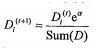AdaBoost元算法学习理解与应用实战
据说在Deep Learning出来之前,SVM和Adaboost是效果最好的 两个算法。上一节,我们已经学习理解了SVM,本节让我们一起学习理解Adaboost并且应用吧!
1、拟解决基本问题描述
数据集:航天飞机数据集
摘要:穿梭数据集包含9个属性,全部都是数值。大约80%的数据属于第1类
来源:http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Statlog+%28Shuttle%29
数据集信息:
约80%的数据属于第1类。因此默认精度约为80%。这里的目标是获得99-99.9%的准确度。
原始数据集中的例子按时间顺序排列,这个时间顺序可能与分类有关。但是,这与StatLog目的并不相关,因此原始数据集中示例的顺序是随机的,并且为验证目的而移除了原始数据集的一部分。
属性信息:
穿梭数据集包含9个属性,所有这些属性都是数字。第一个是时间。最后一列是编码如下的类: 1 Rad Flow 2 Fpv Close 3 Fpv Open 4 High 5 Bypass 6 Bpv Close 7 Bpv Open
2.模型基本原理与算法实现
【Boosting】也称为增强学习或提升法,是一种重要的集成学习技术,能够将预测精度仅比随机猜度略高的弱学习器增强为预测精度高的强学习器,这在直接构造强学习器非常困难的情况下,为学习算法的设计提供了一种有效的新思路和新方法。其中最为成功应用的是,YoavFreund和Robert Schapire在1995年提出的AdaBoost算法。
【AdaBoost】 "Adaptive Boosting"(自适应增强)的缩写,它的自适应在于:前一个基本分类器被错误分类的样本的权值会增大,而正确分类的样本的权值会减小,并再次用来训练下一个基本分类器。同时,在每一轮迭代中,加入一个新的弱分类器,直到达到某个预定的足够小的错误率或达到预先指定的最大迭代次数才确定最终的强分类器。
【算法步骤】
(1) 如果有N个样本,创建一个N维权向量D。
初始化:相等值(1/N,1/N,…,1/N)
(2) 训练弱分类器对于每个训练样本点
权值更新过的样本集被用于训练下一个分类器,整个训练过程如此迭代地进行下去。
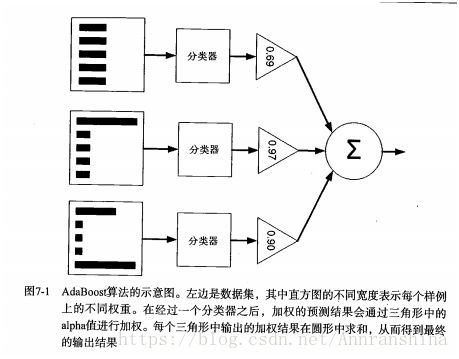
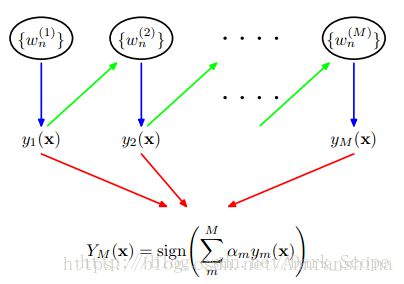
(3)最后,将各个训练得到的弱分类器组合成一个强分类器。各个弱分类器的训练过程结束后,加大分类误差率小的弱分类器的权重,使其在最终的分类函数中起着较大的决定作用,而降低分类误差率大的弱分类器的权重,使其在最终的分类函数中起着较小的决定作用。
换而言之,误差率低的弱分类器在最终分类器中占的权重较大,否则较小。
【注意】Adaboost为每个分类器分配了一个权重值:alpha,它通过每个弱分类器的错误率计算。
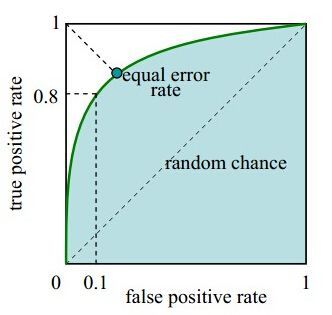
【Roc曲线】
受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,简称ROC曲线),又称为感受性曲线(sensitivitycurve)。得此名的原因在于曲线上各点反映着相同的感受性,它们都是对同一信号刺激的反应,只不过是在两种不同的判定标准下所得的结果而已。
受试者工作特征曲线就是以假阳性概率(False positive rate)为横轴。
真阳性(True positive rate)为纵轴所组成的坐标图。
作用:
1.ROC曲线能很容易地查出任意界限值时的对疾病的识别能力。
2.选择最佳的诊断界限值。ROC曲线越靠近左上角,试验的准确性就越高。最靠近左上角的ROC曲线的点是错误最少的最好阈值,其假阳性和假阴性的总数最少。
3.两种或两种以上不同诊断试验对疾病识别能力的比较。在对同一种疾病的两种或两种以上诊断方法进行比较时,可将各试验的ROC曲线绘制到同一坐标中,以直观地鉴别优劣,靠近左上角的ROC曲线所代表的受试者工作最准确。亦可通过分别计算各个试验的ROC曲线下的面积(AUC)进行比较,哪一种试验的 AUC最大,则哪一种试验的诊断价值最佳。
3.测试方法与结果
注意:采用基于单层决策树构建弱分类器。
程序见附录。
【运行结果】
runfile('D:/python/untitled1.py',wdir='D:/python')
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
total error: 0.20841379310344826
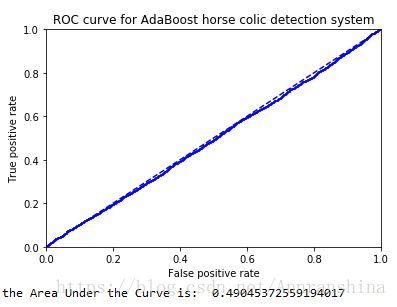
【ROC曲线绘制】
the Area Under the Curve is: 0.49045372559194017
4.总结
【优缺点】
优点:泛化错误率低,易编码。可以应用在大部分分类器上,无参数调整。
缺点:对离群点敏感。
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型数据。
【小结】
本节以单层决策树作为弱学习构建了AdaBoost分类器。实际上,AdaBoost函数可以应用于任意分类器,只要分类器能处理加权数据即可。Adaboost算法十分强大,它能够快速处理其他分类器很难处理的数据集。
5.参考文献
- Peter, Harrington. 机器学习实战[M]. 北京:人民邮电出版社, 2013. 115-133
- pan_jinquan. Adaboost算法原理分析和实例+代码(简明易懂)[EB/OL]. https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/70995333.
- Dark_Scope. AdaBoost--从原理到实现[EB/OL]. https://blog.csdn.net/dark_scope/article/details/14103983.
- 百度百科. ROC曲线[EB/OL]. https://baike.baidu.com/item/ROC%E6%9B%B2%E7%BA%BF/775606?fr=aladdin.
6.附录
【adaboost.py】
【代码来源:机器学习实战】
【作者改写适合于python3.0】
'''
Created on Nov 28, 2010
Adaboost is short for Adaptive Boosting
@author: Peter
'''
from numpy import *
def loadSimpData():
datMat = matrix([[ 1. , 2.1],
[ 2. , 1.1],
[ 1.3, 1. ],
[ 1. , 1. ],
[ 2. , 1. ]])
classLabels = [1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0]
return datMat,classLabels
def loadDataSet(fileName): #general function to parse tab -delimited floats
numFeat = len(open(fileName).readline().split(' ')) #get number of fields
dataMat = []; labelMat = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr =[]
curLine = line.strip().split(' ')
for i in range(numFeat-1):
lineArr.append(float(curLine[i]))
dataMat.append(lineArr)
labelMat.append(float(curLine[-1]))
return dataMat,labelMat
def stumpClassify(dataMatrix,dimen,threshVal,threshIneq):#just classify the data
retArray = ones((shape(dataMatrix)[0],1))
if threshIneq == 'lt':
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen] <= threshVal] = -1.0
else:
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen] > threshVal] = -1.0
return retArray
def buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D):
dataMatrix = mat(dataArr); labelMat = mat(classLabels).T
m,n = shape(dataMatrix)
numSteps = 10.0; bestStump = {}; bestClasEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
minError = inf #init error sum, to +infinity
for i in range(n):#loop over all dimensions
rangeMin = dataMatrix[:,i].min(); rangeMax = dataMatrix[:,i].max();
stepSize = (rangeMax-rangeMin)/numSteps
for j in range(-1,int(numSteps)+1):#loop over all range in current dimension
for inequal in ['lt', 'gt']: #go over less than and greater than
threshVal = (rangeMin + float(j) * stepSize)
predictedVals = stumpClassify(dataMatrix,i,threshVal,inequal)#call stump classify with i, j, lessThan
errArr = mat(ones((m,1)))
errArr[predictedVals == labelMat] = 0
weightedError = D.T*errArr #calc total error multiplied by D
#print "split: dim %d, thresh %.2f, thresh ineqal: %s, the weighted error is %.3f" % (i, threshVal, inequal, weightedError)
if weightedError < minError:
minError = weightedError
bestClasEst = predictedVals.copy()
bestStump['dim'] = i
bestStump['thresh'] = threshVal
bestStump['ineq'] = inequal
return bestStump,minError,bestClasEst
def adaBoostTrainDS(dataArr,classLabels,numIt=40):
weakClassArr = []
m = shape(dataArr)[0]
D = mat(ones((m,1))/m) #init D to all equal
aggClassEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
for i in range(numIt):
bestStump,error,classEst = buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D)#build Stump
#print "D:",D.T
alpha = float(0.5*log((1.0-error)/max(error,1e-16)))#calc alpha, throw in max(error,eps) to account for error=0
bestStump['alpha'] = alpha
weakClassArr.append(bestStump) #store Stump Params in Array
#print "classEst: ",classEst.T
expon = multiply(-1*alpha*mat(classLabels).T,classEst) #exponent for D calc, getting messy
D = multiply(D,exp(expon)) #Calc New D for next iteration
D = D/D.sum()
#calc training error of all classifiers, if this is 0 quit for loop early (use break)
aggClassEst += alpha*classEst
#print "aggClassEst: ",aggClassEst.T
aggErrors = multiply(sign(aggClassEst) != mat(classLabels).T,ones((m,1)))
errorRate = aggErrors.sum()/m
print ("total error: ",errorRate)
if errorRate == 0.0: break
return weakClassArr,aggClassEst
def adaClassify(datToClass,classifierArr):
dataMatrix = mat(datToClass)#do stuff similar to last aggClassEst in adaBoostTrainDS
m = shape(dataMatrix)[0]
aggClassEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
for i in range(len(classifierArr)):
classEst = stumpClassify(dataMatrix,classifierArr[i]['dim'],\
classifierArr[i]['thresh'],\
classifierArr[i]['ineq'])#call stump classify
aggClassEst += classifierArr[i]['alpha']*classEst
print (aggClassEst)
return sign(aggClassEst)
def plotROC(predStrengths, classLabels):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cur = (1.0,1.0) #cursor
ySum = 0.0 #variable to calculate AUC
numPosClas = sum(array(classLabels)==1.0)
yStep = 1/float(numPosClas); xStep = 1/float(len(classLabels)-numPosClas)
sortedIndicies = predStrengths.argsort()#get sorted index, it's reverse
fig = plt.figure()
fig.clf()
ax = plt.subplot(111)
#loop through all the values, drawing a line segment at each point
for index in sortedIndicies.tolist()[0]:
if classLabels[index] == 1.0:
delX = 0; delY = yStep;
else:
delX = xStep; delY = 0;
ySum += cur[1]
#draw line from cur to (cur[0]-delX,cur[1]-delY)
ax.plot([cur[0],cur[0]-delX],[cur[1],cur[1]-delY], c='b')
cur = (cur[0]-delX,cur[1]-delY)
ax.plot([0,1],[0,1],'b--')
plt.xlabel('False positive rate'); plt.ylabel('True positive rate')
plt.title('ROC curve for AdaBoost horse colic detection system')
ax.axis([0,1,0,1])
plt.show()
print ("the Area Under the Curve is: ",ySum*xStep)
【Ceshi.py】
from adaboost import *
#datArr,labelArr=loadDataSet('shuttle.txt')
'''
datArr,labelArr=loadDataSet('horseColicTraining2.txt')
classifierArray,aggClassEst=adaBoostTrainDS(datArr,labelArr,10)
testArr,testLabelArr=loadDataSet('horseColicTest2.txt')
prediction10=adaClassify(testArr,classifierArray)
errArr=mat(ones((67,1)))
errArr[prediction10!=mat(testLabelArr).T].sum()
datArr,labelArr=loadDataSet('horseColicTraining2.txt')
classifierArray,aggClassEst=adaBoostTrainDS(datArr,labelArr,10)
plotROC(aggClassEst.T,labelArr)
'''
datArr,labelArr=loadDataSet('shuttle.txt')
classifierArray,aggClassEst=adaBoostTrainDS(datArr,labelArr,10)
plotROC(aggClassEst.T,labelArr)