Docker 的入门部署教程
简单的说,容器是镜像的实例,先声明(描述)镜像,再创建容器,所以容器可以有多个。
详细介绍:
Docker是一个开源的引擎,可以轻松的为任何应用创建一个轻量级的、可移植的、自给自足的容器。开发者在笔记本上编译测试通过的容器可以批量地在生产环境中部署,包括VMs(虚拟机)、bare metal、OpenStack 集群和其他的基础应用平台。
Docker通常用于如下场景:
web应用的自动化打包和发布;
自动化测试和持续集成、发布;
在服务型环境中部署和调整数据库或其他的后台应用;
从头编译或者扩展现有的OpenShift或Cloud Foundry平台来搭建自己的PaaS环境。
Docker开源镜像传送门
详细步骤
1. 下载MySQL镜像
2. 创建运行容器
查看Docker MySQL文档
MySQL文档地址:
https://hub.docker.com/mysql/
第一步,拉取MySQL镜像
$ docker pull mysql
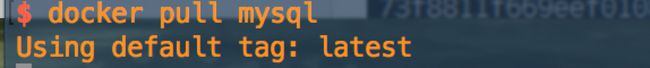
不指明tag,就会默认docker hub上最新的版本
之后docker会自动拉取(下载)MySQL镜像。
国内的网速有点慢,可以选择国内的镜像.比如DaoCloud上的镜像和官方保持同步的,试了下速还行
拉取成功后我们查看一下:
$ docker images
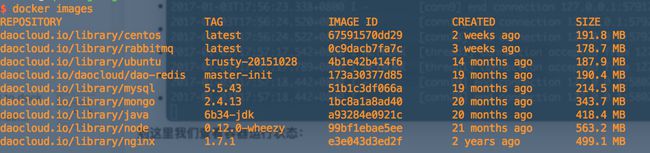
执行命令后可以看到本地所有的镜像
第二步,创建并启动一个MySQL容器
输入以下命令:
$ docker run –name pwc-mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -p 3306:3306 -d mysql
![]()
–name:给新创建的容器命名,此处命名为pwc-mysql
-e:配置信息,此处配置mysql的root用户的登陆密码
-p:端口映射,此处映射主机3306端口到容器pwc-mysql的3306端口
-d:成功启动容器后输出容器的完整ID,例如上图 73f8811f669ee…
最后一个mysql指的是mysql镜像名字
特别注意:端口号一定要指定,系统会开发此端口访问,方便后面连接docker的mysql容器
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/33175361/accessing-to-mysql-from-host-to-container-in-cli
$ docker ps
![]()
上图可以看到容器的简写ID,容器的源镜像,创建时间,状态,端口映射信息,容器名字等。
连接成功,接下来就可以进行相关数据库操作
其他
1.可以启动多个MySQL服务,因为我们启动的是容器,容器可以有多个,只要容器名字映射段端口不一样就可以了,例如:
$ docker run –name dbdb -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -p 6666:3306 -d mysql
2.查看所有容器(启动状态或者关闭状态)
$ docker ps -a
3.启动和关闭容器
启动命令:
$ docker start mysql //通过指定容器名字
$ docker start 67591570dd29 //通过指定容器ID
关闭命令:
$ docker stop mysql //通过指定容器名字
$ docker stop 67591570dd29 //通过指定容器ID
4.删除:
$ docker rm 67591570dd2 //删除容器,docker rm CONTAINER I
$ docker rmi 67591570dd29 //通过指定镜像id
$ docker docker images //通过所有本地镜像
6.修改MySQL配置文件有两种方法:
一是进入容器,修改容器里的MySQL的配置文件,然后重新启动容器,例如:
$ docker exec -it mysql bash
然后可以进入容器的命令行模式,接着修改 /etc/mysql/my.cnf 文件即可
二是挂载主机的mysql配置文件,官方文档如下:
The MySQL startup configuration is specified in the file /etc/mysql/my.cnf, and that file in turn includes any files found in the /etc/mysql/conf.d directory that end with .cnf. Settings in files in this directory will augment and/or override settings in /etc/mysql/my.cnf. If you want to use a customized MySQL configuration, you can create your alternative configuration file in a directory on the host machine and then mount that directory location as /etc/mysql/conf.d inside the mysql container.
If /my/custom/config-file.cnf is the path and name of your custom configuration file, you can start your mysql container like this (note that only the directory path of the custom config file is used in this command):
$ docker run –name some-mysql -v /my/custom:/etc/mysql/conf.d -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mysql:tag
This will start a new container some-mysql where the MySQL instance uses the combined startup settings from /etc/mysql/my.cnf and /etc/mysql/conf.d/config-file.cnf, with settings from the latter taking precedence.