【Tensorflow】迁移学习: 使用ImageNet训练好的inception v3模型tensorflow_inception_graph.pb训练flowers数据集
虽然在数据量足够的情况下,迁移学习的效果不如完全重新训练。但是迁移学习所需要的训练时间和训练样本数要远远小于训练完整的模型。
在新的数据集上,直接利用训练好的神经网络对图像进行特征提取,然后再将提取到的特征向量作为输入来训练一个新的单层全连接神经网络处理新的图像分类问题。
数据集下载地址:flower数据集
flower数据集有五个子文件夹,每一个子文件夹的名称对应一种花的名称。平均每一种花有734张图片,都是RGB色彩模式,大小各不相同。
模型下载地址:Inception-v3模型
首先,导入相应的包和设置全局参数。
import glob
import os.path
import random
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile
#Inception-v3模型瓶颈层的节点数
BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE = 2048
#Inception-v3模型瓶颈层的输出的张量名称
BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME = 'pool_3/_reshape:0'
#图像输入张量名称
JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME = 'DecodeJpeg/contents:0'
MODEL_DIR = './inception_dec_2015'
MODEL_FILE = 'tensorflow_inception_graph.pb'
CACHE_DIR = './tmp/bottleneck'
INPUT_DATA = './flower_photos'
#验证集百分比
VALIDATION_PERCENTAGE = 10
#测试集百分比
TEST_PERCENTAGE = 10
LEARNING_RATE = 0.01
STEPS = 4000
BATCH = 100定义一个函数从数据文件夹中读取所有的图片列表并按训练、验证、测试数据分开。
def create_image_lists(testing_percentage, validation_percentage):
result = {}
sub_dirs = [x[0] for x in os.walk(INPUT_DATA)]
is_root_dir = True
for sub_dir in sub_dirs:
if is_root_dir:
is_root_dir = False
continue
extensions = ['jpg', 'jpeg', 'JPG', 'JPEG']
file_list = []
dir_name = os.path.basename(sub_dir)
for extension in extensions:
file_glob = os.path.join(sub_dir, '*.' + extension)
file_list.extend(glob.glob(file_glob))
if not file_list:
continue
label_name = dir_name.lower()
traning_images = []
testing_images = []
validation_images = []
for file_name in file_list:
base_name = os.path.basename(file_name)
#随机将数据分到训练数据集、测试数据集和验证数据集
chance = np.random.randint(100)
if chance < validation_percentage:
validation_images.append(base_name)
elif chance < (testing_percentage + validation_percentage):
testing_images.append(base_name)
else:
traning_images.append(base_name)
#将当前类别的数据放入字典
result[label_name] = {
'dir': dir_name,
'training': traning_images,
'testing': testing_images,
'validation': validation_images
}
return result通过类别名称、所属数据集和图片编号获取一张图片的地址。
def get_image_path(image_lists, image_dir, label_name, index, category):
#获取给定类别中所有图片的信息
label_lists = image_lists[label_name]
#根据所属数据集的名称获取集合中的全部图片信息
category_list = label_lists[category]
mod_index = index % len(category_list)
base_name = category_list[mod_index]
sub_dir = label_lists['dir']
#最终的地址为数据根目录的地址加上类别的文件夹加上图片的名称
full_path = os.path.join(image_dir, sub_dir, base_name)
return full_path获取经常Inception-v3模型处理之后的特征向量的文件地址。
def get_bottleneck_path(image_lists, label_name, index, category):
return get_image_path(image_lists, CACHE_DIR, label_name, index, category) + '.txt'使用加载的训练好的Inception-v3模型处理一张图片,得到其特征向量。
def run_bottleneck_on_image(sess, image_data, image_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
bottleneck_values = sess.run(bottleneck_tensor, {image_data_tensor: image_data})
bottleneck_values = np.squeeze(bottleneck_values)
return bottleneck_valuesdef get_or_create_bottleneck(sess, image_lists, label_name, index, category, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
#获取一张图片对应的特征向量文件的路径
label_lists = image_lists[label_name]
sub_dir = label_lists['dir']
sub_dir_path = os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, sub_dir)
if not os.path.exists(sub_dir_path):
os.makedirs(sub_dir_path)
bottleneck_path = get_bottleneck_path(image_lists, label_name, index, category)
#如果特征向量文件不存在,则通过Inception-v3计算,并将计算结果存入文件
if not os.path.exists(bottleneck_path):
image_path = get_image_path(image_lists, INPUT_DATA, label_name, index, category)
image_data = gfile.FastGFile(image_path, 'rb').read()
bottleneck_values = run_bottleneck_on_image(sess, image_data, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
bottleneck_string = ','.join(str(x) for x in bottleneck_values)
with open(bottleneck_path, 'w') as bottleneck_file:
bottleneck_file.write(bottleneck_string)
else:
with open(bottleneck_path, 'r') as bottleneck_file:
bottleneck_string = bottleneck_file.read()
bottleneck_values = [float(x) for x in bottleneck_string.split(',')]
return bottleneck_values随机获取一个batch的图片作为训练数据。
def get_random_cached_bottlenecks(sess, n_classes, image_lists, how_many, category, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
bottlenecks = []
ground_truths = []
for _ in range(how_many):
label_index = random.randrange(n_classes)
label_name = list(image_lists.keys())[label_index]
image_index = random.randrange(65536)
bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(sess, image_lists, label_name, image_index, category,
jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
ground_truth = np.zeros(n_classes, dtype=np.float32)
ground_truth[label_index] = 1.0
bottlenecks.append(bottleneck)
ground_truths.append(ground_truth)
return bottlenecks, ground_truths定义一个函数获取全部测试数据。
def get_test_bottlenecks(sess, image_lists, n_classes, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
bottlenecks = []
ground_truths = []
label_name_list = list(image_lists.keys())
#枚举所有类别和每个类别中的测试图片
for label_index, label_name in enumerate(label_name_list):
category = 'testing'
for index, unused_base_name in enumerate(image_lists[label_name][category]):
bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(sess, image_lists, label_name, index, category,
jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
ground_truth = np.zeros(n_classes, dtype=np.float32)
ground_truth[label_index] = 1.0
bottlenecks.append(bottleneck)
ground_truths.append(ground_truth)
return bottlenecks, ground_truths下面定义main函数。
def main(_):
image_lists = create_image_lists(TEST_PERCENTAGE, VALIDATION_PERCENTAGE)
n_classes = len(image_lists.keys())
#读取已经训练好的Ince-v3模型
with gfile.FastGFile(os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, MODEL_FILE), 'rb') as f:
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
#获取tensor
bottleneck_tensor, jpeg_data_tensor = tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, return_elements=[BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME, JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME])
#定义新的神经网络输入
bottleneck_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE], name='BottleneckInputPlaceholder')
ground_truth_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes], name='GroundTruthInput')
#定义一个新的全连接层解决新的图片分类问题
with tf.name_scope('final_traning_ops'):
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE, n_classes], stddev=0.001))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n_classes]))
logits = tf.matmul(bottleneck_input, weights) + biases
final_tensor = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=ground_truth_input)
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(LEARNING_RATE).minimize(cross_entropy_mean)
with tf.name_scope('evaluation'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(final_tensor, 1), tf.argmax(ground_truth_input, 1))
evaluation_step = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
for i in range(STEPS):
train_bottlenecks, train_ground_truth = get_random_cached_bottlenecks(sess, n_classes, image_lists,
BATCH, 'training', jpeg_data_tensor,
bottleneck_tensor)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={bottleneck_input: train_bottlenecks,
ground_truth_input: train_ground_truth})
if i % 10 == 0 or i + 1 == STEPS:
validation_bottlenecks, validation_ground_truth = get_random_cached_bottlenecks(sess, n_classes, image_lists,
BATCH, 'validation',
jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
validation_accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict={bottleneck_input: validation_bottlenecks,
ground_truth_input: validation_ground_truth})
print('Step %d: Validation accuracy on random sampled %d examples = %.1f%%' % (i, BATCH, validation_accuracy * 100))
test_bottlenecks, test_ground_truth = get_test_bottlenecks(sess, image_lists, n_classes, jpeg_data_tensor,
bottleneck_tensor)
test_accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict={bottleneck_input: test_bottlenecks,
ground_truth_input: test_ground_truth})
print('Final test accuracy = %.1f%%' % (test_accuracy * 100))
if __name__ == '__main__':
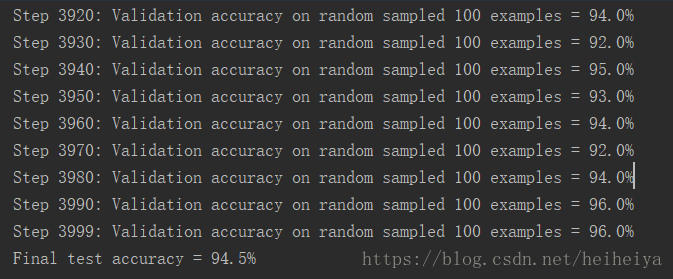
tf.app.run()经过几分钟的训练,在test数据集上的准确率为94.5%。