Java多线程(线程池)
系统启动一个新线程的成本是比较高的,因为它涉及与操作系统交互。在这种情况下,使用线程池可以很好的提高性能,尤其是当程序中需要创建大量存在周期很短暂的线程时,更应该考虑线程池。
与数据库连接池比较相似的是,线程池在系统启动时即创建大量空闲的线程,程序将一个Runable对象或者Callable对象传递给线程池,线程池就会启动一个线程来执行它们的run方法或者call方法。当run方法或者call方法执行结束后,线程并不会死亡,而是再次返回线程池成为一个空闲线程,等待执行下一个Runable的run方法或者Callable对象的call方法。
除此之外,使用线程池可以有效的控制系统中并发线程的数量。当系统中包含大量并发线程时,会导致系统性能剧烈下降,甚至导致JVM崩溃,而线程池最大线程数参数可以控制系统中并发线程的数量不会超过此数。
>线程池创建:
从Java5开始,Java提供了一个内建的支持线程池的操作。Java5增加了一个Executors工厂类来生成线程池,该工厂类提供了如下几个静态方法来创建线程池。
- newCachedThreadPool():创建一个具有缓存功能的线程池,系统根据需要创建线程,这些线程将会被缓存到线程池中。
- newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads):创建一个可重用的、具有固定线程数的线程池。
- newSingleThreadExecutor():创建一个只有单线程的线程池,相当于调用了newFixedThreadPool方法时,只传入了1.
- newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize):创建具有指定线程数的线程池,它可以在指定延迟后执行线程任务,corePoolSize是指线程池中的线程数,即使线程是空闲的也会被保存线程池中。
- newSingleThreadScheduleExecutor():创建只有一个线程的线程池,它可以在指定的延迟后执行线程任务。
在上面5个方法中的前3个方法返回一个ExecutorService对象,该对象代表一个线程池,它可以执行Runable对象或者Callable对象所代表的线程;而后2个方法返回一个ScheduleExecutorService线程池,它是ExecutorService子类,它可以在指定延迟后执行线程任务。
ExecutorService代表尽快执行线程的线程池,程序只要将一个Runable对象或者Callable对象提交给线程池,该线程池就会尽快的执行该任务。ExecutorService提供如下3个方法:
- Future submit(Runable target):将一个Runable对象提交给线程池,线程池将会在有空闲线程的时候执行该Runable对象的代表的任务。Future代表执行Runable任务的返回值,但是Runable的run方法是没有返回值的,所以Future对象在run方法执行完成后返回null,但是可以调用Future的isDone、isCancelled的方法来获得Runable对象的执行状态。
Future submit(Runable task,T result):将一个Runable对象提交给指定的线程池,线程池将在有空闲线程时执行Runable对象代表的任务。其中result为显示的指定线程执行结束后的返回值,所以Future对象将在run方法执行结束后返回result。 Future submit(Callable task):将一个Callable对象提交给指定的线程池,线程池将在有空闲线程时执行Callable对象代表的任务。其中Future代表Callable对象里的call方法的返回值。
ScheduleExecutorService代表可在指定的延迟后或者周期性的执行线程任务的线程池,它提供了如下4个方法:
- ScheduledFuture
schedule(Callable call,long delay,TimeUnit unit):指定callable任务将在delay延迟后执行,unit为时间单位。 - ScheduledFuture
schedule(Runable command,long delay,TimeUnit unit):指定command任务将在delay延迟后执行,unit为时间单位。 - ScheduledFuture
scheduleAtFixedRate(Runable command,long delay,long period,TimeUnit unit):指定command任务将在delay延迟后执行,而且以设定的频率重复执行。也就是说在delay后开始执行,并且在delay+period、delay+2*period…处进行重复执行,依次类推。 - ScheduledFuture
scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runable command,long delay,long period,TimeUnit unit):创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用任务的定期操作,随后在每一次终止和下次开始之间都存在给定的延迟。如果任务在任意一次执行时遇到异常,就会取消后续的操作;否则只能通过程序来进行显示的取消或终止该任务。
当用完一个线程池后,应该调用该线程池的shutdown方法,该方法将启动线程池的关闭序列,调用shutdown方法后的线程池不再接受新任务,但会将以前所有已提交任务执行完成。当线程池中的所有任务都执行完成后,池中的所有线程都会死亡。另外也可以调用线程池的shutdownNow的方法来关闭线程池,该方法会试图停止所有正在执行的活动线程,暂停处理正在等待的任务,并返回正在等待执行的任务列表。
使用线程池来执行线程任务的步骤如下:
- 调用Executors类的静态工厂方法来创建一个ExecutorService对象,该对象代表一个线程池。
- 创建Runable的实例对象或Callable的实例对象,作为线程执行的任务。
- 调用ExecutorService的submit方法来提交Runable或者Callable对象的实例。
- 当不想提交任何任务时,调用ExecutorService的shutdown方法来关闭线程池。
测试:
public class TestThreadPool implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===="+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
pool.submit(new TestThreadPool());
pool.submit(new TestThreadPool());
pool.shutdown();
}
}
> Java7新增的ForkJoinPool
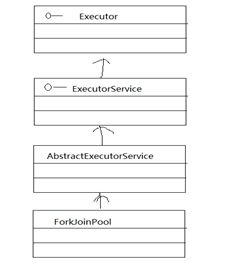
Java7提供了ForkJoinPool来支持将一个任务拆分成多个小任务并行计算,再把多个小任务的运行结果合并成总的计算结果。ForkJoinPool是ExecutorService的实现类,因此一种特殊的线程池,ForkJoinPool提供了如下两个构造方法:
- ForkJoinPool(int parallelism):创建一个包含parallelism个并行线程的ForkJoinPool。
- ForkJoinPool():以Runtime.availableProcessors()方法的返回值作为parallelism参数来创建ForkJoinPool的线程池。
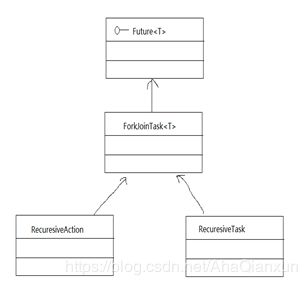
创建了ForkJoinPool的实例之后,就可以调用ForkJoinPool的submit(ForkJoinTask task)或者invoke(ForkJoinTask task)方法来执行指定任务了。其中ForkJoinTask代表可以并行、合并的任务。ForkJoinTask是一个抽象类,它还有两个抽象子类:RecuresiveAction和RecuresiveTask。其中ResuresiveAction代表没有返回值的任务,RecuresiveTask代表有返回值的任务。
ForkJoinPool和ForkJoinTask的类图示意图:
测试:执行一个没有返回值的大任务,程序将一个大任务拆分成多个小任务,并将任务交个ForkJoinPool来执行。
public class PrintTask extends RecursiveAction {
private int start;
private int end;
public PrintTask(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
protected void compute() {
if (this.end - this.start < 50) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "======" + i);
}
} else {
int middle = (this.start + this.end) / 2;
PrintTask left = new PrintTask(start, middle);
PrintTask right = new PrintTask(middle, end);
// 执行任务的拆分
left.fork();
right.fork();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
PrintTask task = new PrintTask(0, 300);
pool.submit(task);
// 用于等待子线程结束,再继续执行下面的代码
pool.awaitTermination(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
System.out.println("程序执行结束!");
}
}
测试:有返回值的
public class Test extends RecursiveTask {
private int startLine = 0;
private int endLine = 0;
private File file = null;
public Test(int startLine, int endLine, File file) {
this.startLine = startLine;
this.endLine = endLine;
this.file = file;
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
if (this.endLine - this.startLine <= 10) {
Scanner scan = null;
try {
scan = new Scanner(this.file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < this.startLine; i++) {
scan.nextLine();
}
int size = 0;
for (int i = this.startLine; i < this.endLine; i++) {
size += scan.nextLine().getBytes().length + 2;
}
return size;
} else {
int middle = (this.startLine + this.endLine) / 2;
Test left = new Test(this.startLine, middle, this.file);
Test right = new Test(middle, this.endLine, this.file);
try {
return left.fork().get() + right.fork().get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("线程中断......");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.out.println("执行异常......");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
File file = new File("./src/com/blocking/Test.java");
Test test = new Test(0, 61, file);
ForkJoinTask task = pool.submit(test);
System.out.println(task.get());
System.out.println(test.get());
}
}
通过上面的程序运行可以看出,ForkJoinPool启动了四个线程来打印这个任务,虽然打印了0-299这300个数字,但并不是连续打印的,这是因为程序将这个任务进行了分解,分解后的任务会并行运行。
>补充:集合线程安全的方法
使用Collections.synchronizedXXX函数接收特定的Collection,将转换成包装类型的SynchronizedXXX类型
实现集合的线程同步,安全访问