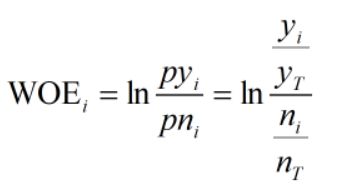IV值计算及分箱
1.离散的优势:
(1)离散化后的特征对异常数据有很强的鲁棒性:比如一个特征是年龄>30是1,否则0。如果特征没有离散化,一个异常数据“年龄300岁”会给模型造成很大的干扰;
(2)逻辑回归属于广义线性模型,表达能力受限,单变量离散化为N个后,每个变量有单独的权重,相当于为模型引入了非线性,能够提升模型表达能力,加大拟合;
(3)离散化后可以进行特征交叉,由M+N个变量变为M*N个变量,进一步引入非线性,提升表达能力;
(4)可以将缺失作为独立的一类带入模型;
(5)将所有变量变换到相似的尺度上。
WOE:
WOE的全称是“Weight of Evidence”,即证据权重,WOE是对原始自变量的一种编码形式。要对一个变量进行WOE编码,需要首先把这个变量进行分箱。分箱后,对于第i组,WOE的计算公式如下:
yi是这个分组中响应客户(即取值为1)的数量,yT是全部样本中所有响应客户(即取值为1)的数量
ni是这个分组中未响应客户(即取值为0)的数量,nT是全部样本中所有未响应客户(即取值为0)的数量
IV值:
IV的全称是Information Value,用来衡量自变量的预测能力
对于分组i的IV值:
计算整个变量的IV值,n为变量分组个数:
- 过高的IV,可能有潜在的风险
- 特征分箱越细,IV越高
![]()
def compute_WOE_IV(df,col,target):
"""
param df:DataFrame|包含feature和label
param col:str|feature名称,col这列已经经过分箱
param taget:str|label名称,0,1
return 每箱的WOE(字典类型)和总的IV之和,注意考虑计算时候分子分母为零的溢出情况
"""
import numpy as np
total = df.groupby([col])[target].count() #计算col每个分组中的样本总数
total = pd.DataFrame({'total': total})
bad = df.groupby([col])[target].sum() #计算col每个分组中的目标取值为1的总数,关注的正样本
bad = pd.DataFrame({'bad': bad})
regroup = total.merge(bad,left_index=True,right_index=True,how='left')
regroup.reset_index(level=0,inplace=True)
N = sum(regroup['total']) #样本总数
B = sum(regroup['bad']) #正样本总数
regroup['good'] = regroup['total'] - regroup['bad'] #计算col每个分组中的目标取值为0的总数,关注的负样本
G = N - B #负样本总数
regroup['bad_pcnt'] = regroup['bad'].map(lambda x: x*1.0/B)
regroup['good_pcnt'] = regroup['good'].map(lambda x: x * 1.0 / G)
regroup["WOE"] = regroup.apply(lambda x:np.log(x.good_pcnt*1.0/x.bad_pcnt),axis=1)
WOE_dict = regroup[[col,"WOE"]].set_index(col).to_dict(orient="index")
IV = regroup.apply(lambda x:(x.good_pcnt-x.bad_pcnt)*np.log(x.good_pcnt*1.0/x.bad_pcnt),axis = 1)
IV = sum(IV)
return {"WOE":WOE_dict,"IV":IV}
![]()
等频分箱
区间的边界值要经过选择,使得每个区间包含大致相等的实例数量。比如说 N=10 ,每个区间应该包含大约10%的实例。
等距分箱
从最小值到最大值之间,均分为 N 等份。 如果 A,B 为最小最大值, 则每个区间的长度为 W=(B−A)/N , 则区间边界值为A+W,A+2W,….A+(N−1)W 。这里只考虑边界,每个等份的实例数量可能不等。
![]()
import pandas as pd import seaborn as sn from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split df = sn.load_dataset(name="titanic") train,test = train_test_split(df,test_size=0.2) #####################等频分箱################################################# train["age_bin"] = pd.qcut(train["age"],10) group_by_age_bin = train.groupby(["age_bin"],as_index=True) df_min_max_bin = pd.DataFrame()#用来记录每个箱体的最大最小值 df_min_max_bin["min_bin"] = group_by_age_bin.age.min() df_min_max_bin["max_bin"] = group_by_age_bin.age.max() df_min_max_bin.reset_index(inplace=True) #####################等宽分箱################################################### train["age_bin"] = pd.cut(train["age"],10) group_by_age_bin = train.groupby(["age_bin"],as_index=True) df_min_max_bin = pd.DataFrame()#用来记录每个箱体的最大最小值 df_min_max_bin["min_bin"] = group_by_age_bin.age.min() df_min_max_bin["max_bin"] = group_by_age_bin.age.max() df_min_max_bin.reset_index(inplace=True)
![]()
卡方分箱
转载:https://github.com/tatsumiw/ChiMerge/blob/master/ChiMerge.py
![]()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Oct 28 21:39:24 2018
@author: WZD
"""
def ChiMerge(df,variable,flag,confidenceVal=3.841,bin=10,sample=None):
'''
param df:DataFrame| 必须包含标签列
param variable:str| 需要卡方分箱的变量名称(字符串)
param flag:str | 正负样本标识的名称(字符串)
param confidenceVal:float| 置信度水平(默认是不进行抽样95%)
param bin:int | 最多箱的数目
param sample: int | 为抽样的数目(默认是不进行抽样),因为如果观测值过多运行会较慢
note: 停止条件为大于置信水平且小于bin的数目
return :DataFrame|采样结果
'''
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
#进行是否抽样操作
if sample != None:
df = df.sample(n=sample)
else:
df
#进行数据格式化录入
total_num = df.groupby([variable])[flag].count() #统计需分箱变量每个值数目
total_num = pd.DataFrame({'total_num': total_num}) #创建一个数据框保存之前的结果
positive_class = df.groupby([variable])[flag].sum() #统计需分箱变量每个值正样本数
positive_class = pd.DataFrame({'positive_class': positive_class}) #创建一个数据框保存之前的结果
regroup = pd.merge(total_num, positive_class, left_index=True, right_index=True,
how='inner') # 组合total_num与positive_class
regroup.reset_index(inplace=True)
regroup['negative_class'] = regroup['total_num'] - regroup['positive_class'] #统计需分箱变量每个值负样本数
regroup = regroup.drop('total_num', axis=1)
np_regroup = np.array(regroup) #把数据框转化为numpy(提高运行效率)
#print('已完成数据读入,正在计算数据初处理')
#处理连续没有正样本或负样本的区间,并进行区间的合并(以免卡方值计算报错)
i = 0
while (i <= np_regroup.shape[0] - 2):
if ((np_regroup[i, 1] == 0 and np_regroup[i + 1, 1] == 0) or ( np_regroup[i, 2] == 0 and np_regroup[i + 1, 2] == 0)):
np_regroup[i, 1] = np_regroup[i, 1] + np_regroup[i + 1, 1] # 正样本
np_regroup[i, 2] = np_regroup[i, 2] + np_regroup[i + 1, 2] # 负样本
np_regroup[i, 0] = np_regroup[i + 1, 0]
np_regroup = np.delete(np_regroup, i + 1, 0)
i = i - 1
i = i + 1
#对相邻两个区间进行卡方值计算
chi_table = np.array([]) # 创建一个数组保存相邻两个区间的卡方值
for i in np.arange(np_regroup.shape[0] - 1):
chi = (np_regroup[i, 1] * np_regroup[i + 1, 2] - np_regroup[i, 2] * np_regroup[i + 1, 1]) ** 2 \
* (np_regroup[i, 1] + np_regroup[i, 2] + np_regroup[i + 1, 1] + np_regroup[i + 1, 2]) / \
((np_regroup[i, 1] + np_regroup[i, 2]) * (np_regroup[i + 1, 1] + np_regroup[i + 1, 2]) * (
np_regroup[i, 1] + np_regroup[i + 1, 1]) * (np_regroup[i, 2] + np_regroup[i + 1, 2]))
chi_table = np.append(chi_table, chi)
#print('已完成数据初处理,正在进行卡方分箱核心操作')
#把卡方值最小的两个区间进行合并(卡方分箱核心)
while (1):
if (len(chi_table) <= (bin - 1) and min(chi_table) >= confidenceVal):
break
chi_min_index = np.argwhere(chi_table == min(chi_table))[0] # 找出卡方值最小的位置索引
np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] = np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 1]
np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2] = np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2] + np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 2]
np_regroup[chi_min_index, 0] = np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 0]
np_regroup = np.delete(np_regroup, chi_min_index + 1, 0)
if (chi_min_index == np_regroup.shape[0] - 1): # 最小值试最后两个区间的时候
# 计算合并后当前区间与前一个区间的卡方值并替换
chi_table[chi_min_index - 1] = (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] * np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2] - np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2] * np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1]) ** 2 \
* (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2]) / \
((np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2]))
# 删除替换前的卡方值
chi_table = np.delete(chi_table, chi_min_index, axis=0)
else:
# 计算合并后当前区间与前一个区间的卡方值并替换
chi_table[chi_min_index - 1] = (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] * np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2] - np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2] * np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1]) ** 2 \
* (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2]) / \
((np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index - 1, 2] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2]))
# 计算合并后当前区间与后一个区间的卡方值并替换
chi_table[chi_min_index] = (np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] * np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 2] - np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2] * np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 1]) ** 2 \
* (np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2] + np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 2]) / \
((np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 2]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index, 1] + np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 1]) * (np_regroup[chi_min_index, 2] + np_regroup[chi_min_index + 1, 2]))
# 删除替换前的卡方值
chi_table = np.delete(chi_table, chi_min_index + 1, axis=0)
#print('已完成卡方分箱核心操作,正在保存结果')
#把结果保存成一个数据框
result_data = pd.DataFrame() # 创建一个保存结果的数据框
result_data['variable'] = [variable] * np_regroup.shape[0] # 结果表第一列:变量名
list_temp = []
for i in np.arange(np_regroup.shape[0]):
if i == 0:
x = '0' + ',' + str(np_regroup[i, 0])
elif i == np_regroup.shape[0] - 1:
x = str(np_regroup[i - 1, 0]) + '+'
else:
x = str(np_regroup[i - 1, 0]) + ',' + str(np_regroup[i, 0])
list_temp.append(x)
result_data['interval'] = list_temp #结果表第二列:区间
result_data['flag_0'] = np_regroup[:, 2] # 结果表第三列:负样本数目
result_data['flag_1'] = np_regroup[:, 1] # 结果表第四列:正样本数目
return result_data
##############################测试#############################################
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import seaborn as sn
import pandas as pd
df = sn.load_dataset(name="titanic")
train,test = train_test_split(df,test_size=0.2)
result_data = ChiMerge(df=df,variable="age",flag="survived",confidenceVal=3.841,bin=10,sample=None)
bins = [] #卡方的区间值
bins.append(-float('inf'))
for i in range(result_data["interval"].shape[0]-1):
St = result_data["interval"][i].split(",")
bins.append(float(St[1]))
bins.append(float('inf'))
train["age"] = pd.cut(x=train["age"],bins=bins,labels=[1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17])
test["age"] = pd.cut(x=test["age"],bins=bins,labels=[1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17])
![]()