一、激活函数以及图像的学习
#coding:utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F # log(1+e^x)激励函数
from torch.autograd import Variable
# 做一些假数据来观看图像
x = torch.linspace(-5, 5, 200) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = Variable(x)
x_np = x.data.numpy() # 换成 numpy array, 出图时用
# 几种常用的 激励函数
y_relu = torch.relu(x).data.numpy()
y_sigmoid = torch.sigmoid(x).data.numpy()
y_tanh = torch.tanh(x).data.numpy()
y_softplus =F.softplus(x).data.numpy()
# y_softmax = F.softmax(x) softmax 比较特殊, 不能直接显示, 不过他是关于概率的, 用于分类
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # python 的可视化模块
plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x_np, y_relu, c='red', label='relu')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc='best') #显示图例
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x_np, y_sigmoid, c='red', label='sigmoid')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best') #显示图例
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(x_np, y_tanh, c='red', label='tanh')
plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best') #显示图例
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(x_np, y_softplus, c='red', label='softplus')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 6)) #y轴限制
plt.legend(loc='best') #显示图例
plt.show()
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(4,3),facecolor='blue') #figsize:指定figure的宽和高,单位为英寸
plt.show()

二、线性回归
#coding:utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
#torch.linspace()线性等分向量 torch.unsqueeze扩充维度,再制定位置维度1,原来是100,转换后变为(100,1)
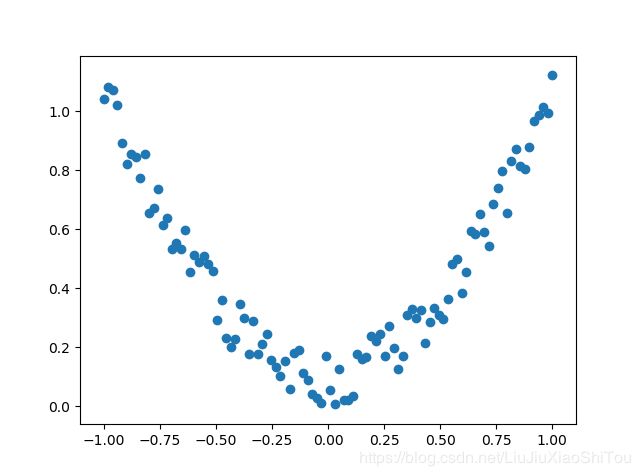
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
#print(x)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
print(y)
#plt.scatter()画散点图,画图的时候都是numpy类型
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.show()
#网络模型
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
#torch.nn.Linear()两个参数分别为inputSize 和 outputSize
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
#采用ReLU激活函数
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.predict(x) # linear output
return x
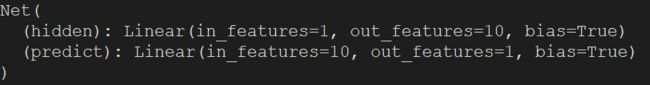
net = Net(n_feature=1, n_hidden=10, n_output=1) # define the network
print(net) # net architecture
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2) #采用SGD优化函数,学习率默认为0.2
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # 均方损失函数
plt.ion() # 打开交互模式
for t in range(200):
prediction = net(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target)
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if t % 5 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla() #plt.cla() # 清除axes,即当前 figure 中的活动的axes,但其他axes保持不变
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(0.5, 0, 'Loss=%.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1) #暂停功能
plt.ioff()#关闭交互模式
plt.show()

三、分类
#coding:UTF-8
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# make fake data
n_data = torch.ones(100, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(100) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(100) # class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
# The code below is deprecated in Pytorch 0.4. Now, autograd directly supports tensors
# x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y)
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=y.data.numpy(), s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
# plt.show()
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.out = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.out(x)
return x
net = Net(n_feature=2, n_hidden=10, n_output=2) # define the network
print(net) # net architecture
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.02)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is NOT an one-hotted
plt.ion() # something about plotting
for t in range(100):
out = net(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(out, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target), the target label is NOT one-hotted
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if t % 2 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(out, 1)[1]
pred_y = prediction.data.numpy()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
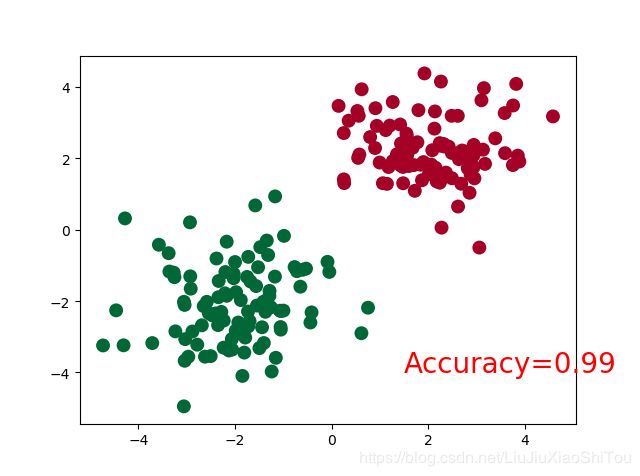
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = float((pred_y == target_y).astype(int).sum()) / float(target_y.size)
plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
四、快速搭建
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# replace following class code with an easy sequential network
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.predict(x) # linear output
return x
net1 = Net(1, 10, 1)
# easy and fast way to build your network
net2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
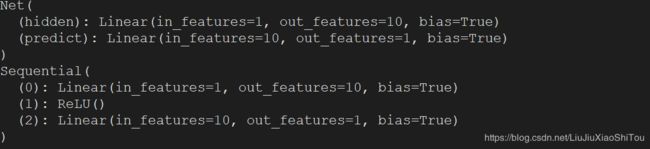
print(net1) # net1 architecture
"""
Net (
(hidden): Linear (1 -> 10)
(predict): Linear (10 -> 1)
)
"""
print(net2) # net2 architecture
"""
Sequential (
(0): Linear (1 -> 10)
(1): ReLU ()
(2): Linear (10 -> 1)
)
"""
五、保存提取
#coding:UTF-8
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# fake data
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
# The code below is deprecated in Pytorch 0.4. Now, autograd directly supports tensors
# x, y = Variable(x, requires_grad=False), Variable(y, requires_grad=False)
def save():
# save net1
net1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net1.parameters(), lr=0.5)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for t in range(100):
prediction = net1(x)
loss = loss_func(prediction, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# plot result
plt.figure(1, figsize=(10, 3))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.title('Net1')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
# 2 ways to save the net
torch.save(net1, 'net.pkl') # save entire net
torch.save(net1.state_dict(), 'net_params.pkl') # save only the parameters
def restore_net():
# restore entire net1 to net2
net2 = torch.load('net.pkl')
prediction = net2(x)
# plot result
plt.subplot(132)
plt.title('Net2')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
def restore_params():
# restore only the parameters in net1 to net3
net3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
# copy net1's parameters into net3
net3.load_state_dict(torch.load('net_params.pkl'))
prediction = net3(x)
# plot result
plt.subplot(133)
plt.title('Net3')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.show()
# save net1
save()
# restore entire net (may slow)
restore_net()
# restore only the net parameters
restore_params()

六、批训练
#coding:UTF-8
import torch
import torch.utils.data as Data
torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
BATCH_SIZE = 5
# BATCH_SIZE = 8
x = torch.linspace(1, 10, 10) # this is x data (torch tensor)
y = torch.linspace(10, 1, 10) # this is y data (torch tensor)
torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y)
loader = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=torch_dataset, # torch TensorDataset format
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, # mini batch size
shuffle=True, # random shuffle for training
num_workers=2, # subprocesses for loading data
)
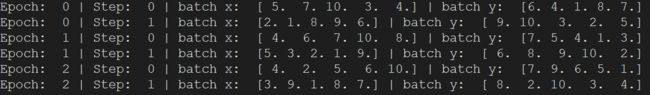
def show_batch():
for epoch in range(3): # train entire dataset 3 times
for step, (batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(loader): # for each training step
# train your data...
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| Step: ', step, '| batch x: ',
batch_x.numpy(), '| batch y: ', batch_y.numpy())
if __name__ == '__main__':
show_batch()
七、优化器
#coding:UTF-8
import torch
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
LR = 0.01
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCH = 12
# fake dataset
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 1000), dim=1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.1*torch.normal(torch.zeros(*x.size()))
# plot dataset
plt.scatter(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
plt.show()
# put dateset into torch dataset
torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y)
loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=torch_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, num_workers=2,)
# default network
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(1, 20) # hidden layer
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(20, 1) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.predict(x) # linear output
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
# different nets
net_SGD = Net()
net_Momentum = Net()
net_RMSprop = Net()
net_Adam = Net()
nets = [net_SGD, net_Momentum, net_RMSprop, net_Adam]
# different optimizers
opt_SGD = torch.optim.SGD(net_SGD.parameters(), lr=LR)
opt_Momentum = torch.optim.SGD(net_Momentum.parameters(), lr=LR, momentum=0.8)
opt_RMSprop = torch.optim.RMSprop(net_RMSprop.parameters(), lr=LR, alpha=0.9)
opt_Adam = torch.optim.Adam(net_Adam.parameters(), lr=LR, betas=(0.9, 0.99))
optimizers = [opt_SGD, opt_Momentum, opt_RMSprop, opt_Adam]
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
losses_his = [[], [], [], []] # record loss
# training
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
print('Epoch: ', epoch)
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(loader): # for each training step
for net, opt, l_his in zip(nets, optimizers, losses_his):
output = net(b_x) # get output for every net
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # compute loss for every net
opt.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
opt.step() # apply gradients
l_his.append(loss.data.numpy()) # loss recoder
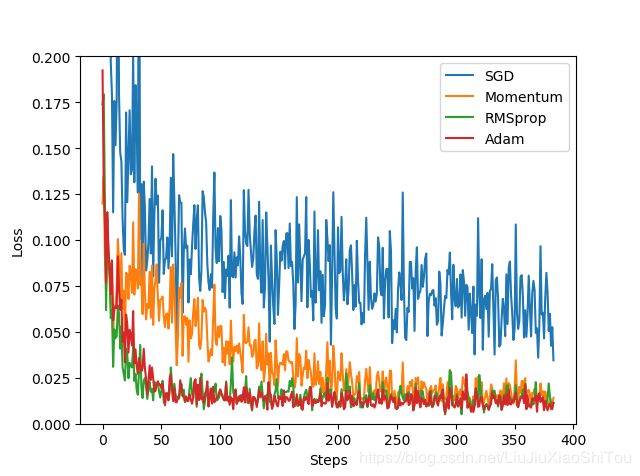
labels = ['SGD', 'Momentum', 'RMSprop', 'Adam']
for i, l_his in enumerate(losses_his):
plt.plot(l_his, label=labels[i])
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.xlabel('Steps')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.ylim((0, 0.2))
plt.show()
八、训练手写数据集
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*- #编码注释
import os
# third-party library
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision #torchvision是独立于pytorch的关于图像操作的一些方便工具库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 50
LR = 0.001 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
# Mnist digits dataset 如果不存在数据集,置DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
#利用torchvision.datasets.MNIST()提取数据集
train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # 把PIL格式转换为tensor
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, #布尔类型:没有下载就进行下载,下载过就不用再下载
)
# 绘制一个例子
#train_data(train_data+train.lables) 图像+标签
print(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
print(train_data.targets.size()) # (60000)
plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray') #展示图片
plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[0]) #图像title为标签
plt.show()
# 数据加载器 the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
# pick 2000 samples to speed up testing
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False) #测试数据
# shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1) #测试前2000个
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_data.test_data, dim=1).type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255.
test_y = test_data.test_labels[:2000]
# class 来建立 CNN 模型. 这个 CNN 整体流程是 卷积(Conv2d) -> 激励函数(ReLU) -> 池化,
#向下采样 (MaxPooling) -> 再来一遍 -> 展平多维的卷积成的特征图 -> 接入全连接层 (Linear) -> 输出
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1, # input height
out_channels=16, # n_filters
kernel_size=5, # filter size
stride=1, # filter movement/step
padding=2, # if want same width and length of this image after Conv2d, padding=(kernel_size-1)/2 if stride=1
), # output shape (16, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2), # choose max value in 2x2 area, output shape (16, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (16, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32, 14, 14)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(2), # output shape (32, 7, 7)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10) # fully connected layer, output 10 classes
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # 展平多维的卷积图成 (batch_size, 32 * 7 * 7)
return output, x # return x for visualization
cnn = CNN()
print(cnn) # net architecture
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(cnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted
# 可视化操作
from matplotlib import cm
try: from sklearn.manifold import TSNE; HAS_SK = True
except: HAS_SK = False; print('Please install sklearn for layer visualization')
def plot_with_labels(lowDWeights, labels):
plt.cla()
X, Y = lowDWeights[:, 0], lowDWeights[:, 1]
for x, y, s in zip(X, Y, labels):
c = cm.rainbow(int(255 * s / 9)); plt.text(x, y, s, backgroundcolor=c, fontsize=9)
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*- #编码注释
import os
# third-party library
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision #torchvision是独立于pytorch的关于图像操作的一些方便工具库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 50
LR = 0.001 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
# Mnist digits dataset 如果不存在数据集,置DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
#利用torchvision.datasets.MNIST()提取数据集
train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # 把PIL格式转换为tensor
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, #布尔类型:没有下载就进行下载,下载过就不用再下载
)
# 绘制一个例子
#train_data(train_data+train.lables) 图像+标签
print(train_data.data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
print(train_data.targets.size()) # (60000)
plt.imshow(train_data.data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray') #展示图片
plt.title('%i' % train_data.targets[0]) #图像title为标签
plt.show()
# 数据加载器 the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
# pick 2000 samples to speed up testing
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False) #测试数据
# shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1) #测试前2000个
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_data.data, dim=1).type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255.
test_y = test_data.targets[:2000]
# class 来建立 CNN 模型. 这个 CNN 整体流程是 卷积(Conv2d) -> 激励函数(ReLU) -> 池化,
#向下采样 (MaxPooling) -> 再来一遍 -> 展平多维的卷积成的特征图 -> 接入全连接层 (Linear) -> 输出
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1, # input height
out_channels=16, # n_filters
kernel_size=5, # filter size
stride=1, # filter movement/step
padding=2, # if want same width and length of this image after Conv2d, padding=(kernel_size-1)/2 if stride=1
), # output shape (16, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2), # choose max value in 2x2 area, output shape (16, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (16, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32, 14, 14)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(2), # output shape (32, 7, 7)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10) # fully connected layer, output 10 classes
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # 展平多维的卷积图成 (batch_size, 32 * 7 * 7)
output = self.out(x)
return output, x # return x for visualization
cnn = CNN()
print(cnn) # net architecture
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(cnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted
# 可视化操作
from matplotlib import cm
try: from sklearn.manifold import TSNE; HAS_SK = True
except: HAS_SK = False; print('Please install sklearn for layer visualization')
def plot_with_labels(lowDWeights, labels):
plt.cla()
X, Y = lowDWeights[:, 0], lowDWeights[:, 1]
for x, y, s in zip(X, Y, labels):
c = cm.rainbow(int(255 * s / 9)); plt.text(x, y, s, backgroundcolor=c, fontsize=9)
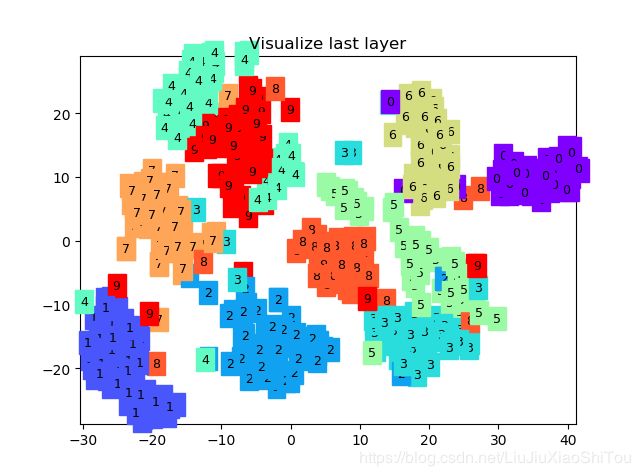
plt.xlim(X.min(), X.max()); plt.ylim(Y.min(), Y.max()); plt.title('Visualize last layer'); plt.show(); plt.pause(0.01)
plt.ion()
# 训练测试
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader): # gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
output = cnn(b_x)[0] # cnn output 因为cnn返回两个值[0] 取第一个值
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if step % 50 == 0:
test_output, last_layer = cnn(test_x)
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
#astype 转换数据类型
accuracy = float((pred_y == test_y.data.numpy()).astype(int).sum()) / float(test_y.size(0))
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), '| test accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy)
if HAS_SK:
# Visualization of trained flatten layer (T-SNE)
tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init='pca', n_iter=5000)
plot_only = 500
low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(last_layer.data.numpy()[:plot_only, :])
labels = test_y.numpy()[:plot_only]
plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels)
plt.ioff()
# print 10 predictions from test data
test_output, _ = cnn(test_x[:10])
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:10].numpy(), 'real number')