3. java缓存-进程内缓存guava cache
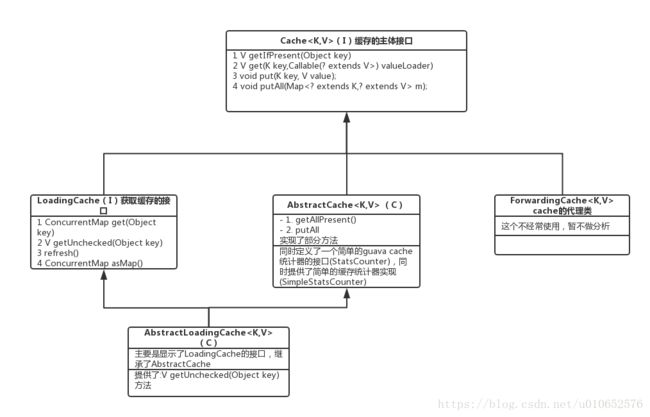
guava cache的缓存结构
常用的guava cache缓存
根据上图中的缓存框架,我们常用的一些缓存实例有:LocalManualCache和LocalLoadingCache,两者唯一的区别就是LocalLoadingCache extends LocalManualCache implements LoadingCache
LocalManualCache和LocalLoadingCache两者都是对LoaclCache的包装,而LocalCache就是一个缓存的存储器,通过继承AbstractMap和实现ConcurrentMap接口,实现了支持并发的本地map(可以看成类似的ConcunrrentHashMap),LocalCache不对外暴露,因此只能通过其他方式提供实例,这就是CacheBuilder,以后建议大家也可以通过Builder的形式对外暴露实例。
范例
手动加载缓存
手动加载缓存:需要提前把数据put,当数据不存在返回null
public class MyCache {
private static Cache cache;
static {
// removeListener 从缓存中移除,调用这个方法
// initialCapacity 初始化容量
// concurrentLevel 并发的线程数
// expireAfterWrite 写入多长时间后,失效
cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.removalListener(new RemovalListener() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification removalNotification) {
System.out.println("remove "+removalNotification.getKey()+":"+removalNotification.getValue());
}
})
.initialCapacity(30)
.concurrencyLevel(5)
.expireAfterWrite(20, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build();
//手动加载数据
cache.put("1","name11");
cache.put("2","name12");
cache.put("3","name13");
cache.put("4","name14");
cache.put("5","name15");
cache.put("6","name16");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException {
//获取一个不存在的key
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("7'"));
//获取一个存在的key
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("1"));
//获取一个不存在的key,自己定义一个加载方法
System.out.println(cache.get("7",new Callable(){
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
//返回值,一定不能为null
return "dadad";
}
}));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("7"));
cache.invalidate("1");
System.out.println("------------------");
}
}
----输出:
------------------
null
name11
dadad
dadad
remove 1:name11
------------------
上述缓存就可以看做是一个手动加载数据的缓存,即使用前自己手动的加载完成数据,当然也可以调用特殊的方法,当调用时,数据不存在后再调用加载方法。
自动加载缓存
自动加载缓存:不需要提前加载数据,当get时,不存在数据,会自动根据CacheLoader加载数据。
public class MyLoadingCache {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 自动加载的缓存
// expireAfterWrite 缓存加载指定时间后,自动失效
// maximumSize 缓存数量超出指定数量后,加载新的缓存,会根据指定策略淘汰老的缓存
// initialCapacity 创建是默认的大小
// concurrencyLevel 并发线程数,类似于concurrentHashMap的segmentShift
// CacheLoader 当缓存没有命中时,自动调用方法加载,返回值不能为空
LoadingCache loadingCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(30,TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.maximumSize(300L)
.concurrencyLevel(20)
.initialCapacity(300)
.build(new CacheLoader() {
@Override
public User load(String key) throws Exception {
User user = getUserInfoFromDB(key);
return user;
}
});
System.out.println(loadingCache.getUnchecked("12").toString());
}
// 模拟从数据库获取数据
private static User getUserInfoFromDB(String key) {
if("123".equals(key)){
//模拟数据库中不存在的数据
return null;
}
return new User(key);
}
}
class User{
String id;
public User(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "id="+this.id;
}
}
---输出内容
id=12
Cache和LoadingCache的醉醉哒区别,就是LoadingCache创建时,指定缓存未命中后的加载来源即可,同时还提供getUnchecked方法,如果你的CacherLoader没有返回检查异常,可以调用getUnchecked方法。
当我们在上述LoadingCache中执行:
System.out.println(loadingCache.getUnchecked("12").toString());
---输出:
Exception in thread "main" com.google.common.cache.CacheLoader$InvalidCacheLoadException: CacheLoader returned null for key 123.
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache$Segment.getAndRecordStats(LocalCache.java:2353)
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache$Segment.loadSync(LocalCache.java:2323)
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache$Segment.lockedGetOrLoad(LocalCache.java:2285)
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache$Segment.get(LocalCache.java:2200)
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.get(LocalCache.java:3947)
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache.getOrLoad(LocalCache.java:3951)
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache$LocalLoadingCache.get(LocalCache.java:4874)
at com.google.common.cache.LocalCache$LocalLoadingCache.getUnchecked(LocalCache.java:4880)
这就是LoadingCache的load方法,不能返回null。因此在load的时候,我们返回对象前必须处理null的问题。
Cache为什么不能返回null
先不说为什么不可以返回null,先假设cache可以接收null值。null的存在主要是影响判断加载的时机,下面列出两种情况下,判断加载的时机
允许null
get时,key不存在,返回的是null。
get时,key存在,缓存的value是null,返回的是null。
不能通过get的valuenull,来判断加载的时机,只能通过containsKey来判断,如果通过valuenull作为是否加载缓存的标准,就会产生一个问题,如果缓存的是null,那么即使加载过一次,但是每次get时,同样会再加载一次,这样就没有起到缓存的作用。
不允许null
get时,key不存在返回null,返回null。
get时,key存在,缓存的value不为null,返回非null值。
可以通过get的value==null,来判断加载时机。
根据上述两种方式,我们现在看看LocalCache中,如何处理get得到的null。
通过定位,找到LocalCache.Segment的如下代码
V get(K key, int hash, CacheLoader loader) throws ExecutionException {
checkNotNull(key);
checkNotNull(loader);
try {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile
// don't call getLiveEntry, which would ignore loading values
ReferenceEntry e = getEntry(key, hash);
if (e != null) {
long now = map.ticker.read();
V value = getLiveValue(e, now);
if (value != null) {
recordRead(e, now);
statsCounter.recordHits(1);
return scheduleRefresh(e, key, hash, value, now, loader);
}
ValueReference valueReference = e.getValueReference();
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {
return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference);
}
}
}
// 看到这段注释,我们就发现,LocalCache是通过value == null,就进行load
// at this point e is either null or expired;
return lockedGetOrLoad(key, hash, loader);
} catch (ExecutionException ee) {
Throwable cause = ee.getCause();
if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw new ExecutionError((Error) cause);
} else if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(cause);
}
throw ee;
} finally {
postReadCleanup();
}
}
通过分析LocalCache代码,LocalCache是根据get的value==null来判断加载时机,因此通过load加载时,不允许返回null值,因此需要特殊判断load的返回值,建议使用Optional进行包装。
示例代码:
import com.google.common.base.Optional;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheBuilder;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheLoader;
import com.google.common.cache.LoadingCache;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class UserLocalCache {
private final LoadingCache> loadingCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(60*24, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.maximumSize(500)
.build(new CacheLoader>() {
@Override
public Optional load(Long key) throws Exception {
// 模拟访问数据库
User userFromDb = getUserFromDb(key);
// 使用Optional进行包装,虽然Optional里面为null,但是对cache来说,该对象不为空
return Optional.fromNullable(userFromDb);
}
});
private UserLocalCache(){}
public User getUser(Long userId){
if(userId != null) {
Optional userOpt = loadingCache.getUnchecked(2L);
if (userOpt.isPresent()) {
return userOpt.get();
}
}
return null;
}
private static User getUserFromDb(Long id) {
Long temp = 1L;
if(temp.equals(id)){
return null;
}else{
return new User(id,"name"+id);
}
}
}
class User{
private Long id;
private String name;
public User(Long id, String name){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
}
更多的guava cache的分析,请等待。