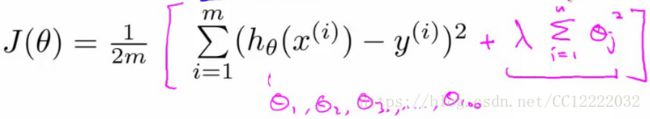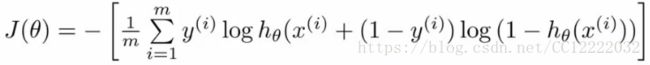吴恩达机器学习总结:第四课 正则化(大纲摘要及课后作业)
为了更好的学习,充分复习自己学习的知识,总结课内重要知识点,每次完成作业后
都会更博。
英文非官方笔记
总结
1.过拟合问题
(1)线性回归的过拟合
a .过拟合导致高方差,欠拟合导致高偏差
b.泛化能力差
(2)逻辑回归的过拟合
(3)解决过拟合方法
a.减少特征数量(会造成信息缺失)
b.正则化
2.正则化的代价函数优化
(1)代价函数(其中正则想不包括θ0)
(2)正则化参数λ
a.控制我们两个目标之间的权衡(拟合训练集很好、保持参数小)
b.如果λ太大,就会过度惩罚,导致参数接近0
3.正则化的线性回归
(1)梯度下降
4.正则化的正规方程
4.正则化的逻辑回归
(1)代价函数
(2)梯度下降
作业
(1)可视化
data = load('ex2data2.txt');
X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = data(:, 3);
plotData(X, y);
hold on;
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0')
hold off;(2)正则化逻辑回归
X = mapFeature(X(:,1), X(:,2));
%初始化参数
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
lambda = 1;
[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda);
% theta为1 λ为10
test_theta = ones(size(X,2),1);
[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(test_theta, X, y, 10);
%costFunctionReg函数
m = length(y);
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
theta_1 = [0;theta(2:end)];
J =(-1/m)*sum( y.*log(sigmoid(X *theta)) + (1 - y).*log(1 - sigmoid(X*theta)) ) + 1/(2*m)*lambda*theta_1' *theta_1;
grad = ( X' * (sigmoid(X*theta) - y ) )/ m + lambda/m * theta_1 ;
end
(3)正则化和准确度
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
lambda = 100;
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda))
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off;
p = predict(theta, X);
%决策边界函数
plotData(X(:,2:3), y);
hold on
if size(X, 2) <= 3
% Only need 2 points to define a line, so choose two endpoints
plot_x = [min(X(:,2))-2, max(X(:,2))+2];
% Calculate the decision boundary line
plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1));
% Plot, and adjust axes for better viewing
plot(plot_x, plot_y)
% Legend, specific for the exercise
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary')
axis([30, 100, 30, 100])
else
% Here is the grid range
u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50);
v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50);
z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
% Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
for i = 1:length(u)
for j = 1:length(v)
z(i,j) = mapFeature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
end
end
z = z'; % important to transpose z before calling contour
contour(u, v, z, [0, 0], 'LineWidth', 2)
end
hold off
end
&预测函数
m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples
p = zeros(m, 1);
k = find(sigmoid(X *theta)>= 0.5);
p(k) = 1;
%sigmoid函数
g = zeros(size(z));
g = 1./(1 + exp(-z));
end