SpringBoot(三):Web开发
引入依赖
在使用SpringBoot开发web时,我们先得引入web模块的启动器的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
一、Spring Boot Web开发的默认配置
1.静态资源的映射规则:
静态资源又分为webjars和普通的静态资源。
WebJars是将Web前端Javascript和CSS等资源打包成Java的Jar包,这样在Java Web开发中我们可以借助Maven这些依赖库的管理,保证这些Web资源版本唯一性。
我们可以在WebMVCAutoConfiguration类中的静态类的WebMvcConfigurerAdpter类中的addResourceHandlers方法。以下是源码:
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled"); } else { Integer cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCachePeriod(); if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) { this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}) .addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}) .setCachePeriod(cachePeriod)); } String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(); if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) { this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern}) .addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) .setCachePeriod(cachePeriod)); } } } 我们可以看到SpringBoot默认扫描的的webjars文件夹为classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars文件夹下(所有的jar下的/META-INF/resources/webjars的文件夹)。
所有“/webjars/*” 请求 ,都去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找资源
而默认的静态文件的文件夹则需要在ResourceProperties类的StaticLocations属性中进一步查找。
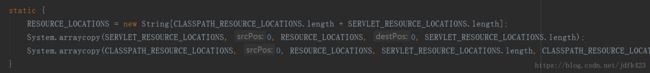
静态代码块
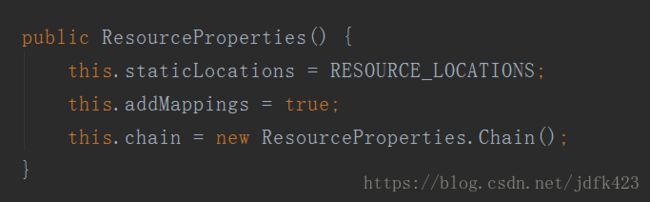
构造函数
属性定义
private static final String[] SERVLET_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"/"}; private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"}; private static final String[] RESOURCE_LOCATIONS; private String[] staticLocations; 可知访问当前项目的任何资源("/*" ),都去以下文件夹找映射
- classpath:/META-INF/resources/
- classpath:/resources/
- classpath:/static/
- classpath:/public/
- “/”:当前项目的根路径
2.欢迎页的映射规则
"/"请求会查找所有静态资源文件夹下面的所有index.html文件。
3.favicon的映射规则
所有的"**/favicon.ico "都是在静态资源文件夹下查找。
4.SpringMVC的自动配置
(1)SpringMVC的自动配置
具体详情可以查看:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.10.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-developing-web-applications
SpringBoot自动配置好了SpringMVC。以下是SpringBoot对SpringMVC的默认配置(WebMVCAutoConfiguration类中):
- Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.(包含了ContentNegotiatingViewResolverd两个视图解析器)
- Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars .(支持静态资源和WebJars,就是前三个介绍的)
- Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, Formatter beans.(自动注册了转换器,类转换器,格式化器)
- Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean(自动使用ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer)
(2)扩展SpringMVC
SpringBoot的自动配置是符合我们大多数需求的,在你既需要保留SpringBoot提供的便利又需要增加自己的额外的配置的时候,可以定义一个配置类并继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter。
(3)接管SpringBoot的Web配置
如果SpringBoot提供的SpringMVC默认配置不符合你的需求,则可以通过一个配置类(注解有@Configuration的类)加上@EnableWebMvc注解来实现自己控制MVC的配置。
二、模板引擎
JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf都是模板引擎。可以用一下的图来解释什么是模板引擎。

模板引擎的功能就是将数据填充到页面中。
SpringBoot推荐使用Thymeleaf。Thymleaf语法更简单,功能更加强大。
1、在SpringBoot中使用Thymeleaf首先得引入Thymeleaf。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<properties>
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.9.RELEASEthymeleaf.version>
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.2.2thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
properties>
2、Thymeleaf使用
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf") public class ThymeleafProperties { private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); private static final MimeType DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = MimeType.valueOf("text/html"); public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; 我们查看了Thymeleaf的自动配置中properties类可知:
只要我们把HTML页面放在classpath:/templates,Thymeleaf会默认扫描这个路径进行渲染。
我们在html文件中需要引入Thymeleaf的名称空间。
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> 编写html文件
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>成功!h1> <div th:text="${hello}">这是显示欢迎信息div> body> html> 