拥塞控制算法分类
这几天写了一份项目书,正好对之前看过的拥塞控制算法进行了一次整理,主要是从算法机制分析优缺点。
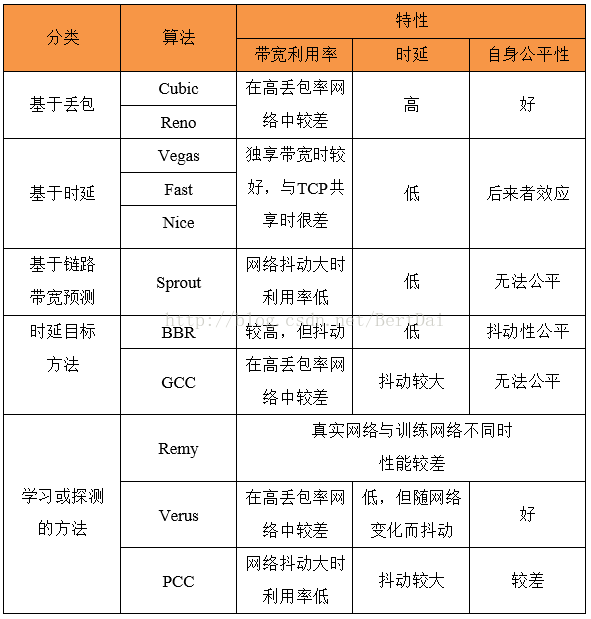
我把现有的拥塞控制技术分成了五大类:传统的基于丢包或基于延迟方法,这两个类别是通用的分类,那些比较远古的算法基本上就可以这么二分;基于链路容量预测,基于延迟目标和基于学习或探测的这三类,主要包含了近几年的一些算法,其中延迟目标方法和传统的基于延迟的方法有些类似,但是也有本身的特点,我就单列了。每个类别举了几个典型的算法:
- 传统的基于丢包的方法:主要以TCP Reno [1]和TCP Cubic [2]为代表。它们将丢包视为拥塞信号,遇到丢包时将发送窗口减半来规避拥塞。但是在没有丢包时会不断填充缓冲区,使缓冲区长期保持过满状态,造成了过大的排队延迟,同时,在链路丢包的网络环境中,带宽利用率也很差。
- 传统的基于延迟的方法:包括了TCP Vegas [3],Fast TCP [4]和TCP Nice [5]等,它们使用了延迟作为拥塞信号,包括单向延迟、排队延迟和往返延迟等,虽然在测量过程中会有噪声干扰,但延迟可以粗略的表示网络中数据包的数量。这种机制可以保证它们在限制延迟上有不错的性能表现,但是在与基于丢包的数据流共享瓶颈带宽时,会因为缺乏竞争力而导致带宽分配的不公平 [6]。此外,如果网络中已经存在数据流或者已经拥塞,新加入的数据流会检测到比真实值更小的排队延迟,进而夺取更多的带宽分配,这也是所谓的“后来者效应”。
- 基于链路容量预测的方法:以Sprout [7]为代表。它是一个专门为无线网络设计的拥塞控制算法,并没有采取传统算法那样以丢包或延迟为拥塞信号,而是通过收端观察到数据包到达的时间间隔,再使用概率论来推测瓶颈链路的容量,发端的发送速率直接采用这个预测值。但在网络环境变动较大时,Sprout对瓶颈链路带宽的预测会产生较大误差,进而导致算法性能大幅下降。
- 基于延迟目标的方法:包含了Ledbat [8]、BBR和WebRTC中的GCC [9]算法。这些算法都设定了一个低延迟目标,并且希望可以收敛于该目标值。但是GCC和Ledbat都无法做到良好的公平性,因为它们无法获知网络中数据流的数量,也就无法设定一个公平的窗口大小。在BBR [10]中,借助传播延迟的测量,通过周期性的重置所有的数据流到初始状态,可以做到数据流之间公平的共享瓶颈带宽,但是这种周期性初始化的机制会造成传输速率的抖动。
-
基于学习和探测的方法:包含了Remy [11],Verus [12]和PCC [13]。它们与传统的拥塞控制算法不同,没有设置特定的拥塞信号,而是借助评价函数,使用学习或探测的方法去形成一个更优的控制策略。但是Remy和Verus的控制策略均依赖于训练数据形成,当真实网络情况有所差异时,性能表现会大幅下降。PCC使用的探测方法使其面对网络环境的变动应对迟缓,并且它仍然考虑了丢包因素,造成与传统TCP相似的带宽利用率问题。
上述提到的算法在参考文献里一一对应。我也整理了一个表格,粗略介绍了算法在带宽,时延和intra-fairness上的特性:
如果有大牛看到这篇文章,有什么不同见解可以交流一下,或者发现文中有什么错误,欢迎指正~~
参考文献:
[1] V.Jacobson, “Congestion avoidance and control,” in ACM SIGCOMM ComputerCommunication Review, vol. 18. ACM, 1988, pp. 314–329.
[2] L. X. I. R. Sangtae Ha. Cubic: A new TCP -friendlyhigh-speed TCP variant. In SIGOPS-OSR, July 2008. ACM, 2008.
[3] S.O. L. Brakmo and L. Peterson. TCP Vegas: New techniques for congestiondetection and avoidance. In SIGCOMM, 1994. Proceedings. 1994 InternationalConference on. ACM, 1994.
[4] S. H. L. D. X. Wei, C. Jin and S. Hegde. Fast TCP:motivation, architecture, algorithms, performance. IEEE/ACM Transactions onNetworking (TON), 12(4):458{472, 2006.
[5] A. Venkataramani, R. Kokku, and M. Dahlin. TCPNice: a mechanism for background transfers. SIGOPS Oper. Syst. Rev., 36(SI):329–343,Dec. 2002.
[6] L.A. Grieco and S. Mascolo, “Performance evaluation and comparison of Westwood+,new Reno, and Vegas TCP congestion control,” Computer Communication Review,vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 25–38, 2004.
[7] K.Winstein, A. Sivaraman, and H. Balakrishnan. Stochastic forecasts achieve high throughputand low delay over cellular networks. In Proceedings of the 10th USENIXconference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, 2013.
[8] S.V. D. Rossi, C. Testa and L. Muscariello. Ledbat: the newbittorrent congestioncontrol protocol. In Proceedings of ICCCN, 2010. IEEE, 2010.
[9] L.D. Cicco, G. Carlucci, and S. Mascolo, “Experimental investigation of thegoogle congestion control for real-time flows,” 2013.
[10] C.S. G. S. H. Y. Neal Cardwell, Yuchung Cheng and V. Jacobson. BBR:congestion-based congestion control. ACM Queue, 14(5):20{53, 2016.
[11] K.Winstein and H. Balakrishnan. TCP Ex Machina: Computer-generated Congestion Control.In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2013 Conference, 2013.
[12] ZakiY, Potsch T, Chen J, et al. Adaptive Congestion Control for UnpredictableCellular Networks[J]. ACM special interest group on data communication, 2015,45(4): 509-522.
[13] M.Dong, Q. Li, D. Zarchy, B. Godfrey, and M. Schapira. PCC: Re-architectingcongestion control for consistent high performance. 12th USENIXSymposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI), 2015.