?很多博文以较大篇幅来描述这个,其实我觉得这个概念很简单
// 你可以认为是系统定义了很多全局函数指针signal,各个模块可以调用这些函数指针
// 而具体函数的实现就是handler, 通过connect函数来将实现(handler)赋值给指针signal来实现,并且可以动态更改
noui_connect();
//所以实际性的初始化就是AppInit函数了
return (
AppInit
(argc, argv) ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE);
}
void
SetupEnvironment
()
{
#ifdef HAVE_MALLOPT_ARENA_MAX
// glibc-specific: On 32-bit systems set the number of arenas to 1.
// By default, since glibc 2.10, the C library will create up to two heap
// arenas per core. This is known to cause excessive virtual address space
// usage in our usage. Work around it by setting the maximum number of
// arenas to 1.
if (sizeof(void*) == 4) {
mallopt(M_ARENA_MAX, 1);
}
#endif
// On most POSIX systems (e.g. Linux, but not BSD) the environment's locale
// may be invalid, in which case the "C" locale is used as fallback.
#if !defined(WIN32) && !defined(MAC_OSX) && !defined(__FreeBSD__) && !defined(__OpenBSD__)
try {
std::locale(""); // Raises a runtime error if current locale is invalid
} catch (const std::runtime_error&) {
setenv("LC_ALL", "C", 1);
}
#endif
// The path locale is lazy initialized and to avoid deinitialization errors
// in multithreading environments, it is set explicitly by the main thread.
// A dummy locale is used to extract the internal default locale, used by
// fs::path, which is then used to explicitly imbue the path.
std::locale loc = fs::path::imbue(std::locale::classic());
fs::path::imbue(loc);
}
void noui_connect()
{
// Connect bitcoind signal handlers
// 将具体实现绑定到各个全局函数指针signal
//这几个函数也没啥什么用,可以不用看
uiInterface.ThreadSafeMessageBox.connect(noui_ThreadSafeMessageBox);
uiInterface.ThreadSafeQuestion.connect(noui_ThreadSafeQuestion);
uiInterface.InitMessage.connect(noui_InitMessage);
}
还是看核心函数AppInit吧
bool AppInit(int argc, char* argv[])
{
bool fRet = false;
#if ENABLE_WALLET
//如果钱包功能开启了,就会初始化钱包模块,这里是由宏控制,所以这是一个编译选项而不是运行参数
g_wallet_init_interface.reset(new WalletInit);
#else
g_wallet_init_interface.reset(new DummyWalletInit);
#endif
//
// Parameters
//
// If Qt is used, parameters/bitcoin.conf are parsed in qt/bitcoin.cpp's main()
gArgs.ParseParameters(argc, argv);
// Process help and version before taking care about datadir
if (HelpRequested(gArgs) || gArgs.IsArgSet("-version")) {
std::string strUsage = strprintf(_("%s Daemon"), _(PACKAGE_NAME)) + " " + _("version") + " " + FormatFullVersion() + "\n";
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-version"))
{
strUsage += FormatParagraph(LicenseInfo());
}
else
{
strUsage += "\n" + _("Usage:") + "\n" +
" bitcoind [options] " + strprintf(_("Start %s Daemon"), _(PACKAGE_NAME)) + "\n";
strUsage += "\n" + HelpMessage(HelpMessageMode::BITCOIND);
}
fprintf(stdout, "%s", strUsage.c_str());
return true;
}
try
{
//检测程序配置目录是否存在,如果是通过参数指定的,必须存在,否则会创建默认的目录
if (!fs::is_directory(GetDataDir(false)))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Specified data directory \"%s\" does not exist.\n", gArgs.GetArg("-datadir", "").c_str());
return false;
}
try
{
//读取配置文件bitcoin.conf
gArgs.ReadConfigFile(gArgs.GetArg("-conf",
BITCOIN_CONF_FILENAME
));
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
fprintf(stderr,"Error reading configuration file: %s\n", e.what());
return false;
}
// Check for
-testnet or -regtest
parameter (Params() calls are only valid after this clause)
// 选择网络,比如是testnet,还mainnet还是私有网络
try {
SelectParams(ChainNameFromCommandLine());
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", e.what());
return false;
}
// -server defaults to true for bitcoind but not for the GUI so do this here
gArgs.SoftSetBoolArg("-server", true);
// Set this early so that parameter interactions go to console
// 和log相关的配置,比如是否打印ip等,不太重要
InitLogging();
//这个是和网络相关的配置,比如监听端口,ip, 白名单ip, dnsseed等, dnsseed比较重要,因为peer节点最开始就是这些seed,然后这些节点又可以返回更多节点信息
InitParameterInteraction
();
//系统相关的配置,比如SIGTERM, SIGINT, SIGUP信号的处理, 系统默认权限sysperm配置
if (!AppInitBasicSetup())
{
// InitError will have been called with detailed error, which ends up on console
return false;
}
// 这个是个核心函数,大部分的参数解释在这里, 比如最大连接数,是否prune,mempool的大小,checkpoint点
if (!
AppInitParameterInteraction
())
{
// InitError will have been called with detailed error, which ends up on console
return false;
}
//这个是程序完整性验证, 比如依赖库是否存在啊
if (!AppInitSanityChecks())
{
// InitError will have been called with detailed error, which ends up on console
return false;
}
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-daemon", false))
{
#if HAVE_DECL_DAEMON
fprintf(stdout, "Bitcoin server starting\n");
// Daemonize
if (daemon(1, 0)) { // don't chdir (1), do close FDs (0)
fprintf(stderr, "Error: daemon() failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return false;
}
#else
fprintf(stderr, "Error: -daemon is not supported on this operating system\n");
return false;
#endif // HAVE_DECL_DAEMON
}
// Lock data directory after daemonization
//锁定数据目录
if (!
AppInitLockDataDirectory
())
{
// If locking the data directory failed, exit immediately
return false;
}
//这个是最大核心,前面的初始化都是局限在参数解释等小打小闹
fRet = AppInitMain();
}
catch (const std::exception& e) {
PrintExceptionContinue(&e, "AppInit()");
} catch (...) {
PrintExceptionContinue(nullptr, "AppInit()");
}
if (!fRet)
{
Interrupt();
} else {
WaitForShutdown();
}
Shutdown();
return fRet;
}
总结下来,有这几个函数:
- InitLogging():日志记录以及打印配置初始化, 比如是输出到终端还是文件。
-
InitParameterInteraction():监听端口,代理等网络参数初始化。
-
AppInitBasicSetup():系统相关的配置,比如SIGTERM, SIGINT, SIGUP消息的处理, 系统默认权限sysperm配置。
-
AppInitParameterInteraction():设置区块链运行参数,例如最大连接数,是否prune,mempool,交易费等等。
-
AppInitSanityChecks():程序运行环境比如库是否完整。
-
AppInitMain():核心初始化函数。
- ShutDown():关闭所有后台进程并清理程序。
上面橙色的函数才是需要重点看的,其他的大家基本可以忽略,等有具体业务再看都行。
AppInitParameterInteraction函数
bool AppInitParameterInteraction()
{
const CChainParams& chainparams = Params();
// ********************************************************* Step 2: parameter interactions
// also see: InitParameterInteraction()
//存储block数据的目录是否存在
if (!fs::is_directory(GetBlocksDir(false))) {
return InitError(strprintf(_("Specified blocks directory \"%s\" does not exist.\n"), gArgs.GetArg("-blocksdir", "").c_str()));
}
// if using block pruning, then disallow txindex
if (gArgs.GetArg("-prune", 0)) {
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-txindex", DEFAULT_TXINDEX))
return InitError(_("Prune mode is incompatible with -txindex."));
}
// -bind and -whitebind can't be set when not listening
// 监听网络绑定到哪个ip,可以绑定哪些ip, 这个主要是多网卡时(无线,有限网络),主动选择网络,一般设置为0.0.0.0自动即可,比如有些VPS用的是虚拟网络,可能会变化
size_t nUserBind = gArgs.GetArgs("-bind").size() + gArgs.GetArgs("-whitebind").size();
if (nUserBind != 0 && !gArgs.GetBoolArg("-listen", DEFAULT_LISTEN)) {
return InitError("Cannot set -bind or -whitebind together with -listen=0");
}
// Make sure enough file descriptors are available
int nBind = std::max(nUserBind, size_t(1));
//获取用户配置的最大连接数,并检测系统网络最大连接数
nUserMaxConnections = gArgs.GetArg("-maxconnections", DEFAULT_MAX_PEER_CONNECTIONS);
nMaxConnections = std::max(nUserMaxConnections, 0);
// Trim requested connection counts, to fit into system limitations
nMaxConnections = std::max(std::min(nMaxConnections, FD_SETSIZE - nBind - MIN_CORE_FILEDESCRIPTORS - MAX_ADDNODE_CONNECTIONS), 0);
nFD = RaiseFileDescriptorLimit(nMaxConnections + MIN_CORE_FILEDESCRIPTORS + MAX_ADDNODE_CONNECTIONS);
if (nFD < MIN_CORE_FILEDESCRIPTORS)
return InitError(_("Not enough file descriptors available."));
nMaxConnections = std::min(nFD - MIN_CORE_FILEDESCRIPTORS - MAX_ADDNODE_CONNECTIONS, nMaxConnections);
if (nMaxConnections < nUserMaxConnections)
InitWarning(strprintf(_("Reducing -maxconnections from %d to %d, because of system limitations."), nUserMaxConnections, nMaxConnections));
// ********************************************************* Step 3: parameter-to-internal-flags
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-debug")) {
// Special-case: if -debug=0/-nodebug is set, turn off debugging messages
const std::vector categories = gArgs.GetArgs("-debug");
if (std::none_of(categories.begin(), categories.end(),
[](std::string cat){return cat == "0" || cat == "none";})) {
for (const auto& cat : categories) {
uint32_t flag = 0;
if (!GetLogCategory(&flag, &cat)) {
InitWarning(strprintf(_("Unsupported logging category %s=%s."), "-debug", cat));
continue;
}
logCategories |= flag;
}
}
}
// Now remove the logging categories which were explicitly excluded
for (const std::string& cat : gArgs.GetArgs("-debugexclude")) {
uint32_t flag = 0;
if (!GetLogCategory(&flag, &cat)) {
InitWarning(strprintf(_("Unsupported logging category %s=%s."), "-debugexclude", cat));
continue;
}
logCategories &= ~flag;
}
// Check for -debugnet
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-debugnet", false))
InitWarning(_("Unsupported argument -debugnet ignored, use -debug=net."));
// Check for -socks - as this is a privacy risk to continue, exit here
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-socks"))
return InitError(_("Unsupported argument -socks found. Setting SOCKS version isn't possible anymore, only SOCKS5 proxies are supported."));
// Check for -tor - as this is a privacy risk to continue, exit here
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-tor", false))
return InitError(_("Unsupported argument -tor found, use -onion."));
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-benchmark", false))
InitWarning(_("Unsupported argument -benchmark ignored, use -debug=bench."));
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-whitelistalwaysrelay", false))
InitWarning(_("Unsupported argument -whitelistalwaysrelay ignored, use -whitelistrelay and/or -whitelistforcerelay."));
//新版本不支持这个参数了,打印提示
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-blockminsize"))
InitWarning("Unsupported argument -blockminsize ignored.");
// Checkmempool and checkblockindex default to true in regtest mode
int ratio = std::min(std::max(gArgs.GetArg("-checkmempool", chainparams.DefaultConsistencyChecks() ? 1 : 0), 0), 1000000);
if (ratio != 0) {
mempool.setSanityCheck(1.0 / ratio);
}
// checkpointindex读取,checkpoint是一中类似milestone的快照,不可逆的区块历史快照,这个我会在后面单独一篇博文介绍的
fCheckBlockIndex = gArgs.GetBoolArg("-checkblockindex", chainparams.DefaultConsistencyChecks());
fCheckpointsEnabled = gArgs.GetBoolArg("-checkpoints", DEFAULT_CHECKPOINTS_ENABLED);
hashAssumeValid = uint256S(gArgs.GetArg("-assumevalid", chainparams.GetConsensus().defaultAssumeValid.GetHex()));
if (!hashAssumeValid.IsNull())
LogPrintf("Assuming ancestors of block %s have valid signatures.\n", hashAssumeValid.GetHex());
else
LogPrintf("Validating signatures for all blocks.\n");
//最小工作量
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-
minimumchainwork
")) {
const std::string minChainWorkStr = gArgs.GetArg("-minimumchainwork", "");
if (!IsHexNumber(minChainWorkStr)) {
return InitError(strprintf("Invalid non-hex (%s) minimum chain work value specified", minChainWorkStr));
}
nMinimumChainWork = UintToArith256(uint256S(minChainWorkStr));
} else {
nMinimumChainWork = UintToArith256(chainparams.GetConsensus().nMinimumChainWork);
}
LogPrintf("Setting nMinimumChainWork=%s\n", nMinimumChainWork.GetHex());
if (nMinimumChainWork < UintToArith256(chainparams.GetConsensus().nMinimumChainWork)) {
LogPrintf("Warning: nMinimumChainWork set below default value of %s\n", chainparams.GetConsensus().nMinimumChainWork.GetHex());
}
// mempool limits
// mempool大小值
int64_t nMempoolSizeMax = gArgs.GetArg("-maxmempool", DEFAULT_MAX_MEMPOOL_SIZE) * 1000000;
int64_t nMempoolSizeMin = gArgs.GetArg("-limitdescendantsize", DEFAULT_DESCENDANT_SIZE_LIMIT) * 1000 * 40;
if (nMempoolSizeMax < 0 || nMempoolSizeMax < nMempoolSizeMin)
return InitError(strprintf(_("-maxmempool must be at least %d MB"), std::ceil(nMempoolSizeMin / 1000000.0)));
// incremental relay fee sets the minimum feerate increase necessary for BIP 125 replacement in the mempool
// and the amount the mempool min fee increases above the feerate of txs evicted due to mempool limiting.
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-
incrementalrelayfee
"))
{
CAmount n = 0;
if (!ParseMoney(gArgs.GetArg("-incrementalrelayfee", ""), n))
return InitError(AmountErrMsg("incrementalrelayfee", gArgs.GetArg("-incrementalrelayfee", "")));
incrementalRelayFee = CFeeRate(n);
}
// -par=0 means autodetect, but nScriptCheckThreads==0 means no concurrency
//脚本执行线程的数量
nScriptCheckThreads = gArgs.GetArg("-par", DEFAULT_SCRIPTCHECK_THREADS);
if (nScriptCheckThreads <= 0)
nScriptCheckThreads += GetNumCores();
if (nScriptCheckThreads <= 1)
nScriptCheckThreads = 0;
else if (nScriptCheckThreads > MAX_SCRIPTCHECK_THREADS)
nScriptCheckThreads = MAX_SCRIPTCHECK_THREADS;
// block pruning; get the amount of disk space (in MiB) to allot for block & undo files
int64_t nPruneArg = gArgs.GetArg("-prune", 0);
if (nPruneArg < 0) {
return InitError(_("Prune cannot be configured with a negative value."));
}
nPruneTarget
= (uint64_t) nPruneArg * 1024 * 1024;
if (nPruneArg == 1) { // manual pruning: -prune=1
LogPrintf("Block pruning enabled. Use RPC call pruneblockchain(height) to manually prune block and undo files.\n");
nPruneTarget = std::numeric_limits::max();
fPruneMode = true;
} else if (nPruneTarget) {
if (nPruneTarget < MIN_DISK_SPACE_FOR_BLOCK_FILES) {
return InitError(strprintf(_("Prune configured below the minimum of %d MiB. Please use a higher number."), MIN_DISK_SPACE_FOR_BLOCK_FILES / 1024 / 1024));
}
LogPrintf("Prune configured to target %uMiB on disk for block and undo files.\n", nPruneTarget / 1024 / 1024);
fPruneMode = true;
}
nConnectTimeout = gArgs.GetArg("-timeout", DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
if (nConnectTimeout <= 0)
nConnectTimeout = DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT;
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-minrelaytxfee")) {
CAmount n = 0;
if (!ParseMoney(gArgs.GetArg("-
minrelaytxfee
", ""), n)) {
return InitError(AmountErrMsg("minrelaytxfee", gArgs.GetArg("-minrelaytxfee", "")));
}
// High fee check is done afterward in WalletParameterInteraction()
::minRelayTxFee = CFeeRate(n);
} else if (incrementalRelayFee > ::minRelayTxFee) {
// Allow only setting incrementalRelayFee to control both
::minRelayTxFee = incrementalRelayFee;
LogPrintf("Increasing minrelaytxfee to %s to match incrementalrelayfee\n",::minRelayTxFee.ToString());
}
// Sanity check argument for min fee for including tx in block
// TODO: Harmonize which arguments need sanity checking and where that happens
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-
blockmintxfee
"))
{
CAmount n = 0;
if (!ParseMoney(gArgs.GetArg("-blockmintxfee", ""), n))
return InitError(AmountErrMsg("blockmintxfee", gArgs.GetArg("-blockmintxfee", "")));
}
// Feerate used to define dust. Shouldn't be changed lightly as old
// implementations may inadvertently create non-standard transactions
if (gArgs.IsArgSet("-
dustrelayfee
"))
{
CAmount n = 0;
if (!ParseMoney(gArgs.GetArg("-dustrelayfee", ""), n))
return InitError(AmountErrMsg("dustrelayfee", gArgs.GetArg("-dustrelayfee", "")));
dustRelayFee = CFeeRate(n);
}
return true;
}
-prune参数在SPV章节也有提到过,用于删除raw block,undo data这两种数据, 取值有以下几种:
- 0:默认值,该功能不开启。
- 1:允许手动使用RPC命令删除旧的区块。
- 大于等于550:允许保存的文件大小是:raw block + undo data,其中550MB = MIN_DISK_SPACE_FOR_BLOCK_FILES。
raw block 保存在~/.bitcoin/blocks 对应文件为blk***.dat
undo block 保存在~/.bitcoin/blocks 对应文件为rec***.dat,
与费用相关的配置,这些配置可以让每个节点内部过滤一些交易以避免接收过多的交易,
- minrelaytxfee:最小的转发费用,如果交易费小于这个值,节点就直接忽略该交易。默认值为0.00001 BTC/KB。
- dustrelayfee:dust 交易是一种特殊的交易,费用一般较低,这个就是用了设置这类交易的最低费用的,低于这个值则忽略该交易。默认值为0.00001BTC/KB。
- incrementalrelayfee:这个有点像分时电价,白天电价贵,晚上电价便宜,当mempool交易量不超过阈值时采用minrelaytxfee,当mempool中的交易数量超过阈值时,交易费用阈值便会增加,增加的程度就由incrementalrelayfee决定。默认值为0.00001BTC/KB。
AppInitMain
backgroundScheduler线程
backgroundScheduler线程是一个后台线程,backgroundScheduler用作来调度任务在该线程上执行
bool AppInitMain()
{
const CChainParams& chainparams = Params();
// ********************************************************* Step 4a: application initialization
//创建脚本执行线程,这个在script脚本博文中已经提到过了,更多细节 // https://blog.csdn.net/itleaks/article/details/79922497
LogPrintf("Using %u threads for script verification\n", nScriptCheckThreads);
if (nScriptCheckThreads) {
for (int i=0; i
threadGroup.create_thread(&ThreadScriptCheck);
}
// Start the lightweight task scheduler thread
CScheduler::Function
serviceLoop
= boost::
bind
(&CScheduler::serviceQueue, &scheduler);
threadGroup.create_thread(boost::
bind
(&TraceThread, "scheduler", serviceLoop));
GetMainSignals().RegisterBackgroundSignalScheduler(scheduler);
GetMainSignals().RegisterWithMempoolSignals(mempool);
/* Register RPC commands regardless of -server setting so they will be
* available in the GUI RPC console even if external calls are disabled.
*/
RegisterAllCoreRPCCommands(tableRPC);
g_wallet_init_interface->RegisterRPC(tableRPC);
boost:bind的作用是封装函数,比如:
CScheduler::Function serviceLoop = boost::
bind
(&CScheduler::serviceQueue, &scheduler);
调用serviceLoop() 等价于调用scheduler->serviceQueue(),这样的好处是什么呢?解耦合,就是有些模块只需要一个函数,不需要知道对象。比如而这里的serviceQueue是类对象的非静态函数,没法作为thread的入口函数
GetMainSignals().RegisterBackgroundSignalScheduler(scheduler);
void CMainSignals::RegisterBackgroundSignalScheduler(CScheduler& scheduler) {
assert(!m_internals);
m_internals.reset(new MainSignalsInstance(&scheduler));
}
struct MainSignalsInstance {
SingleThreadedSchedulerClient m_schedulerClient;
explicit MainSignalsInstance(CScheduler *pscheduler) : m_schedulerClient(pscheduler) {}
};
void CallFunctionInValidationInterfaceQueue(std::function func) {
//让backgroudScheduler线程执行某一函数
g_signals.m_internals->m_schedulerClient.AddToProcessQueue(std::move(func));
}
void CMainSignals::UpdatedBlockTip(const CBlockIndex *pindexNew, const CBlockIndex *pindexFork, bool fInitialDownload) {
m_internals->m_schedulerClient.AddToProcessQueue([pindexNew, pindexFork, fInitialDownload, this] {
//该函数在backgroudScheduler线程执行
m_internals->UpdatedBlockTip(pindexNew, pindexFork, fInitialDownload);
});
}
void CMainSignals::TransactionAddedToMempool(const CTransactionRef &ptx) {
m_internals->m_schedulerClient.AddToProcessQueue([ptx, this] {
//该函数在backgroudScheduler线程执行
m_internals->
TransactionAddedToMempool
(ptx);
});
}
从上可知RegisterBackgroundSignalScheduler(scheduler)是将scheduler作为全局signal暴露出去,可以让任何模块代码调用全局的函数让BackgroundSignalScheduler线程执行某一任务(函数的形式)
各种网络服务初始化
/* Start the RPC server already. It will be started in "warmup" mode
* and not really process calls already (but it will signify connections
* that the server is there and will be ready later). Warmup mode will
* be disabled when initialisation is finished.
*/
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-server", false))
{
uiInterface.InitMessage.connect(SetRPCWarmupStatus);
if (!
AppInitServers
())
return InitError(_("Unable to start HTTP server. See debug log for details."));
}
bool AppInitServers()
{
RPCServer::OnStarted(&OnRPCStarted);
RPCServer::OnStopped(&OnRPCStopped);
if (!
InitHTTPServer
())
return false;
if (!
StartRPC
())
return false;
if (!
StartHTTPRPC
())
return false;
if (gArgs.GetBoolArg("-rest", DEFAULT_REST_ENABLE) && !
StartREST
())
return false;
if (!
StartHTTPServer
())
return false;
return true;
}
大家能看出上面5个蓝色字体函数的差异吗?只有第一个是Init,其他都是Start,这说明啥,RPC, HTTPRPC, REST都是基于http服务的。bitcoin使用evhttp搭建的http 服务,evhttp接收到http数据后转发给RPC, REST服务解释处理, 具体细节如下:
bool InitHTTPServer()
{
/* Create a new evhttp object to handle requests. */
raii_evhttp http_ctr =
obtain_evhttp
(base_ctr.get());
struct evhttp* http = http_ctr.get();
if (!http) {
LogPrintf("couldn't create evhttp. Exiting.\n");
return false;
}
evhttp_set_timeout(http, gArgs.GetArg("-rpcservertimeout", DEFAULT_HTTP_SERVER_TIMEOUT));
evhttp_set_max_headers_size(http, MAX_HEADERS_SIZE);
evhttp_set_max_body_size(http, MAX_SIZE);
evhttp_set_gencb(http, http_request_cb, nullptr);
if (!
HTTPBindAddresses
(http)) {
LogPrintf("Unable to bind any endpoint for RPC server\n");
return false;
}
LogPrint(BCLog::HTTP, "Initialized HTTP server\n");
int workQueueDepth = std::max((long)gArgs.GetArg("-rpcworkqueue", DEFAULT_HTTP_WORKQUEUE), 1L);
LogPrintf("HTTP: creating work queue of depth %d\n", workQueueDepth);
workQueue = new WorkQueue(workQueueDepth);
// transfer ownership to eventBase/HTTP via .release()
eventBase = base_ctr.release();
eventHTTP = http_ctr.release();
return true;
}
//http_request_cb处理http请求并生成HTTPWorkItem,然后push到WorkQueue
static void
http_request_cb
(struct evhttp_request* req, void* arg)
{
// Find registered handler for prefix
std::string strURI = hreq->GetURI();
std::string path;
std::vector::const_iterator i =
pathHandlers.begin
();
std::vector::const_iterator iend = pathHandlers.end();
for (; i != iend; ++i) {
bool match = false;
if (i->exactMatch)
match = (strURI == i->prefix);
else
match = (strURI.substr(0, i->prefix.size()) == i->prefix);
if (match) {
path = strURI.substr(i->prefix.size());
break;
}
}
// Dispatch to worker thread
if (i != iend) {
std::unique_ptr item(new HTTPWorkItem(std::move(hreq), path, i->handler));
assert(workQueue);
if (workQueue->Enqueue(item.get()))
item.release(); /* if true, queue took ownership */
}
} else {
hreq->WriteReply(HTTP_NOTFOUND);
}
}
class WorkQueue
{
private:
std::deque>
queue
;
public:
/** Enqueue a work item */
//evhttp接收到Http请求处理完后会调用该函数将数据入队列
bool Enqueue(WorkItem* item)
{
std::unique_lock lock(cs);
if (queue.size() >= maxDepth) {
return false;
}
queue.emplace_back
(std::unique_ptr(item));
cond.notify_one();
return true;
}
/** Thread function */
//这个在StartHttpServer时调用
void Run()
{
while (true) {
std::unique_ptr i;
{
std::unique_lock lock(cs);
while (running && queue.empty())
cond.wait(lock);
if (!running)
break;
i = std::move(queue.front());
queue.pop_front();
}
(*i)(); //这个函数就是下面的HTTPWorkItem::operator()()
}
}
};
class HTTPWorkItem final : public HTTPClosure
{
public:
HTTPWorkItem(std::unique_ptr _req, const std::string &_path, const HTTPRequestHandler&
_func
):
req(std::move(_req)), path(_path),
func(_func)
{
}
void operator()() override
{
//这个func是HTTPRequestHandler
func(req.get(), path);
}
std::unique_ptr req;
private:
std::string path;
HTTPRequestHandler func;
};
//上面的HTTPRequestHandler是通过RegisterHTTPHandler注册的
void
RegisterHTTPHandler
(const std::string &prefix, bool exactMatch, const HTTPRequestHandler &
handler
)
{
LogPrint(BCLog::HTTP, "Registering HTTP handler for %s (exactmatch %d)\n", prefix, exactMatch);
pathHandlers.push_back
(HTTPPathHandler(prefix, exactMatch,
handler
));
}
bool
StartHTTPRPC
()
{
LogPrint(BCLog::RPC, "Starting HTTP RPC server\n");
if (!InitRPCAuthentication())
return false;
RegisterHTTPHandler
("/", true, HTTPReq_JSONRPC);
#ifdef ENABLE_WALLET
// ifdef can be removed once we switch to better endpoint support and API versioning
RegisterHTTPHandler
("/wallet/", false, HTTPReq_JSONRPC);
#endif
}
bool
StartREST
()
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < ARRAYLEN(uri_prefixes); i++)
RegisterHTTPHandler
(uri_prefixes[i].prefix, false, uri_prefixes[i].handler);
return true;
}
bool StartHTTPServer()
{
//为evhttp服务创建执行线程
threadHTTP = std::thread(std::move(task), eventBase, eventHTTP);
for (int i = 0; i < rpcThreads; i++) {
//为workQueue分配执行线程,线程的入口函数是HTTPWorkQueueRun
g_thread_http_workers.emplace_back(HTTPWorkQueueRun, workQueue);
}
return true;
return true;
}
static void
HTTPWorkQueueRun
(WorkQueue* queue)
{
RenameThread("bitcoin-httpworker");
queue->Run();
}
总结,节点收到http请求时,evhttp服务线程会解释http请求的path,并将数据push到WorkQueue队列, 而RPC,REST等网络服务注册HTTPHandler,这些handler就会被WorkQueue线程调用继续处理http请求。这些服务的具体处理逻辑我后面会单独写一篇博文来分析,这里就不深入了。
PeerLogicValidation初始化
PeerLogicValidation这个类在前面分析message的时候应该经常看到,这个是一个新区块发现或者生成时的事件处理类。为了实现解耦和可扩展性,作者通过boost的signal的动态绑定特性实现解耦和高扩展性。具体事件定义及绑定代码如下:
void AppInitMain()
{
CConnman& connman = *g_connman;
peerLogic.reset(new PeerLogicValidation(&connman, scheduler));
RegisterValidationInterface
(peerLogic.get());
}
//RegisterValidationInterface里涉及的signal其实就是区块层事件的接口抽象
void
RegisterValidationInterface
(CValidationInterface* pwalletIn) {
g_signals.m_internals->UpdatedBlockTip.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::UpdatedBlockTip, pwalletIn, _1, _2, _3));
g_signals.m_internals->TransactionAddedToMempool.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::TransactionAddedToMempool, pwalletIn, _1));
g_signals.m_internals->BlockConnected.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::BlockConnected, pwalletIn, _1, _2, _3));
g_signals.m_internals->BlockDisconnected.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::BlockDisconnected, pwalletIn, _1));
g_signals.m_internals->TransactionRemovedFromMempool.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::TransactionRemovedFromMempool, pwalletIn, _1));
g_signals.m_internals->SetBestChain.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::SetBestChain, pwalletIn, _1));
g_signals.m_internals->Inventory.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::Inventory, pwalletIn, _1));
g_signals.m_internals->Broadcast.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::ResendWalletTransactions, pwalletIn, _1, _2));
g_signals.m_internals->BlockChecked.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::BlockChecked, pwalletIn, _1, _2));
g_signals.m_internals->NewPoWValidBlock.connect(boost::bind(&CValidationInterface::NewPoWValidBlock, pwalletIn, _1, _2));
}
bool CChainState::
AcceptBlock
(const std::shared_ptr& pblock, CValidationState& state, const CChainParams& chainparams, CBlockIndex** ppindex, bool fRequested, const CDiskBlockPos* dbp, bool* fNewBlock)
if (!IsInitialBlockDownload() && chainActive.Tip() == pindex->pprev)
GetMainSignals().NewPoWValidBlock(pindex, pblock);
}
从本地文件及数据库中恢复区块信息
区块信息包括区块链表,钱包信息(比如utxos),具体涉及到如下几个重要变量的构建:
- BlockMap& mapBlockIndex = g_chainstate.mapBlockIndex;
- std::unique_ptr
pcoinsdbview; - std::unique_ptr
pcoinsTip; - std::unique_ptr
pblocktree;
由于这个过程涉及的内容过多,我打算后面单独写一篇博文来解读,这里也不再详谈了,大家可先看看源码
bool fLoaded = false;
while (!fLoaded && !fRequestShutdown) {
bool fReset = fReindex;
std::string strLoadError;
uiInterface.InitMessage(_("Loading block index..."));
LOCK(cs_main);
nStart = GetTimeMillis();
do {
try {
UnloadBlockIndex();
//这些是钱包相关功能的数据
pcoinsTip
.reset();
pcoinsdbview
.reset();
pcoinscatcher.reset();
// new CBlockTreeDB tries to delete the existing file, which
// fails if it's still open from the previous loop. Close it first:
pblocktree
.reset();
pblocktree.reset(new CBlockTreeDB(nBlockTreeDBCache, false, fReset));
// LoadBlockIndex will load fTxIndex from the db, or set it if
// we're reindexing. It will also load fHavePruned if we've
// ever removed a block file from disk.
// Note that it also sets fReindex based on the disk flag!
// From here on out fReindex and fReset mean something different!
//加载区块链信息,会构建mapBlockIndex变量
if (!
LoadBlockIndex
(chainparams)) {
strLoadError = _("Error loading block database");
break;
}
// At this point we're either in reindex or we've loaded a useful
// block tree into mapBlockIndex!
pcoinsdbview
.reset(new CCoinsViewDB(nCoinDBCache, false, fReset || fReindexChainState));
pcoinscatcher.reset(new CCoinsViewErrorCatcher(pcoinsdbview.get()));
// If necessary, upgrade from older database format.
// This is a no-op if we cleared the coinsviewdb with -reindex or -reindex-chainstate
if (!pcoinsdbview->Upgrade()) {
strLoadError = _("Error upgrading chainstate database");
break;
}
// ReplayBlocks is a no-op if we cleared the coinsviewdb with -reindex or -reindex-chainstate
if (!ReplayBlocks(chainparams, pcoinsdbview.get())) {
strLoadError = _("Unable to replay blocks. You will need to rebuild the database using -reindex-chainstate.");
break;
}
// The on-disk coinsdb is now in a good state, create the cache
pcoinsTip
.reset(new CCoinsViewCache(pcoinscatcher.get()));
bool is_coinsview_empty = fReset || fReindexChainState || pcoinsTip->GetBestBlock().IsNull();
if (!is_coinsview_empty) {
// LoadChainTip sets chainActive based on pcoinsTip's best block
if (!
LoadChainTip
(chainparams)) {
strLoadError = _("Error initializing block database");
break;
}
assert(chainActive.Tip() != nullptr);
}
if (!fReset) {
// Note that RewindBlockIndex MUST run even if we're about to -reindex-chainstate.
// It both disconnects blocks based on chainActive, and drops block data in
// mapBlockIndex based on lack of available witness data.
uiInterface.InitMessage(_("Rewinding blocks..."));
if (!RewindBlockIndex(chainparams)) {
strLoadError = _("Unable to rewind the database to a pre-fork state. You will need to redownload the blockchain");
break;
}
}
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
LogPrintf("%s\n", e.what());
strLoadError = _("Error opening block database");
break;
}
fLoaded = true;
} while(false);
}
P2P相关部分初始化
P2P负责区块链的去中心化,可想而知P2P是核心模块,它的初始化如下:
Void AppInitMain()
{
if (!connman.Start(scheduler, connOptions)) {
return false;
}
}
bool CConnman::Start(CScheduler& scheduler, const Options& connOptions)
{
Init(connOptions);
//创建listen网络
if (fListen && !
InitBinds(connOptions.vBinds, connOptions.vWhiteBinds)
) {
}
for (const auto& strDest : connOptions.vSeedNodes) {
AddOneShot(strDest);
}
if (clientInterface) {
clientInterface->InitMessage(_("Loading P2P addresses..."));
}
// Load addresses from peers.dat
int64_t nStart = GetTimeMillis();
{
CAddrDB adb;
//从peer 节点地址数据库中读取地址信息
if (adb.Read(addrman))
LogPrintf("Loaded %i addresses from peers.dat %dms\n", addrman.size(), GetTimeMillis() - nStart);
else {
addrman.Clear(); // Addrman can be in an inconsistent state after failure, reset it
LogPrintf("Invalid or missing peers.dat; recreating\n");
DumpAddresses();
}
}
…..
uiInterface.InitMessage(_("Starting network threads..."));
fAddressesInitialized = true;
//
// Start threads
//
assert(m_msgproc);
InterruptSocks5(false);
interruptNet.reset();
flagInterruptMsgProc = false;
{
std::unique_lock lock(mutexMsgProc);
fMsgProcWake = false;
}
// Send and receive from sockets, accept connections
threadSocketHandler
= std::thread(&TraceThread >, "net", std::function(std::bind(&CConnman::ThreadSocketHandler, this)));
if (!gArgs.GetBoolArg("-dnsseed", true))
LogPrintf("DNS seeding disabled\n");
else
threadDNSAddressSeed
= std::thread(&TraceThread >, "dnsseed", std::function(std::bind(&CConnman::ThreadDNSAddressSeed, this)));
// Initiate outbound connections from -addnode
threadOpenAddedConnections
= std::thread(&TraceThread >, "addcon", std::function(std::bind(&CConnman::ThreadOpenAddedConnections, this)));
if (connOptions.m_use_addrman_outgoing && !connOptions.m_specified_outgoing.empty()) {
if (clientInterface) {
clientInterface->ThreadSafeMessageBox(
_("Cannot provide specific connections and have addrman find outgoing connections at the same."),
"", CClientUIInterface::MSG_ERROR);
}
return false;
}
if (connOptions.m_use_addrman_outgoing || !connOptions.m_specified_outgoing.empty())
threadOpenConnections
= std::thread(&TraceThread >, "opencon", std::function(std::bind(&CConnman::ThreadOpenConnections, this, connOptions.m_specified_outgoing)));
// Process messages
threadMessageHandler
= std::thread(&TraceThread >, "msghand", std::function(std::bind(&CConnman::ThreadMessageHandler, this)));
// Dump network addresses
scheduler.scheduleEvery(std::bind(&CConnman::DumpData, this), DUMP_ADDRESSES_INTERVAL * 1000);
return true;
}
从上面的源码可知,其核心就是定义了几个handler, 并为每个handler创建了一个线程执行:
-
threadSocketHandler该线程会维护所有已经建立连接的节点信息,并等待所有网络事件(新网络连接,新发送网络数据,新接收网络数据),并将相关事件数据转给合适的处理逻辑,比如区块消息数据就转给threadMessageHandler线程处理
-
threadDNSAddressSeed该线程解释参数"-dnsseed"中指定的种子节点peer域名(一般是社区维护的节点,可信节点),然后主动连接节点,这个解决了鸡蛋问题,本地节点要加入到p2p网络,有两种途径,一种是本地节点主动连接网络中的节点,另一种是网络中的其他节点主动联系本地节点。本地节点是第一次加入网络,其他节点肯定不知道本地节点,所以只能靠本地节点主动联系其他节点了,因而就出现了一些种子节点,这些种子节点会公开自己的域,任何新节点都可以使用域名主动连接这些已经存在的种子节点。
-
threadOpenAddedConnections用户通过钱包或者RCP命令主动添加外部节点信息,这时threadOpenAddedConnections就会解释这些信息然后连接节点
-
threadOpenConnections该线程解释参数“-connect”中指定的外部节点地址并主动连接这些节点,比如我们自己部署了多台机器,我们就可以将彼此的地址添加到参数中;这个线程和threadOpenAddedConnections类似,只是该线程处理参数中的地址,而threadOpenAddedConnections处理运行时用户主动添加的地址
- threadMessageHandler
这个线程负责处理区块消息,前面源码情景分析的几篇博文已经多次提到过了
threadDNSAddressSeed,threadOpenAddedConnections,threadOpenConnections都是解释地址并主动连接,相对比较简单,就不分析了,threadMessageHandler在前几篇博文也分析了很多,这里也没必要分析了,所以就剩下threadSocketHandler这个线程了,接下来我们就细细分析这个线程
threadSocketHandler
void CConnman::ThreadSocketHandler()
{
unsigned int nPrevNodeCount = 0;
while (!interruptNet)
{
//
// Disconnect nodes
//
{
LOCK(cs_vNodes);
// Disconnect unused nodes
// DNSSeed等其他网络线程解释地址主动连接节点成功后都会添加一个CNode到vNodes里
// 已经建立连接的outbound节点都会保存在vNodes
std::vector vNodesCopy = vNodes;
}
{
// Delete disconnected nodes
// 删除已经失去连接的节点
std::list vNodesDisconnectedCopy = vNodesDisconnected;
for (CNode* pnode : vNodesDisconnectedCopy)
{
// wait until threads are done using it
if (pnode->GetRefCount() <= 0) {
bool fDelete = false;
{
TRY_LOCK(pnode->cs_inventory, lockInv);
if (lockInv) {
TRY_LOCK(pnode->cs_vSend, lockSend);
if (lockSend) {
fDelete = true;
}
}
}
if (fDelete) {
vNodesDisconnected.remove(pnode);
DeleteNode(pnode);
}
}
}
}
size_t vNodesSize;
{
LOCK(cs_vNodes);
vNodesSize = vNodes.size();
}
//
// Find which sockets have data to receive
//
struct timeval timeout;
timeout.tv_sec = 0;
timeout.tv_usec = 50000; // frequency to poll pnode->vSend
fd_set fdsetRecv;
fd_set fdsetSend;
fd_set fdsetError;
FD_ZERO(&fdsetRecv);
FD_ZERO(&fdsetSend);
FD_ZERO(&fdsetError);
SOCKET hSocketMax = 0;
bool have_fds = false;
for (const ListenSocket& hListenSocket : vhListenSocket) {
FD_SET(hListenSocket.socket, &fdsetRecv);
hSocketMax = std::max(hSocketMax, hListenSocket.socket);
have_fds = true;
}
{
LOCK(cs_vNodes);
//将所有socket连接添加到FD_SET,为接下来的select准备数据
for (CNode* pnode : vNodes)
{
// Implement the following logic:
// * If there is data to send, select() for sending data. As this only
// happens when optimistic write failed, we choose to first drain the
// write buffer in this case before receiving more. This avoids
// needlessly queueing received data, if the remote peer is not themselves
// receiving data. This means properly utilizing TCP flow control signalling.
// * Otherwise, if there is space left in the receive buffer, select() for
// receiving data.
// * Hand off all complete messages to the processor, to be handled without
// blocking here.
bool select_recv = !pnode->fPauseRecv;
bool select_send;
{
LOCK(pnode->cs_vSend);
select_send = !pnode->vSendMsg.empty();
}
LOCK(pnode->cs_hSocket);
if (pnode->hSocket == INVALID_SOCKET)
continue;
FD_SET(pnode->hSocket, &fdsetError);
hSocketMax = std::max(hSocketMax, pnode->hSocket);
have_fds = true;
if (select_send) {
FD_SET(pnode->hSocket, &fdsetSend);
continue;
}
if (select_recv) {
FD_SET(pnode->hSocket, &fdsetRecv);
}
}
}
// select函数是阻塞函数,直到fdsetRecv,fdsetSend中文件句柄发生事件,比如有新数据,断开连接
int nSelect = select(have_fds ? hSocketMax + 1 : 0,
&fdsetRecv, &fdsetSend, &fdsetError, &timeout);
//
// Accept new connections
//
//hListenSocket出现在fdsetRecv,说明有新连接
for (const ListenSocket& hListenSocket : vhListenSocket)
{
if (hListenSocket.socket != INVALID_SOCKET && FD_ISSET(hListenSocket.socket, &fdsetRecv))
{
//有新的节点连接到本地
AcceptConnection(hListenSocket);
}
}
// select函数返回了,说明有事件发生,但是并不知道是哪个网络连接(节点)发生了事件,因此遍历所有连接(节点)
for (CNode* pnode : vNodesCopy)
{
if (interruptNet)
return;
//
// Receive
//
bool recvSet = false;
bool sendSet = false;
bool errorSet = false;
{
LOCK(pnode->cs_hSocket);
if (pnode->hSocket == INVALID_SOCKET)
continue;
recvSet = FD_ISSET(pnode->hSocket, &fdsetRecv);
sendSet = FD_ISSET(pnode->hSocket, &fdsetSend);
errorSet = FD_ISSET(pnode->hSocket, &fdsetError);
}
//该节点的socket出现在recvSet,说明是该节点发送数据到本地节点了
if (recvSet || errorSet)
{
// typical socket buffer is 8K-64K
char pchBuf[0x10000];
int nBytes = 0;
{
LOCK(pnode->cs_hSocket);
if (pnode->hSocket == INVALID_SOCKET)
continue;
//接收数据
nBytes = recv(pnode->hSocket, pchBuf, sizeof(pchBuf), MSG_DONTWAIT);
}
if (nBytes > 0)
{
bool notify = false;
if (!pnode->ReceiveMsgBytes(pchBuf, nBytes, notify))
pnode->CloseSocketDisconnect();
RecordBytesRecv(nBytes);
if (notify) {
size_t nSizeAdded = 0;
auto it(pnode->vRecvMsg.begin());
for (; it != pnode->vRecvMsg.end(); ++it) {
if (!it->complete())
break;
nSizeAdded += it->vRecv.size() + CMessageHeader::HEADER_SIZE;
}
{
LOCK(pnode->cs_vProcessMsg);
pnode->vProcessMsg.splice(pnode->vProcessMsg.end(), pnode->vRecvMsg, pnode->vRecvMsg.begin(), it);
pnode->nProcessQueueSize += nSizeAdded;
pnode->fPauseRecv = pnode->nProcessQueueSize > nReceiveFloodSize;
}
//唤醒threadMessageHandler线程处理消息
WakeMessageHandler();
}
}
}
//
// Send
//
//该节点的socket出现在sendSet,说明有数据从本地节点发送到该节点
if (sendSet)
{
LOCK(pnode->cs_vSend);
size_t nBytes = SocketSendData(pnode);
if (nBytes) {
RecordBytesSent(nBytes);
}
}
//
// Inactivity checking
//
// 连接状态变化也会唤醒select函数并返回,所以也要检测连接状态
int64_t nTime = GetSystemTimeInSeconds();
if (nTime - pnode->nTimeConnected > 60)
{
if (pnode->nLastRecv == 0 || pnode->nLastSend == 0)
{
LogPrint(BCLog::NET, "socket no message in first 60 seconds, %d %d from %d\n", pnode->nLastRecv != 0, pnode->nLastSend != 0, pnode->GetId());
pnode->fDisconnect = true;
}
else if (nTime - pnode->nLastSend > TIMEOUT_INTERVAL)
{
LogPrintf("socket sending timeout: %is\n", nTime - pnode->nLastSend);
pnode->fDisconnect = true;
}
else if (nTime - pnode->nLastRecv > (pnode->nVersion > BIP0031_VERSION ? TIMEOUT_INTERVAL : 90*60))
{
LogPrintf("socket receive timeout: %is\n", nTime - pnode->nLastRecv);
pnode->fDisconnect = true;
}
else if (pnode->nPingNonceSent && pnode->nPingUsecStart + TIMEOUT_INTERVAL * 1000000 < GetTimeMicros())
{
LogPrintf("ping timeout: %fs\n", 0.000001 * (GetTimeMicros() - pnode->nPingUsecStart));
pnode->fDisconnect = true;
}
else if (!pnode->fSuccessfullyConnected)
{
LogPrint(BCLog::NET, "version handshake timeout from %d\n", pnode->GetId());
pnode->fDisconnect = true;
}
}
}
}
}
关联细节:
CNode新连接创建
void CConnman::AcceptConnection(const ListenSocket& hListenSocket) {
struct sockaddr_storage sockaddr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(sockaddr);
SOCKET hSocket = accept(hListenSocket.socket, (struct sockaddr*)&sockaddr, &len);
CAddress addr;
int nInbound = 0;
int nMaxInbound = nMaxConnections - (nMaxOutbound + nMaxFeeler);
if (hSocket != INVALID_SOCKET) {
if (!addr.SetSockAddr((const struct sockaddr*)&sockaddr)) {
LogPrintf("Warning: Unknown socket family\n");
}
}
bool whitelisted = hListenSocket.whitelisted || IsWhitelistedRange(addr);
{
LOCK(cs_vNodes);
for (const CNode* pnode : vNodes) {
if (pnode->fInbound) nInbound++;
}
}
CNode* pnode = new CNode(id, nLocalServices, GetBestHeight(), hSocket, addr, CalculateKeyedNetGroup(addr), nonce, addr_bind, "", true);
pnode->AddRef();
pnode->fWhitelisted = whitelisted;
m_msgproc->InitializeNode(pnode);
LogPrint(BCLog::NET, "connection from %s accepted\n", addr.ToString());
{
LOCK(cs_vNodes);
vNodes.push_back(pnode);
}
}
网络Listen, bind初始化
bool CConnman::
InitBinds
(const std::vector& binds, const std::vector& whiteBinds) {
bool fBound = false;
for (const auto& addrBind : binds) {
fBound |= Bind(addrBind, (BF_EXPLICIT | BF_REPORT_ERROR));
}
for (const auto& addrBind : whiteBinds) {
}
bool CConnman::
Bind
(const CService &addr, unsigned int flags) {
if (!(flags & BF_EXPLICIT) && IsLimited(addr))
return false;
std::string strError;
if (!BindListenPort(addr, strError, (flags & BF_WHITELIST) != 0)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool CConnman::
BindListenPort
(const CService &addrBind, std::string& strError, bool fWhitelisted)
{
vhListenSocket.push_back(ListenSocket(hListenSocket, fWhitelisted));
if (addrBind.IsRoutable() && fDiscover && !fWhitelisted)
AddLocal(addrBind, LOCAL_BIND);
return true;
}
/********************************
* 本文来自CSDN博主"爱踢门"
* 转载请标明出处
: http://blog.csdn.net/itleaks
******************************************/