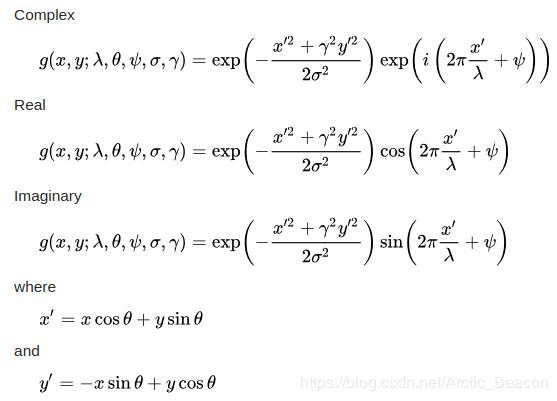Gabor滤波详解
先搬运定义
Its impulse response is defined by a sinusoidal wave (a plane wave for 2D Gabor filters) multiplied by a Gaussian function. Because of the multiplication-convolution property (Convolution theorem), the Fourier transform of a Gabor filter's impulse response is the convolution of the Fourier transform of the harmonic function (sinusoidal function) and the Fourier transform of the Gaussian function. The filter has a real and an imaginary component representing orthogonal directions. The two components may be formed into a complex number or used individually.
In this equation, {lambda } represents the wavelength of the sinusoidal factor, {theta } represents the orientation of the normal to the parallel stripes of a Gabor function, {psi } is the phase offset, {sigma } is the sigma/standard deviation of the Gaussian envelope and {gamma } is the spatial aspect ratio, and specifies the ellipticity of the support of the Gabor function.
滤波器可视化
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
def gabor_fn(sigma, theta, Lambda, psi, gamma):
sigma_x = sigma
sigma_y = float(sigma) / gamma
# Bounding box
nstds = 3 # Number of standard deviation sigma
xmax = max(abs(nstds * sigma_x * np.cos(theta)), abs(nstds * sigma_y * np.sin(theta)))
xmax = np.ceil(max(1, xmax))
ymax = max(abs(nstds * sigma_x * np.sin(theta)), abs(nstds * sigma_y * np.cos(theta)))
ymax = np.ceil(max(1, ymax))
xmin = -xmax
ymin = -ymax
(y, x) = np.meshgrid(np.arange(ymin, ymax + 1), np.arange(xmin, xmax + 1))
# Rotation
x_theta = x * np.cos(theta) + y * np.sin(theta)
y_theta = -x * np.sin(theta) + y * np.cos(theta)
gb = np.exp(-.5 * (x_theta ** 2 / sigma_x ** 2 + y_theta ** 2 / sigma_y ** 2)) * np.cos(2 * np.pi / Lambda * x_theta + psi)
return x,y,gb
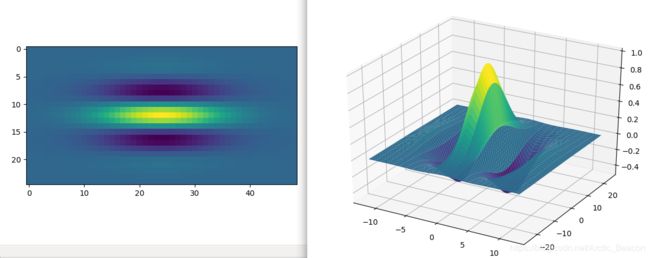
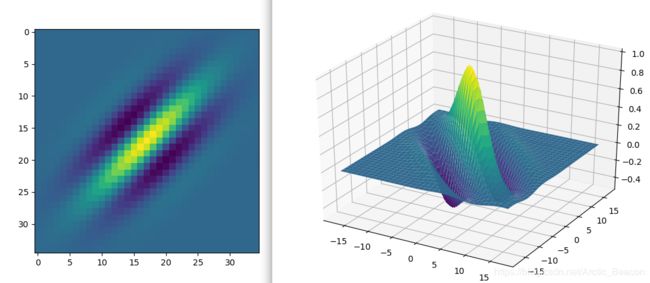
x,y,gb = gabor_fn(4,0,10,0,0.5)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(gb)
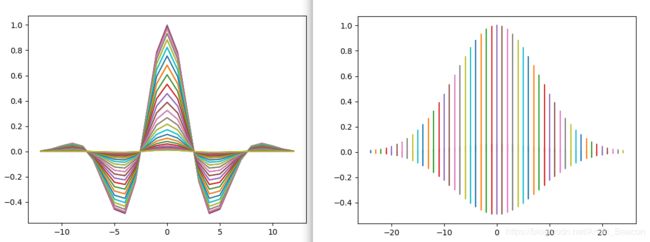
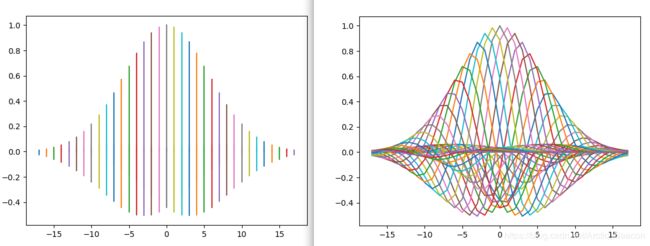
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, gb, '-')
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(y, gb, '-')
plt.show()
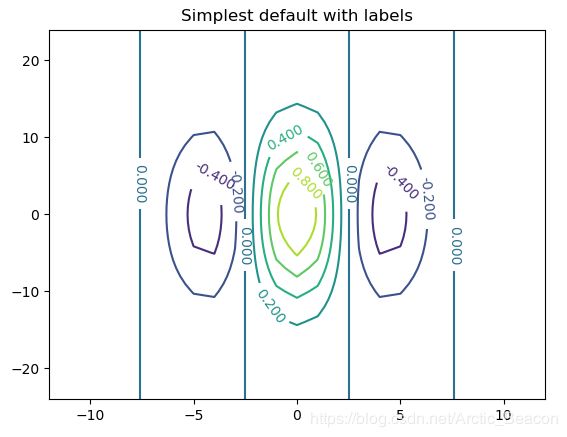
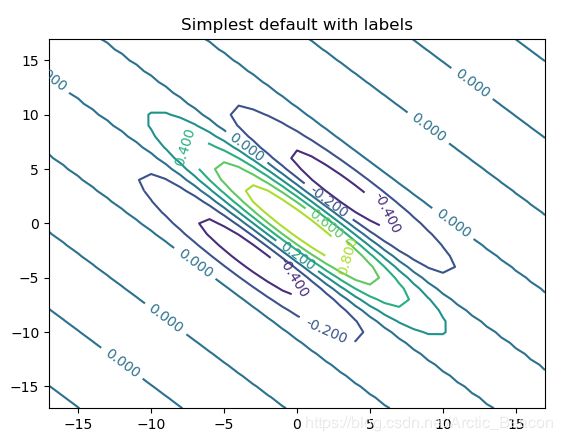
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
CS = ax.contour(x, y, gb)
ax.clabel(CS, inline=1, fontsize=10)
ax.set_title('Simplest default with labels')
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
ax.plot_surface(x, y, gb, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.viridis)
plt.show()
上述是theta = 0的滤波器,下面看看theta = pi/4
filter band滤波图像
import numpy as np
import cv2
import sys
def build_filters():
filters = []
ksize = 31
for theta in np.arange(0, np.pi, np.pi / 16):
kern = cv2.getGaborKernel((ksize, ksize), 4.0, theta, 10.0, 0.5, 0, ktype=cv2.CV_32F)
kern /= 1.5*kern.sum()
filters.append(kern)
return filters
def process(img, filters):
accum = np.zeros_like(img)
for kern in filters:
fimg = cv2.filter2D(img, cv2.CV_8UC3, kern)
np.maximum(accum, fimg, accum)
return accum
if __name__ == '__main__':
print (__doc__)
try:
img_fn = sys.argv[1]
except:
img_fn = 'laska.png'
img = cv2.imread(img_fn)
if img is None:
print ('Failed to load image file:', img_fn)
sys.exit(1)
filters = build_filters()
res1 = process(img, filters)
cv2.imshow('origin',img)
cv2.imshow('result', res1)