Struts2系列教程(三)
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/github_39430101/article/details/75209258
上一篇讲了Struts2框架下HelloWorld的实现,这篇我们将更深入地学习Struts2框架如何使用。首先思考我们在Struts2框架下,是如何将表单数据传递给业务控制器Action呢?前面章节的web.xml
<web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<filter>
<filter-name>struts2filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilterfilter-class>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts2filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
web-app>struts.xml
<struts>
<package name="day01" namespace="/demo" extends="struts-default">
<action name="hello" class="day01.HelloAction" method="sayHello">
<result name="success">/hello.jspresult>
action>
package>
struts>表单
Struts2中,表单向控制器传递参数的方式有两种。它们分别是基本属性注入和域模型注入。
- 基本属性注入:是将表单的数据项分别传入给控制器中的一些基本类型
- 域模型注入:是将表单的数据一起传入给控制器的的一个实体对象
下面我们将分别实现这两种方式。
基本属性注入
步骤1:在前面咱们所建立的项目中新增index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %>
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>jsptitle>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
head>
<body>
This is my JSP page. <br><br>
<form action="/struts/demo/hello.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form>
body>
html>步骤2:还是之前的HelloAction文件,我们做下修改,增加属性用于接收表单传入的姓名参数,该属性的名称要求与文本框的name值相同(username),并且该属性需要具备set方法。
package day01;
public class HelloAction {
private String username;
public void setUsername(String username) {
System.out.println("注入参数username");
this.username = username;
}
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println("姓名:"+username);
return "success";
}
}
项目目录
步骤3:测试,启动tomcat,输入http://localhost:8080/struts
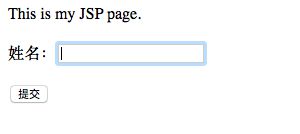
输入hello world ,点击提交
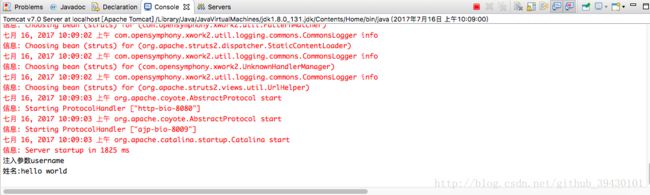
控制器已成功接受到表单的值。
域模型注入
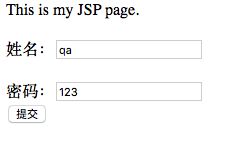
步骤1:在咱们之前的的index.jsp中加入password属性
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %>
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>jsptitle>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
head>
<body>
This is my JSP page. <br><br>
<form action="/struts/demo/hello.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/><br/>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"/><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form>
body>
html>步骤2:创建实体类entity User,用于封装表单中的数据用户名和密码,User中要包含这两个属性,并提供set/get方法。
public class User {
private String userName;// 用户名
private String password;// 密码
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}步骤3:修改HelloAction
package day01;
import com.entity.User;
public class HelloAction {
private User user;
public void setUser(User user) {
System.out.println("注入对象user");
this.user = user;
}
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println("用户名"+user.getUsername());
System.out.println("密码"+user.getPassword());
return "success";
}
}
步骤4:在index.jsp中,修改表单里新增的2个文本框的name属性值。对于域模型注入的方式,文本框name属性值应该是具有“对象名.属性名”格式的表达式。其中对象名指的是Action中的实体类型属性名,属性名指的是实体类型中的属性名
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %>
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>jsptitle>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
head>
<body>
This is my JSP page. <br><br>
<form action="/struts/demo/hello.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="user.username"/><br/><br/>
密码:<input type="text" name="user.password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form>
body>
html>步骤5:测试,启动汤姆猫,输入http://localhost:8080/struts
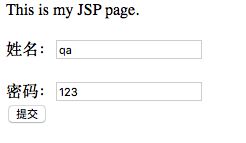
输入姓名和密码点击提交
EL表达式
我们已经学会了Struts2表单 (从前到后)的两种接收参数的方法,下面我们将简单演示一下使用EL(从后到前)表达式接受控制器中的值。
在hello.jsp中加入EL表达式接收控制器的值,注意控制器中属性要有get方法。
<%@page pageEncoding="utf-8" isELIgnored="false"%>
<html>
<head>
head>
<body>
<h1>用户名:${user.username }h1>
<h1>密码:${user.password }h1>
body>
html>