mutation是更改Vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法,mutation类似于事件注册,每个mutation都可以带两个参数,如下:
state ;当前命名空间对应的state
payload ;传入的参数,一般是一个对象
创建Vuex.Store()仓库实例时可以通过mutations创建每个mutation
我们不能直接调用一个mutation,而是通过 store.commit来调用,commit可以带两个参数,如下:
type ;对应的mutation名
payload ;传入的参数
commit还有一种写法,就是传入一个对象即可,该对象可以带一个type参数,type指定为mutation的名称,整个对象会作为参数传递给mutation。注意:mutation里包含的是同步操作
例如:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Documenttitle>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/vue.js">script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/vuex.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{no}}p>
<button @click="test1">测试1button>
<button @click="test2">测试2button>
div>
<script>
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{no:100},
mutations:{
increment(state,payload){state.no+=payload.no;}
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
store:store,
computed:{
no(){return this.$store.state.no }
},
methods:{
test1(){
this.$store.commit('increment',{no:100}) //一般调用mutation的方法
},
test2(){
this.$store.commit({type:'increment',no:100}) //mutation的另一种写法
},
}
})
script>
body>
html>
源码分析
在创建Vuex.Store()初始化时会执行installModule()安装根模块,和mutation相关的如下:
function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) { //安装模块 /*略*/ module.forEachMutation(function (mutation, key) { //遍历module模块的mutations对象,如果找到了,则执行这个匿名函数 参数1:每个mutation值 key:对应的键名 var namespacedType = namespace + key; //拼凑namespacedType registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local); //调用registerMutation注册mutation }); /*略*/ }
registerMutation用于注册mutation的,如下:
function registerMutation (store, type, handler, local) { //注册Mutations var entry = store._mutations[type] || (store._mutations[type] = []); //如果store对象的_mutations对应的为空,则初始化为数组 entry.push(function wrappedMutationHandler (payload) { //则将一个匿名函数push到entry里面 handler.call(store, local.state, payload); //上下文是store,参数1为local.state,参数2为payload }); }
writer by:大沙漠 QQ:22969969
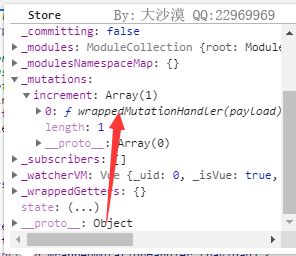
也就是说注册完后对应的mutation会存储在store._mutations里,这是一个对象,每个键是一个mutation,而值就是对应的mutation,是个数组,例如例子里执行到这里时对应的_mutation如下:
等到我们调用this.$store.commit('increment',{no:100})去触发一个mutation时首先会触发Store函数内重定义的commit,它会以当前Store函数对象为上下文继续执行Store原型上的commit函数,如下:
Store.prototype.commit = function commit (_type, _payload, _options) { //对mutation的处理 var this$1 = this; // check object-style commit var ref = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options); //规范一下参数,返回一个对象,例如:{options: undefined,payload: {no: 100},type: "increment"} var type = ref.type; //mutagion类型:比如:increment var payload = ref.payload; //传递过来的参数 var options = ref.options; //选项 var mutation = { type: type, payload: payload }; var entry = this._mutations[type]; //直接从this._mutations里获取type类型的mutaion,是个函数数组 if (!entry) { //如果该mutaion不存在,则报错 { console.error(("[vuex] unknown mutation type: " + type)); } return } this._withCommit(function () { //在this._withCommit()环境下执行该函数 entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) { //遍历entry,依次执行每个handler函数,参数为payload handler(payload); }); }); this._subscribers.forEach(function (sub) { return sub(mutation, this$1.state); }); if ( options && options.silent ) { console.warn( "[vuex] mutation type: " + type + ". Silent option has been removed. " + 'Use the filter functionality in the vue-devtools' ); } };
unifyObjectStyle是一个工具函数,它会修正参数,并返回一个对象,如下:
function unifyObjectStyle (type, payload, options) { //统一object的类型 if (isObject(type) && type.type) { //如果type是个类型且含有type属性,比如这样的格式:this.$store.commit({type:'increment',no:1000}) options = payload; payload = type; type = type.type; } { assert(typeof type === 'string', ("expects string as the type, but found " + (typeof type) + ".")); } return { type: type, payload: payload, options: options } //最后返回该对象 }
我们在例子里可以用两种方式来调用mutation也是这个unifyObjectStyle函数的作用
_withCommit是一个工具函数,如下:
Store.prototype._withCommit = function _withCommit(fn) { //执行fn函数 执行时设置this._committing为true,执行完后设置为false var committing = this._committing; //保存this._committing到局部变量committing里 this._committing = true; //设置this._committing为true fn(); //执行fn函数 this._committing = committing; //恢复this._committing };
它在执行传入的函数时会设置Store._committing为true,这样就相当于设置了一个标记,表示当前是通过mutation来修改state的,还记得上一节说的strict严格模式吗,它就是通过这里的_committing来判断是否合法的。