Spring系列-Spring boot启动原理
我们上一篇文章新建了一个Spring boot的项目:spring-boot-test,稍微做了一些配置就运行起来了。和以前运行普通的项目相比,Spring boot最大的特点就是没有那一堆的配置文件,而且不用配置Tomcat,直接就可以运行了。那Spring boot做了什么,可以让我们的开发变得这么方便呢?
还是要回到我们的项目中,我们的pom中引入了spring-boot-starter-web的依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
这个依赖就会引入内置的Tomcat,还有spring-webmvc。
接下来再看启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootTestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args);
}
}
上一篇文章说过,@SpringBootApplication是个组合注解,最主要的就是组合了@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan这三个注解。
@Configuration声明当前类是一个配置类,相当于xml文件。@ComponentScan的功能是自动扫描需要装配的类,并自动装配到Spring的Bean容器中。
最重要的就是@EnableAutoConfiguration这个注解了,这个注解是进行自动配置的。我们启动Spring Boot项目的时候,这个注解就要起作用,根据我们引入的jar包,来自动的进行一些配置,省去了我们手动配置的麻烦。比如我们引入spring-boot-starter-web的依赖,就会自动的配置web项目中所需要的默认配置。
下面看下@EnableAutoConfiguration这个注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
在EnableAutoConfiguration中还定义了两个属性,exclude和excludeName,用来排除一些自动配置的类。
这里最关键的就是@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)。
@Import的作用是导入一个或多个配置类。
这里导入了EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector,这是EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector的图:
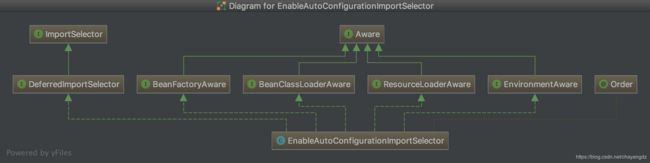
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector实现了ImportSelector接口,
public interface ImportSelector {
/**
* Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on
* the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class.
*/
String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata);
}
ImportSelector接口中定义了selectImports方法,从这个方法的注释也可以看到,这个方法是用来扫描并返回需要导入的类的。
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector实现了selectImports方法:
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
try {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(metadata);
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(metadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set exclusions = getExclusions(metadata, attributes);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = sort(configurations);
recordWithConditionEvaluationReport(configurations, exclusions);
return configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
selectImports中,就会去获取自动配置类,这里最重要的一行就是getCandidateConfigurations方法:
/**
* Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default
* this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return a list of candidate configurations
*/
protected List getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
}
这个getCandidateConfigurations方法,就会返回auto-configuration类。是通过SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames来实现的:
/**
* Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
* given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
* class loader.
* @param factoryClass the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be
* {@code null} to use the default
* @see #loadFactories
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names
*/
public static List loadFactoryNames(Class factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
try {
Enumeration urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List result = new ArrayList();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
"] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
这个方法里就会读取classpath下所有的META-INF/spring.factories文件中的配置,然后返回一个字符串类型的数组。
我们在spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.3.6.RELEASE.jar包的META-INF路径下,就可以找到spring.factories这个文件:
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.hornetq.HornetQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.velocity.VelocityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration
# Template availability providers
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.velocity.VelocityTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
这里面就定义了很多自动配置的类,把这些信息读取到并返回之后,就会把这些xxxAutoConfiguration注入Spring 容器中。
这写xxxAutoConfiguration就是自动配置的类,当满足条件的时候,就会自动配置我们的项目。
所以,现在就大体了解了Spring Boot自动配置的原理了,在我们项目启动的时候,因为有了@EnableAutoConfiguration注解,所以会从classpath下搜索所有的META-INF/spring.factories文件,加载里面的xxxAutoConfiguration,然后根据我们引入的jar包触发的条件,来对项目进行自动配置。