map key value的排序问题
一、简单描述
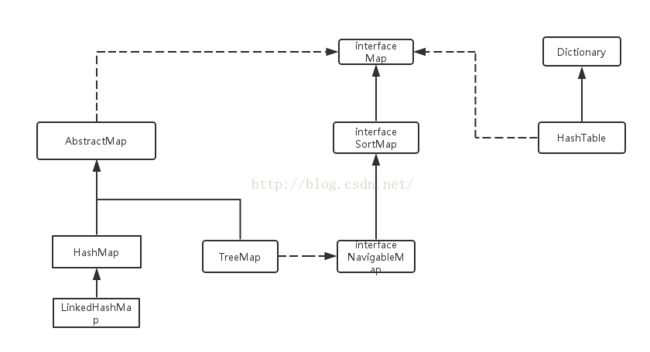
Map是键值对的集合接口,它的实现类主要包括:HashMap,TreeMap,HashTable以及LinkedHashMap等。
TreeMap:能够把它保存的记录根据键(key)排序,默认是按升序排序,也可以指定排序的比较器,该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
HashMap的值是没有顺序的,它是按照key的HashCode来实现的,根据键可以直接获取它的值,具有很快的访问速度。HashMap最多只允许一条记录的键为Null(多条会覆盖);允许多条记录的值为 Null。非同步的。
Map.Entry返回Collections视图。
注:map简单的UML
二、排序的具体实现
(1)较简单的排序方式(直接根据key值进行比较),按key值排序
Map map = new TreeMap(new
Comparator() {
public int compare(String obj1, String obj2) {
return obj1.compareTo(obj2);
}
});
map.put("b", "1111");
map.put("d", "2222");
map.put("c", "3333");
map.put("a", "4444");
for (Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.err.println(entry.getKey() + "========" + entry.getValue());
} TreeMap 接收的comparator的接口默认是key值的排序,源代码如下:
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree map, ordered according to the given
* comparator. All keys inserted into the map must be mutually
* comparable by the given comparator: {@code comparator.compare(k1,
* k2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys
* {@code k1} and {@code k2} in the map. If the user attempts to put
* a key into the map that violates this constraint, the {@code put(Object
* key, Object value)} call will throw a
* {@code ClassCastException}.
*
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this map.
* If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable natural
* ordering} of the keys will be used.
*/
public TreeMap(Comparator comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}(2) 根据Map.Entry进行排序,即可实现key值的排序,也可以实现value值的排序
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("1", "b");
map.put("2", "a");
map.put("4", "e");
map.put("5", "c");
map.put("3", "d");
Set> keyEntries = new TreeSet>(
(Comparator>) (c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey()));
keyEntries.addAll(map.entrySet());
for (Entry entry : keyEntries) {
System.err.println(entry.getKey() + "----" + entry.getValue());
}
Set> valueEntries = new TreeSet>(
(Comparator>) (c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue()));
valueEntries.addAll(map.entrySet());
for (Entry entry : valueEntries) {
System.err.println(entry.getKey() + "----" + entry.getValue());
} 注:java8 在Map接口中的Entry接口中实现了根据key、value排序的接口,源代码如下:
public static , V> Comparator> comparingByKey() {
return (Comparator> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());
}
public static > Comparator> comparingByValue() {
return (Comparator> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue());
} (3) 当要比较的key或者value 是一个对象的时候,你可以定义一个comparator进行排序, java8 在Map接口中的Entry接口有两个接收comparator的方法,源码如下:
public static Comparator> comparingByKey(Comparator cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey());
}
public static Comparator> comparingByValue(Comparator cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue());
}
}
Map personMap = new HashMap();
personMap.put("a", new Person(1, "aaa"));
personMap.put("acd", new Person(4, "acd"));
personMap.put("abc", new Person(3, "abc"));
personMap.put("eda", new Person(2, "eda"));
Set> valueEntries = new TreeSet(Map.Entry.comparingByValue(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
return p1.id - p2.id;
}
}));
// Set> valueEntries = new
// TreeSet>(
// new Comparator>() {
//
// @Override
// public int compare(Entry o1, Entry
// o2) {
// Person p1 = o1.getValue();
// Person p2 = o2.getValue();
// return p1.id - p2.id;
// }
// });
valueEntries.addAll(personMap.entrySet());
for (Entry entry : valueEntries) {
System.err.println(entry.getKey() + "----" + entry.getValue().id);
} 结束语:这是学习源代码时个人的见解,如有不对的地方,请指正,不尽感激