python神经网络实现
前言
最近实习单位在搞电网数据的清洗程序改写,用到了稀疏编码器,关于稀疏编码器的原理部分,可以参见下面的文档,这里可以这么简单理解:就是通过对代价函数设置交叉熵等误差项,使得输出层和输入层是基本一致的。
但是,实际上,Sparse AutoEncoder是来源于传统神经网络的。由于要在集群上跑,对速度要求很高,而且sklearn的包的神经网络api中没有稀疏编码器,有一些如同MLPclassifier等方法。
所以现在的需求是在传统神经网络的基础上写稀疏编码器,那么就需要手动实现NN(Neutral Network)了。
计算过程
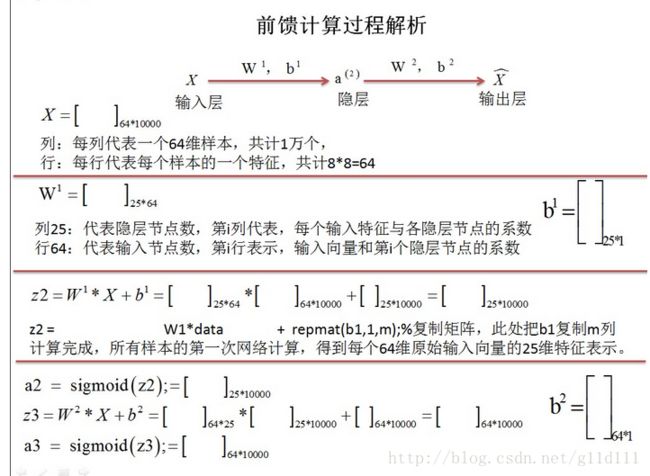
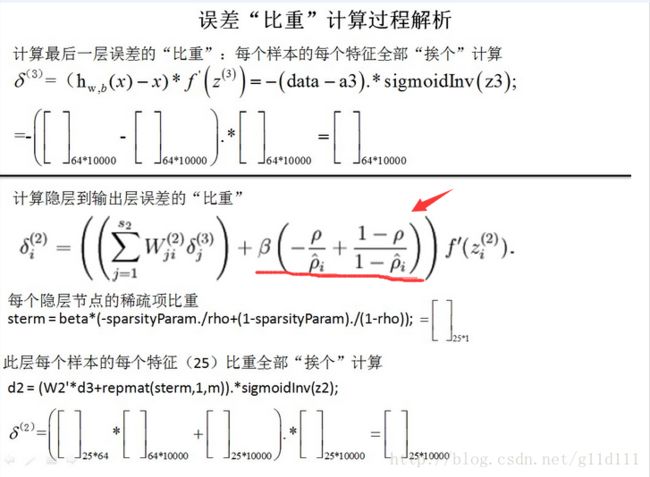
这块是参考http://blog.csdn.net/whiteinblue/article/details/20639629这篇博客的流程,因为我们是神经网络,所以交叉熵等内容就不要了。
ps:对传统神经网络,代价函数J(W,b)可只保留第一项。
啊输出层的误差信号跟神经网络是一样的,隐藏层的误差是删掉红色箭头的内容。
Python实现
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed May 08:40:21 2017
@author: 高岱恒
传统神经网络
"""
# 以输入为5个unit 中间为5 输出为3类 样本数为m为例子进行阐述
import numpy
import math
import time
import scipy.optimize
import numpy as np
###########################################################################################
""" The NN class """
class NeutralNetwork(object):
#######################################################################################
""" Initialization of NN object """
def __init__(self, visible_size, hidden_size, output_size, lamda):
""" Initialize parameters of the NN object """
self.visible_size = visible_size # number of input units
self.hidden_size = hidden_size # number of hidden units
self.output_size = output_size # number of output units
self.lamda = lamda # weight decay parameter
""" Set limits for accessing 'theta' values """
self.limit0 = 0
self.limit1 = hidden_size * visible_size
self.limit2 = hidden_size * visible_size + visible_size * output_size
self.limit3 = hidden_size * visible_size + visible_size * output_size + hidden_size
self.limit4 = hidden_size * visible_size + visible_size * output_size + hidden_size + output_size
self.iterate = 0 # 循环次数计数
""" Initialize Neural Network weights randomly
W1, W2 values are chosen in the range [-r, r] """
# RandomState里面参数为seed:即随机数种子
rand = numpy.random.RandomState(int(time.time()))
# 三层的NN,input layer hidden layer(只有1层) output layer
W1 = numpy.asarray(rand.uniform(low=-2, high=2, size=(hidden_size, visible_size)))
W2 = numpy.asarray(rand.uniform(low=-2, high=2, size=(visible_size, output_size)))
""" Bias values are initialized to zero """
b1 = numpy.zeros((hidden_size, 1))
b2 = numpy.zeros((output_size, 1))
""" Create 'theta' by unrolling W1, W2, b1, b2 """
# flatten() 数据展平 self.theta变成由权重,bias单元组成的1维数组。
self.theta = numpy.concatenate((W1.flatten(), W2.flatten(),
b1.flatten(), b2.flatten()))
#######################################################################################
""" Returns elementwise sigmoid output of input array """
def sigmoid(self, x):
return (1 / (1 + numpy.exp(-x)))
#######################################################################################
""" Returns hidden layer """
# 中间层,经过激活函数的值。
def CaculateHidden(self, theta, input):
W1 = theta[self.limit0: self.limit1].reshape(self.hidden_size, self.visible_size)
b1 = theta[self.limit2: self.limit3].reshape(self.hidden_size, 1)
hidden_layer = self.sigmoid(numpy.dot(W1, input) + b1)
return hidden_layer
#######################################################################################
""" Returns output layer """
# 输出层,经过激活的值
def CaculateOutput(self, theta, input):
W2 = theta[self.limit1: self.limit2].reshape(self.output_size, self.hidden_size)
b2 = theta[self.limit3: self.limit4].reshape(self.output_size, 1)
hidden_layer = self.CaculateHidden(theta, input)
output_layer = self.sigmoid(numpy.dot(W2, hidden_layer) + b2)
return output_layer
#######################################################################################
""" Returns the cost of the NN and gradient at a particular 'theta' """
def NNCost(self, theta, input, label):
if (self.iterate % 50 == 0):
print("当前正在进行第{}次迭代".format(self.iterate))
self.iterate += 1
""" Extract weights and biases from 'theta' input """
W1 = theta[self.limit0: self.limit1].reshape(self.hidden_size, self.visible_size)
W2 = theta[self.limit1: self.limit2].reshape(self.output_size, self.hidden_size)
b1 = theta[self.limit2: self.limit3].reshape(self.hidden_size, 1)
b2 = theta[self.limit3: self.limit4].reshape(self.output_size, 1)
""" Compute output layers by performing a feedforward pass
Computation is done for all the training inputs simultaneously """
# 前向运算FP
# hidden_layer 5*m
hidden_layer = self.sigmoid(numpy.dot(W1, input) + b1)
# output_layer 3*m
output_layer = self.sigmoid(numpy.dot(W2, hidden_layer) + b2)
# rand = numpy.random.RandomState(int(time.time()))
# a = numpy.asarray(rand.uniform(low=-5, high=5, size=(2, 3)))
# print(a)
# c = numpy.sum(a, axis=1)
# print(c)
# [[-2.70721758 0.21224747 4.95405617]
# [-0.97418797 3.36909078 -3.4271098 ]]
# [ 2.45908606 -1.03220698]
# axis=1 按行求和
""" Compute intermediate difference values using Backpropagation algorithm """
# 反向运算BP
# 误差
diff = output_layer - label
# numpy.multiply()不是矩阵乘法,是对应元素相乘
# b = numpy.array([1, 5])
# print(numpy.multiply(b, b)) [ 1 25]
# 均方误差:sum_of_squares_error
sum_of_squares_error = 0.5 * numpy.sum(numpy.multiply(diff, diff)) / input.shape[1]
# 代价函数
costFunction = sum_of_squares_error
# del_out是最后一层误差的误差信号
# del_out为3*m矩阵
# 因为sigmoid函数的导数形式为 y' = y(1-y) numpy.multiply(output_layer, 1 - output_layer)
del_out = numpy.multiply(diff, numpy.multiply(output_layer, 1 - output_layer))
# del_hid是中间层误差的误差信号
# del_hid为(5*5 * 5*m + 5*m).*5*m=5*m
del_hid = numpy.multiply(numpy.dot(numpy.transpose(W2), del_out), numpy.multiply(hidden_layer, 1-hidden_layer))
""" Compute the gradient values by averaging partial derivatives
Partial derivatives are averaged over all training examples """
W1_grad = numpy.dot(del_hid, numpy.transpose(input))
W2_grad = numpy.dot(del_out, numpy.transpose(hidden_layer))
# b1_grad和b2_grad按行求和,分别为1*5 1*3
# 即bias unit的权重,是对应层的误差信号的和求平均
b1_grad = numpy.sum(del_hid, axis=1)
b2_grad = numpy.sum(del_out, axis=1)
#
W1_grad = W1_grad / input.shape[1]
W2_grad = W2_grad / input.shape[1]
b1_grad = b1_grad / input.shape[1]
b2_grad = b2_grad / input.shape[1]
""" Transform numpy matrices into arrays """
W1_grad = numpy.array(W1_grad)
W2_grad = numpy.array(W2_grad)
b1_grad = numpy.array(b1_grad)
b2_grad = numpy.array(b2_grad)
""" Unroll the gradient values and return as 'theta' gradient """
theta_grad = numpy.concatenate((W1_grad.flatten(), W2_grad.flatten(),
b1_grad.flatten(), b2_grad.flatten()))
return [costFunction, theta_grad]
###########################################################################################
def main():
""" Define the parameters of the Autoencoder """
lambdas = 0.05 # desired average activation of hidden units
max_iterations = 1000 # number of optimization iterations(可以加可以不加)
visible_size = 5 # number of input units
hidden_size = 5 # number of hidden units
output_size = 3 # number of output units
""" Load initialized sampled training data """
# 数据形式为5个特征,有5个样本
# 第一个特征:身高
# 第二个特征:体重
# 第三个特征:年龄
# 第四个特征:交往男女朋友数目
# 第五个特征:性别:男1 女0
training_data = numpy.array([[170, 60, 23, 3, 1], [173, 80, 25, 0, 1], [160, 52, 21, 2, 0], [183, 70, 28, 3, 1], [165, 45, 26, 6, 0]]).transpose()
# 标签 [1, 0, 0]表示类别为完美 [0, 1, 0]表示类别为良好 [0, 0, 1]表示类别为不合格
label = numpy.array([[1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0]]).transpose()
""" Initialize the NeutralNetwork with the above parameters """
encoder = NeutralNetwork(visible_size, hidden_size, output_size, lambdas)
""" Run the L-BFGS algorithm to get the optimal parameter values """
opt_solution = scipy.optimize.minimize(encoder.NNCost, encoder.theta,
args=(training_data, label, ),
method='L-BFGS-B',
# options={'maxiter': max_iterations},
jac=True)
opt_theta = opt_solution.x
opt_W1 = opt_theta[encoder.limit0: encoder.limit1].reshape(hidden_size, visible_size) # 第一层权重
opt_W2 = opt_theta[encoder.limit1: encoder.limit2].reshape(output_size, hidden_size)
opt_B1 = opt_theta[encoder.limit2: encoder.limit3].reshape(hidden_size, 1)
opt_B2 = opt_theta[encoder.limit3: encoder.limit4].reshape(output_size, 1)
return opt_W1, opt_W2, opt_B1, opt_B2
def sigmoid(x):
return (1 / (1 + numpy.exp(-x)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 模型训练完成!
w1, w2, b1, b2 = main()
# 测试
example = numpy.array([140, 70, 37, 0, 0]).reshape(5, 1)
b = numpy.dot(w1, example) + b1
b1 = sigmoid(b)
c1 = numpy.dot(w2, b1) + b2
c = sigmoid(c1)
# 第一类是完美, 第二类是正常, 第三类是跑偏
print(c) # 结果显示属于第三类 [140, 70, 37, 0, 0]
即步骤可以分为:
Step one:前向运算算出误差,求代价函数
Step two:反向运算算出每一层的误差信号,wi的梯度和bi的梯度形式为
Step three:将权值flatten()(展平为一个单行的向量)
grad = [W1grad(:) ; W2grad(:) ; b1grad(:) ; b2grad(:)];
Step Four:运用scipy.optimize.minimize(类似于matlab fminunc),用l-bfg-s算法更新权值。
Step Five: 根据求出的权值,预测其他样本,比较准确性。
ps:如果有问题请及时与我联系,qq:314913739