Java注解-手把手教你
Java注解的基本概念在百度百科讲的很清楚, 如果不了解请先移步 http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=qqn1zxPe7NkYR86mXqSkfDNg2leVAUnMtamhuAKjlg5uWwAV09NtWmsabBVTpIL2pDik8GQ5Awwi9ttr-i40sK
本文是要想通过实战demo带你理解java注解。
一、 创建注解
新建一个java文件, 命名为FirstAnnotation.java。
public @interface FirstAnnotation { }我们看到声明注解的方法跟类、接口类似, 关键字是@interface。
二、 使用注解
4大元注解(@Target,@Retention,@Documented,@Inherited)是定义注解的注解, 说起来好像有点绕, 实际上就是限制注解(@interface)怎么用。 下面对类、成员变量、函数、参数进行注解。
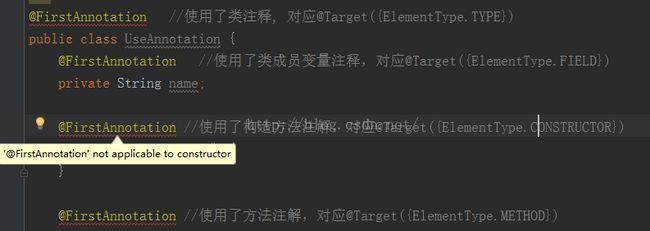
@FirstAnnotation //使用了类注释, 对应@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) public class UseAnnotation { @FirstAnnotation //使用了类成员变量注释,对应@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) private String name; @FirstAnnotation //使用了构造方法注解,对应@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR}) public UseAnnotation() { } @FirstAnnotation //使用了方法注解,对应@Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public void methodA() { @FirstAnnotation //使用局部参数注解,对应@Target({ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE}) String nickname = "zhangsan"; } public void methodB(@FirstAnnotation String param) { //使用了方法参数注解,对应@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER}) } }
你可能会说这个注解毛用没有, 什么值都没传递。 是的, 你说的没错。 这是最简单的注解, 只是为了让你了解最基本用法。
下面对FirstAnnotation稍加改动, 注意@Target后面的{}里是数组!!! 作用是规定该注解可以用在什么地方。
@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) public @interface FirstAnnotation { }我们看到 Android Studio会提示错误, 因为我们规定了@FirstAnnotation只能给类成员变量做注解, 所以private String name;这句代码没提示错误。相信你现在应该理解@Target是做什么用的了。
三、 该理解一下元注解@Retention的参数RetentionPolicy了。
public enum RetentionPolicy {
// 此类型会被编译器丢弃
SOURCE,
// 此类型注解会保留在class文件中,但JVM会忽略它
CLASS,
// 此类型注解会保留在class文件中,JVM会读取它
RUNTIME
}
还是不理解没关系, 先看怎么用。跟定义@Target类似, 在注解类上面使用@Retention关键字。
四、定义注解类的成员函数, 注意注解类的每一个方法实际上声明了一个配置参数, 方法名称就是参数名称, 返回值类型就是参数的类型(只能是java基本数据类型、Class、enum、String), 并可以使用default定义默认值(这点跟SQL语法类似)。完善FirstAnnotation类, 添加类成员函数name、age并设置@Target和@Retention。
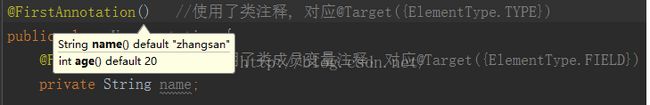
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface FirstAnnotation { String name() default "zhangsan"; int age() default 20; }在添写注解参数时编译器会提示我们允许输入的值。
下面是编写完成的类, 我们看看对类、成员参数、构造函数、成员的注解。
@FirstAnnotation(name="UseAnnotation",age=1) //使用了类注释, 对应@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) public class UseAnnotation { @FirstAnnotation(name="name",age=2) //使用了类成员变量注释,对应@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) private String name; @FirstAnnotation(name="constructor",age=3) //使用了构造方法注解,对应@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR}) public UseAnnotation() { } @FirstAnnotation(name="public",age=4) //使用了方法注解,对应@Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public void methodA() { String nickname = "zhangsan"; } public void methodB(String param) { //使用了方法参数注解,对应@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER}) } }
五、 读取注释, 前几步都是铺垫, 现在该使用了。 在jdk1.5新增了AnnotatedElement接口, 详见源码http://www.grepcode.com/file/repository.grepcode.com/java/root/jdk/openjdk/8u40-b25/java/lang/reflect/AnnotatedElement.java#AnnotatedElement
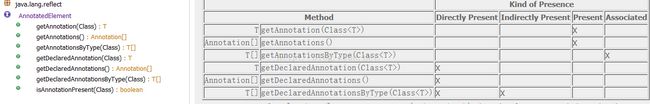
getAnnotation: 获取指定注解, 没有则返回null;从JDK1.5开始支持。
getAnnotations: 获取所有注解,包括继承自基类的,没有则返回长度为0的数组;从JDK1.8开始支持。
getAnnotationByType:获取指定的所有注解, 没有则返回长度为0的数组; 从JDK1.8开始支持。
getDeclaredAnnotation(Class): 获取指定的注解,没有则返回null; 从jdk1.5开始支持;
getDeclaredAnnotationsByType: 获取指定注解, 不包含基类的注解, 没有则返回长度为0的数组; 从jdk1.8开始支持;
isAnnotationPresent: 判断是否标注了指定的注解。从jdk1.5开始支持。
/** * Created by brycegao on 2016/9/9. */ public class ParseAnnotation { /** * 打印出UseAnnotation类的所有类注解 * @throws ClassNotFoundException */ public static void parseTypeAnnotation() throws ClassNotFoundException { Class clz = Class.forName("com.example.annotation.UseAnnotation"); Annotation[] annotations = clz.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation:annotations) { FirstAnnotation firstAnnotation = (FirstAnnotation)annotation; System.out.println("name=" + firstAnnotation.name() + ", age:" + firstAnnotation.age()); } } /** * 打印出UseAnnotation类的构造方法注解 */ public static void parseConstructAnnotation() throws ClassNotFoundException { Class clz = Class.forName("com.example.annotation.UseAnnotation"); Constructor[] constructors = clz.getConstructors(); for (Constructor constructor:constructors) { boolean hasAnnotation = constructor.isAnnotationPresent(FirstAnnotation.class); if (hasAnnotation) { FirstAnnotation annotation = (FirstAnnotation)constructor.getAnnotation(FirstAnnotation.class); System.out.println("name=" + annotation.name() + ", age:" + annotation.age()); } } } /** * 打印出UseAnnotation类所有的方法注解 */ public static void parseMethodAnnotation() throws ClassNotFoundException { Class clz = Class.forName("com.example.annotation.UseAnnotation"); Method[] methods = clz.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method:methods) { boolean hasAnnotation = method.isAnnotationPresent(FirstAnnotation.class); if (hasAnnotation) { Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); for(Annotation annotation:annotations) { FirstAnnotation firstAnnotation = (FirstAnnotation)annotation; System.out.println("name=" + firstAnnotation.name() + ", age:" + firstAnnotation.age()); } } } } /** * 打印出所有成员变量的注解 */ public static void parseParamAnnotation() throws ClassNotFoundException { Class clz = Class.forName("com.example.annotation.UseAnnotation"); Field[] fields = clz.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field:fields) { boolean hasAnnotation = field.isAnnotationPresent(FirstAnnotation.class); if (hasAnnotation) { Annotation[] annotations = field.getAnnotations(); for(Annotation annotation:annotations) { FirstAnnotation firstAnnotation = (FirstAnnotation)annotation; System.out.println("name=" + firstAnnotation.name() + ", age:" + firstAnnotation.age()); } } } } }
public static void main(String[] args) { try { ParseAnnotation.parseMethodAnnotation(); ParseAnnotation.parseTypeAnnotation(); ParseAnnotation.parseConstructAnnotation(); ParseAnnotation.parseParamAnnotation(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
输出结果:
name=public, age:4
name=UseAnnotation, age:1
name=constructor, age:3
name=name, age:2
Ok,搞定! 现在我们看到了注解是如何为类、成员变量、成员函数、局部参数、构造函数添加一些值的。 注解在ButterKnife,EventBus,LitePal等众多开源框架中都有用到, 是Java/Android程序员的必修课之一。
上面对@Rentention留个问号, 我们将值改成Retention.CLASS再运行一下。
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) public @interface FirstAnnotation { String name() default "zhangsan"; int age() default 20; }结果是空的!这下应该理解“ 此类型注解会保留在class文件中,但JVM会忽略它”的意思了吧。
如果写成@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)也跟上面一样, 不会有值。 所以三方开源框架的注解都是用的@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)