分治法基础
分治法(Divide and Conquer)顾名思义,思想核心是将问题拆分为子问题,对子问题求解、最终合并结果,分治法用伪代码表示如下:
function f(input x size n) if(n < k) solve x directly and return else divide x into a subproblems of size n/b call f recursively to solve each subproblem Combine the results of all sub-problems
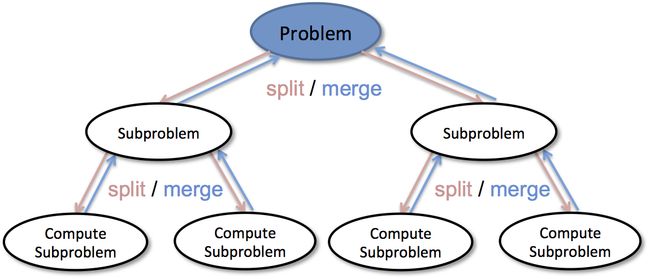
分治法简单而言分三步 Divide、Conquer、Combine,图示如下:
和动态规划、贪心等一样,分治法是一种算法思想,不是用于解决专门某类问题的方法。折半查找(Binary Search)、快速排序/快速选择/归并排序、二叉树处理等都包含了分治法的思想。
关于折半查找、快速排序/归并排序,详见:
算法与数据结构基础 - 折半查找(Binary Search)
算法与数据结构基础 - 排序(Sort)
相关LeetCode题:
169. Majority Element 题解
53. Maximum Subarray 题解
215. Kth Largest Element in an Array 题解
426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List 题解
240. Search a 2D Matrix II 题解
218. The Skyline Problem 题解
4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays 题解
缓存过程结果(Memoization)
一些场景下我们会遇到相同的子问题,这时可以用哈希表等结构缓存子问题的结果,当再次遇到相同子问题时、直接返回结果即可,memoization是常用的减少计算复杂度的技巧。
相关LeetCode题:
241. Different Ways to Add Parentheses 题解
312. Burst Balloons 题解
时间复杂度
分治法中常用到递归,因而其时间复杂度并不直观,关于分治法时间复杂度计算,详见:
Advanced master theorem for divide and conquer recurrences