一个强大的下拉刷新框架
最近在学习github上的一个开源项目:android-Ultra-Pull-To-Refresh(下面简称UltraPtr) 。这个项目主要用于android APP中下拉刷新的功能。
OK,之所以说UltraPtr非常强大,是因为它有以下两个特点:
1. content可以是任意的view;
2. 简介完善的header抽象,用户可以对header高度自定义;
在理解了UltraPtr源码之后,我仿照它写了一个简单的下拉刷新应用。为了直观,先贴上效果图,然后再分析代码。
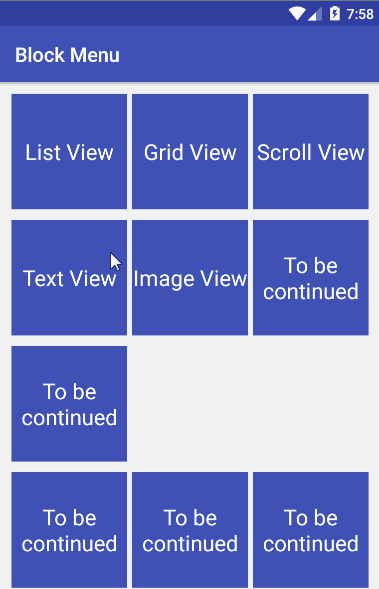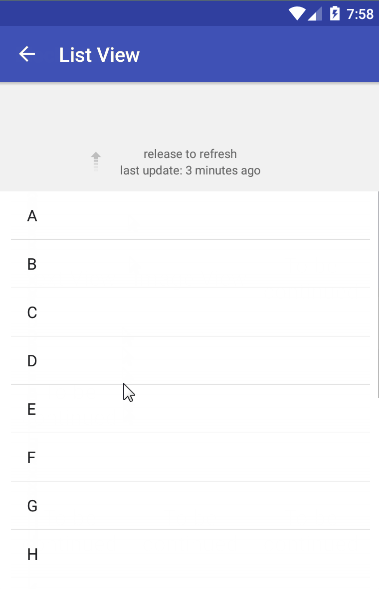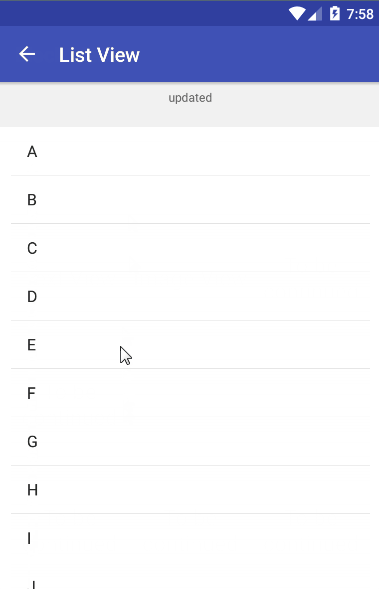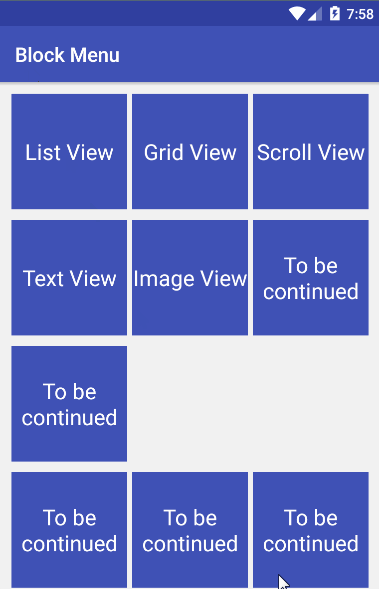

可以看到,UltraPtr框架支持各种content的下拉刷新,并且你也可以对头部header进行自定义,使用各种酷炫的header。
抽象接口
首先抽象出两个接口:PtrHandler和PtrUIHandler;
public interface PtrHandler
{
/**
* check can do refresh or not
*
* @param frame
* @param content
* @param header
* @return
*/
public boolean checkCanDoRefresh(final PtrFrameLayout frame, final View content, final View header);
/**
* when refresh begin
*
* @param frame
*/
public void onRefreshBegin(final PtrFrameLayout frame);
}PtrHandler代表下拉刷新的功能接口,包含下拉刷新的回调,以及判断是否可以下拉。
public interface PtrUIHandler
{
public void onUIReset(PtrFrameLayout frame);
public void onUIRefreshPrepare(PtrFrameLayout frame);
public void onUIRefreshBegin(PtrFrameLayout frame);
public void onUIRefreshComplete(PtrFrameLayout frame);
public void onUIPositionChange(PtrFrameLayout frame, boolean isUnderTouch, byte status, PtrIndicator ptrIndicator);
}PtrUIHandler是下拉刷新的UI接口,包括:准备下拉,下拉中,开始刷新,刷新完成,以及下拉过程中位置变化等回调方法。一般header需要实现此接口。
自定义下拉刷新控件PtrFrameLayout
测量与布局
PtrFrameLayout代表一个下拉刷新的自定义控件,继承自ViewGroup。有且只有两个子view:头部header和内容content。下面对类PtrFrameLayout中的主要方法进行分析。
和所有自定义控件一样,PtrFrameLayout通过重写onFinishInflate,onMeasure, onLayout来确定控件的大小和位置。
public class PtrFrameLayout extends ViewGroup
{
//status enum
public final static byte PTR_STATUS_INIT = 1;
public byte mStatus = PTR_STATUS_INIT;
public final static byte PTR_STATUS_PREPARE = 2;
public final static byte PTR_STATUS_LOADING = 3;
public final static byte PTR_STATUS_COMPLETE = 4;
private PtrIndicator mPtrIndicator;
private int mDurationToClose = 200;
private int mDurationToCloseHeader = 1000;
private long mLoadingStartTime = 0;
private View mHeaderView;
private View mContentView;
private int mPagingTouchSlop;
private final boolean DEBUG = true;
private static int ID = 1;
protected final String TAG = "ptr-frame-" + ++ID;
private int mHeaderHeight;
private boolean mPreventForHorizontal = false;
private ScrollChecker mScrollChecker;
private PtrHandler mPtrHandler;
private PtrUIHandler mPtrUIHandler;
public PtrFrameLayout(Context context)
{
this(context, null);
}
public PtrFrameLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public PtrFrameLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr)
{
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mPtrIndicator = new PtrIndicator();
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.PtrFrameLayout, 0, 0);
mDurationToClose = a.getInt(R.styleable.PtrFrameLayout_ptr_duration_to_close, mDurationToClose);
mDurationToCloseHeader = a.getInt(R.styleable.PtrFrameLayout_ptr_duration_to_close_header, mDurationToCloseHeader);
float resistence = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PtrFrameLayout_ptr_resistence, mPtrIndicator.getResistence());
mPtrIndicator.setResistence(resistence);
float ratio = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PtrFrameLayout_ptr_ratio_of_header_height_to_refresh, //
mPtrIndicator.getRatioOfHeaderHeightToRefresh());
mPtrIndicator.setRatioOfHeaderHeightToRefresh(ratio);
a.recycle();
mScrollChecker = new ScrollChecker();
ViewConfiguration vc = ViewConfiguration.get(getContext());
mPagingTouchSlop = vc.getScaledTouchSlop() * 2;
}
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate()
{
int childCount = getChildCount();
if (childCount > 2) {
throw new IllegalStateException("PtrFrameLayout only can host 2 elements");
} else if (childCount == 2) {
mHeaderView = getChildAt(0);
mContentView = getChildAt(1);
} else if (childCount == 1) {
mContentView = getChildAt(0);
} else {
TextView errorView = new TextView(getContext());
errorView.setClickable(true);
errorView.setTextColor(0xffff6600);
errorView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
errorView.setTextSize(20);
errorView.setText("The content view in PtrFrameLayout is empty!");
mContentView = errorView;
addView(mContentView);
}
if (mHeaderView != null) {
mHeaderView.bringToFront();
}
super.onFinishInflate();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (DEBUG) {
HLog.d(TAG, "onMeasure frame: width: %s, height: %s, padding: %s %s %s %s", getMeasuredWidth(), //
getMeasuredHeight(), getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop(), getPaddingRight(), getPaddingBottom());
}
//测量子view
if (mHeaderView != null) {
measureChildWithMargins(mHeaderView, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) mHeaderView.getLayoutParams();
mHeaderHeight = mHeaderView.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
mPtrIndicator.setHeaderHeight(mHeaderHeight);
}
if (mContentView != null) {
measureContentView(mContentView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
private void measureContentView(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int parentHeightMeasureSpec)
{
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int widthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, //
getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin, lp.width);
int heightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, //
getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin, lp.height);
child.measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b)
{
int offsetY = mPtrIndicator.getCurrentPosY();
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
if (mHeaderView != null) {
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) mHeaderView.getLayoutParams();
final int left = paddingLeft + lp.leftMargin;
final int top = paddingTop + lp.topMargin - mHeaderHeight + offsetY;
final int right = left + mHeaderView.getMeasuredWidth();
final int bottom = top + mHeaderView.getMeasuredHeight();
mHeaderView.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
if (DEBUG) {
HLog.d(TAG, "onLayout header: %s %s %s %s", left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
if (mContentView != null) {
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) mContentView.getLayoutParams();
final int left = paddingLeft + lp.leftMargin;
final int top = paddingTop + lp.topMargin + offsetY;
final int right = left + mContentView.getMeasuredWidth();
final int bottom = top + mContentView.getMeasuredHeight();
mContentView.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
if (DEBUG) {
HLog.d(TAG, "onLayout content: %s %s %s %s", left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams()
{
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p)
{
return new MarginLayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)
{
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
......
......
......
}首先,我们在构造函数PtrFrameLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr)获取自定义属性值,以及初始化一些成员变量,其中mScrollChecker是一个runnable对象,主要用来实现View的平滑移动,下面会有详细解释。
在onFinishInflate()回调方法中,根据布局文件中子view的个数对成员变量mHeaderView和mContentView进行初始化。外部可以同时在布局文件中指定mHeaderView和mContentView,也可以只指定mContentView,mHeaderView通过代码进行设置。
在onMeasure()回调方法中,对子view进行了测量。首先使用measureChildWithMargins()对头部mHeaderView进行了测量,之后将头部的测量的高度更新到PtrIndicator变量中,PtrIndicator是一个工具类,主要负责跟踪记录滑动过程中Y方向的偏移量等等。
在onLayout()回调方法中,通过top = paddingTop + lp.topMargin - mHeaderHeight + offsetY; 计算出header的top值,可以看到header向上偏移了mHeaderHeight,这样头部header初始情况下就会被隐藏。注意,代码中有个offsetY,初始值为0,随着下拉过程中,offsetY会逐渐增大,这样header和content都会向下移动,header就会显示出来,出现下拉位置移动的效果。
计算子view大小的时候用到了MarginLayoutParams,所以我们需要重写generateDefaultLayoutParams()方法。
事件处理
ViewGroup的事件处理,通常重写onInterceptTouchEvent 方法或者 dispatchTouchEvent 方法,PtrFrameLayout重写了dispatchTouchEvent 方法。
事件处理流程图如下:
后面我会附上源码,感兴趣的朋友可以对比源码去理解事件处理流程。
自定义header
经典下拉刷新的头部
PtrClassicDefaultHeader.java
private void resetView()
{
mProgressBar.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
hideRotateView();
}
private void hideRotateView()
{
mRotateView.clearAnimation();
mRotateView.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
}
@Override
public void onUIReset(PtrFrameLayout frame)
{
resetView();
mShoulShowLastUpdate = false;
tryUpdateLastUpdateTime();
}重置header view,隐藏进度条,隐藏箭头,更新最后刷新事件
@Override
public void onUIRefreshPrepare(PtrFrameLayout frame)
{
mShoulShowLastUpdate = true;
tryUpdateLastUpdateTime();
mLastUpdateTimeUpdater.start();
mProgressBar.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
mRotateView.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
mTitleView.setText(R.string.hebut_ptr_pull_down);
}准备刷新,隐藏进度条,显示旋转箭头,提示文字为:pull down;启动一个runnable对象,来实时更新上次刷新时间。
@Override
public void onUIRefreshBegin(PtrFrameLayout frame)
{
hideRotateView();
mProgressBar.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
mTitleView.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
mTitleView.setText(R.string.hebut_ptr_updating);
mShoulShowLastUpdate = false;
tryUpdateLastUpdateTime();
mLastUpdateTimeUpdater.stop();
}开始刷新,隐藏旋转箭头,显示进度条,提示文字:updating。停止mLastUpdateTimeUpdater。
@Override
public void onUIRefreshComplete(PtrFrameLayout frame)
{
hideRotateView();
mProgressBar.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
mTitleView.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
mTitleView.setText(R.string.hebut_ptr_update_complete);
//update last update time
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = getContext().getSharedPreferences(KEY_SharedPreferences, 0);
if(!TextUtils.isEmpty(mLastUpdateTimeKey)) {
mLastUpdateTime = new Date().getTime();
sharedPreferences.edit().putLong(mLastUpdateTimeKey, mLastUpdateTime).commit();
}
}刷新完成,隐藏进度条,隐藏旋转箭头,提示文字:updated;向shared文件中更新最新刷新时间。
@Override
public void onUIPositionChange(PtrFrameLayout frame, boolean isUnderTouch, byte status, PtrIndicator ptrIndicator)
{
final int offsetToRefresh = ptrIndicator.getOffsetToRefresh();
final int currentPos = ptrIndicator.getCurrentPosY();
final int lastPos = ptrIndicator.getLastPos();
if(currentPos < offsetToRefresh && lastPos >= offsetToRefresh) {
if(isUnderTouch && status == frame.PTR_STATUS_PREPARE) {
crossRotateLineFromBottomUnderTouch();
}
} else if(currentPos > offsetToRefresh && lastPos <= offsetToRefresh) {
if(isUnderTouch && status == frame.PTR_STATUS_PREPARE) {
crossRotateLineFromTopUnderTouch();
}
}
}根据用户下拉拖拽的距离,动态改变箭头的方向以及提示文字的内容。当下拉距离从小于下拉刷新高度到大于刷新高度,箭头从向下,变成向上,同时改变提示文字的显示;当下拉距离从大于下拉刷新高度到小于刷新高度,箭头从向上,变成向下,同时改变提示文字的显示。
OK,这里就实现了一个经典的下拉刷新头部header。项目源码中还有很多自定义头部,比如,Material Design风格,StoreHouse风格的头部等等。大家感兴趣可以直接阅读源码。