MPAndroidChart之PieChart源码分析
目前自己的项目用到图表。去github上看到MPAndroidChart很受欢迎,就下载下来了用了,随着项目的迭代,有些本身不具备的需求就来了。所以就花时间看了一下他的代码。非常感谢几个同事的帮忙。
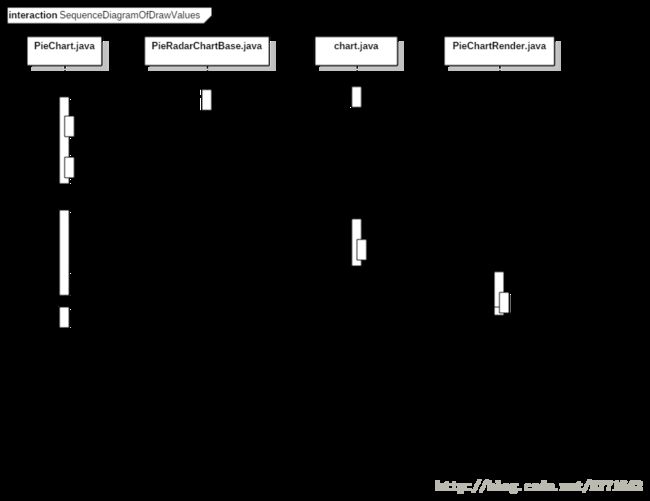
根据时序图
我把这个PieChart模块分成数据加载(1),图表参数准备(2,3,4,5,8),图表绘制(6,7,9,10)三个部分
一 图表绘制(方法10)
绘制方法基本都一样,就主要介绍一下绘制扇形区域。
作者的步骤
(1)移动到B点
(2)绘制CD弧边
(3)绘制DE线段
(4)绘制EB弧边
mPathBuffer.moveTo(arcStartPointX, arcStartPointY);
mPathBuffer.arcTo(
circleBox,
startAngleOuter,
sweepAngleOuter);
mPathBuffer.lineTo(
center.x + innerRadius * (float) Math.cos(endAngleInner * Utils.FDEG2RAD),
center.y + innerRadius * (float) Math.sin(endAngleInner * Utils.FDEG2RAD));
mPathBuffer.arcTo(
mInnerRectBuffer,
endAngleInner,
-sweepAngleInner);
他这样写是有一点小bug。我把他的项目拆解学习运行时发现Path是连贯的操作,就感觉是游戏 一笔画。
所以BC线段和DE线段是不需要绘制的。
lineto代码可以省略。
以上我们就完成了PieChart静态布局。接下来在来看一下开局动画的实现,我也通过这个项目第一次了解Android属性动画的强大。
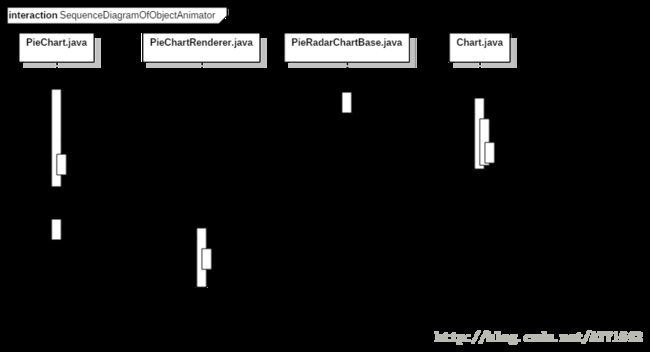
二 属性动画实现
1 初始化时序图
2 调用此方法执行开始动画
(1)创建属性动画对象
(2)设置时间补间器(这个大家可以百度一下。我觉得数学好的人这个可以玩的贼6)
(3)添加动画更新回调
(4)启动动画
public void animateY(int durationMillis, Easing.EasingOption easing) {
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 11)
return;
ObjectAnimator animatorY = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, "phaseY", 0f, 1f);
animatorY.setInterpolator(Easing.getEasingFunctionFromOption(easing));
animatorY.setDuration(durationMillis);
animatorY.addUpdateListener(mListener);
animatorY.start();
}三 监听到动画更新回调时。调用方法postInvaliadate()去让PieChart执行ondraw()方法
(1) 获取时序图中方法6 创建对象时传入的动画对象的phaseY的属性值
(2)设置扇形实际角度乘以当前动画对象的属性phaseY
float sliceAngle = drawAngles[j];
float phaseY = mAnimator.getPhaseY();
float sweepAngleOuter = (sliceAngle - sliceSpaceAngleOuter) * phaseY;
float sweepAngleInner = (sliceAngle - sliceSpaceAngleInner) * phaseY;问题
每次回调被触发时mAnimator.getPhaseY()是有不同的值的,有getPhaseY()那么一定会有方法去SetPhaseY()。在ChartAnimator.java中我确实发现了setPhaseY()。但是我全局搜索这个方法并没有发现有人去调用这个方法。到底是谁在调用这个方法?
回答
(1)这个我没有去细看的原理,google写的注释很明确(this是
ChartAnimator,propertyName是phaseY)这个对象应该有一个公共方法称为setName在其中。我猜测使用了反射。
/**
* Constructs and returns an ObjectAnimator that animates between float values. A single
* value implies that that value is the one being animated to. Two values imply starting
* and ending values. More than two values imply a starting value, values to animate through
* along the way, and an ending value (these values will be distributed evenly across
* the duration of the animation).
*
* @param target The object whose property is to be animated. This object should
* have a public method on it called setName(), where name is
* the value of the propertyName parameter.
* @param propertyName The name of the property being animated.
* @param values A set of values that the animation will animate between over time.
* @return An ObjectAnimator object that is set up to animate between the given values.
*/
public static ObjectAnimator ofFloat(Object target, String propertyName, float... values) {
ObjectAnimator anim = new ObjectAnimator(target, propertyName);
anim.setFloatValues(values);
return anim;
}四 手势触摸滚动
看这个真的太受打击了,数学玩的好的人秒懂,我自己看了一晚上没什么思路,我几个同事秒懂。扎心了,老铁。大体思路是这样:
1 touch事件监听
(1)监听onTouch事件。
(2)事件类型是按下时,获得开始角度
(3)事件类型是滑动时,获得当前角度,在减去开始按下的角度就是旋转角度
(4)通知view去执行ondraw方法。
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
float x = event.getX();
float y = event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
setGestureStartAngle(x, y);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
updateGestureRotation(x, y);
mChart.invalidate();
break;
}
return true;
}4 同一标准换算坐标
1 前提
(1)作者是以圆心为坐标原点,向上为Y轴正半轴,向右为X轴正半轴建立坐标系。
(2)作者规则:所有角度都是从X轴正半轴出发(
一定要按同一标准换算角度)
(3)我假设按下事件的坐标点都是X轴正半轴,旋转角度就都是move事件坐标的角度
public void updateGestureRotation(float x, float y) {
/*Log.e("wjq","mChart.getAngleForPoint(x, y) = " + mChart.getAngleForPoint(x, y));
Log.e("wjq","mStartAngle = " + mStartAngle);*/
mChart.setRotationAngle(mChart.getAngleForPoint(x, y) - mStartAngle);
}public float getAngleForPoint(float x, float y) {
MPPointF c = getCenterOffsets();
double tx = x - c.x, ty = y - c.y;
double length = Math.sqrt(tx * tx + ty * ty);
double r = Math.acos(ty / length);
float angle = (float) Math.toDegrees(r);
if (x > c.x)
angle = 360f - angle;
// add 90° because chart starts EAST
angle = angle + 90f;
// neutralize overflow
if (angle > 360f)
angle = angle - 360f;
MPPointF.recycleInstance(c);
return angle;
}2 角度计算
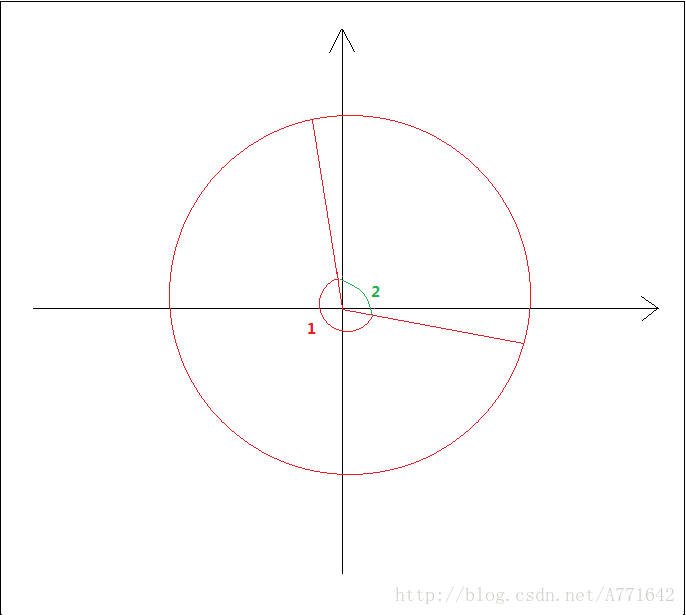
坐标点落四个象限时,所求角如下图示(角1为所求值,角2为反余弦值):
第四象限: 90 - angle
第三象限: 90+angle
第二象限:90+angle
第一象限:360-angle+90

3 zhanghongyang的逻辑判断
http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/43131133
他用的是反正弦值。其实和MPAndroid作者一样,但是他带入的点坐标没有正负之分,导致需要判断象限。从这点来看作者的数学逻辑更为优秀一点
if (getQuadrant(x, y) == 1 || getQuadrant(x, y) == 4)
{
mStartAngle += end - start;
mTmpAngle += end - start;
} else
// 二、三象限,色角度值是付值
{
mStartAngle += start - end;
mTmpAngle += start - end;
}4 换算旋转角度
(1)获取旋转角度
(2)计算开始旋转角度
(3)换算成x,y坐标
protected void drawDataSet(Canvas c, IPieDataSet dataSet) {
float rotationAngle = mChart.getRotationAngle();
final float startAngleOuter = rotationAngle + (angle + sliceSpaceAngleOuter / 2.f) * phaseY;
float arcStartPointX = center.x + radius * (float) Math.cos(startAngleOuter * Utils.FDEG2RAD);
float arcStartPointY = center.y + radius * (float) Math.sin(startAngleOuter * Utils.FDEG2RAD);
}5 图表绘制(同上逻辑)
当监听时间move的x,y坐标在不断改变,旋转角度不断改变,通知view不断绘制,就达到了手势触摸旋转效果。
五 惯性滚动
通过角加速度匀速减小角度,达到惯性滚动的目的。
1 计算角速度
(1)初始化角加速度为0
(2)初始化集合为0
(3)把down事件的点击时间和和坐标X,Y的角度组装成AngularVelocitySample对象存入集合中
(4)把move事件的点击时间和和坐标X,Y的角度组装成AngularVelocitySample对象存入集合中
(5)初始化加速角速度为0
(6)把up事件的点击时间和和坐标X,Y的角度组装成AngularVelocitySample对象存入集合中
(7)计算角速度
(8)通知computeScroll执行
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
stopDeceleration();
resetVelocity();
sampleVelocity(x, y);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
sampleVelocity(x, y);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
stopDeceleration();
sampleVelocity(x, y);
mDecelerationAngularVelocity = calculateVelocity();
mDecelerationLastTime = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();
Utils.postInvalidateOnAnimation(mChart);
break;
}
}2 检查对象
这个方法要注意他检查的是索引第0个到倒数第三个,是为了保证calculateVelocity方法中必定要取到两个对象计算角加速度
private void sampleVelocity(float touchLocationX, float touchLocationY) {
long currentTime = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();
_velocitySamples.add(new AngularVelocitySample(currentTime, mChart.getAngleForPoint(touchLocationX, touchLocationY)));
// Remove samples older than our sample time - 1 seconds
for (int i = 0, count = _velocitySamples.size(); i < count - 2; i++) {
if (currentTime - _velocitySamples.get(i).time > 1000) {
_velocitySamples.remove(0);
i--;
count--;
} else {
break;
}
}
}3 计算速度
(1)获得时间差和角度差,计算角加速度
(2)判断滚动方向是CW(顺时针)和CCW(逆时针)
private float calculateVelocity() {
if (_velocitySamples.isEmpty())
return 0.f;
AngularVelocitySample firstSample = _velocitySamples.get(0);
AngularVelocitySample lastSample = _velocitySamples.get(_velocitySamples.size() - 1);
// Look for a sample that's closest to the latest sample, but not the same, so we can deduce the direction
AngularVelocitySample beforeLastSample = firstSample;
for (int i = _velocitySamples.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
beforeLastSample = _velocitySamples.get(i);
if (beforeLastSample.angle != lastSample.angle) {
break;
}
}
// Calculate the sampling time
float timeDelta = (lastSample.time - firstSample.time) / 1000.f;
if (timeDelta == 0.f) {
timeDelta = 0.1f;
}
// Calculate clockwise/ccw by choosing two values that should be closest to each other,
// so if the angles are two far from each other we know they are inverted "for sure"
boolean clockwise = lastSample.angle >= beforeLastSample.angle;
if (Math.abs(lastSample.angle - beforeLastSample.angle) > 270.0) {
clockwise = !clockwise;
}
// Now if the "gesture" is over a too big of an angle - then we know the angles are inverted, and we need to move them closer to each other from both sides of the 360.0 wrapping point
if (lastSample.angle - firstSample.angle > 180.0) {
firstSample.angle += 360.0;
} else if (firstSample.angle - lastSample.angle > 180.0) {
lastSample.angle += 360.0;
}
// The velocity
float velocity = Math.abs((lastSample.angle - firstSample.angle) / timeDelta);
// Direction?
if (!clockwise) {
velocity = -velocity;
}
return velocity;
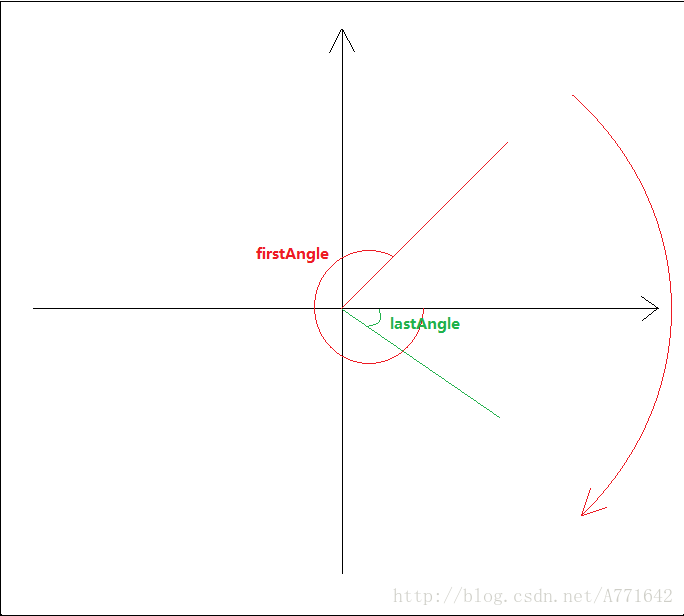
}(1)判断正反转
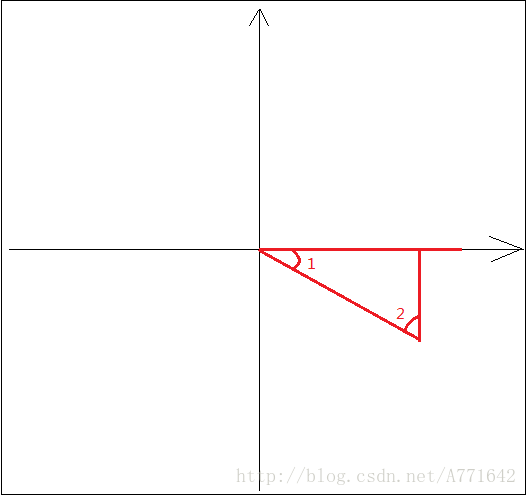
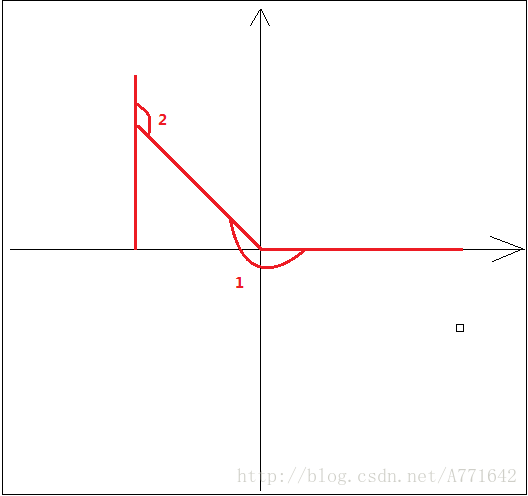
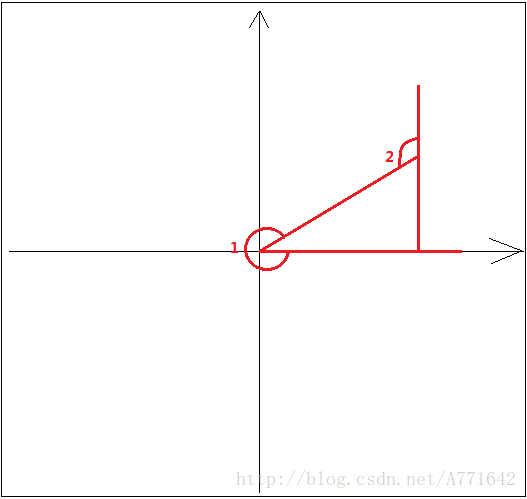
后一次的角度大于前一次的就是顺时针,反之则是逆时针。但是有两个特殊情况,反生在360和0度交界处。
lastAngle与firstAngle,判断结果(如下图)与实际情况相悖。所以就有了下面的逻辑。
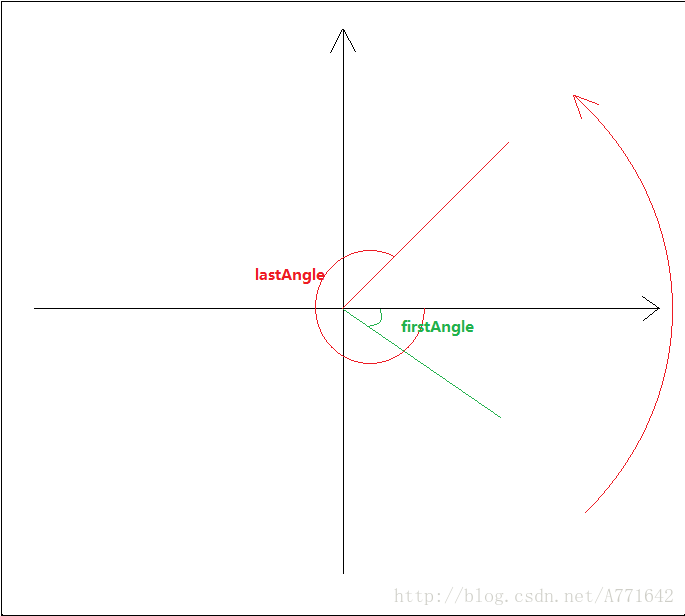
(2)角度修正
作者认为两者超过180度以后,换算的速度过大,所以就取∠1的补角∠2如下图:
3 执行滚动
(1)获取当前时间
(2)把计算出来的速度乘以大于0小于1的系数。
(3)计算时间差,换算成秒
(4)设置旋转角
(5)当速度大于0.01继续通知执行computeScroll。
这个方法执行完毕会去执行ondraw方法,重新绘制view
public void computeScroll() {
if (mDecelerationAngularVelocity == 0.f)
return; // There's no deceleration in progress
final long currentTime = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();
mDecelerationAngularVelocity *= mChart.getDragDecelerationFrictionCoef();
final float timeInterval = (float) (currentTime - mDecelerationLastTime) / 1000.f;
mChart.setRotationAngle(mChart.getRotationAngle() + mDecelerationAngularVelocity * timeInterval);
mDecelerationLastTime = currentTime;
if (Math.abs(mDecelerationAngularVelocity) >= 0.001)
Utils.postInvalidateOnAnimation(mChart); // This causes computeScroll to fire, recommended for this by Google
else
stopDeceleration();
}