JQuery时代,我们使用ajax向后台提交数据请求,Vue时代,Axios提供了前端对后台数据请求的各种方式。
一、什么是Axios
Axios是基于Promise的Http客户端,可以在浏览器和node.js中使用。
二、为什么使用Axios
Axios非常适合前后端数据交互,另一种请求后端数据的方式是vue-resource,vue-resource已经不再更新了,且只支持浏览器端使用,而Axios同时支持浏览器和Node端使用。
Vue开发者推荐使用更好的第三方工具,这就是Axios
三、安装
Axios的安装支持多种方式
npm安装
npm install axioscdn
四、使用方式介绍
接下来,我们使用Django,搭建一个后台程序,并使用Vue Cli搭建一个前端程序,使用Axios进行前后端数据交互。
使用Vue Cli创建一个前端程序
vue init webpack luffy_fontend使用Django创建一个后端程序luffy_backend
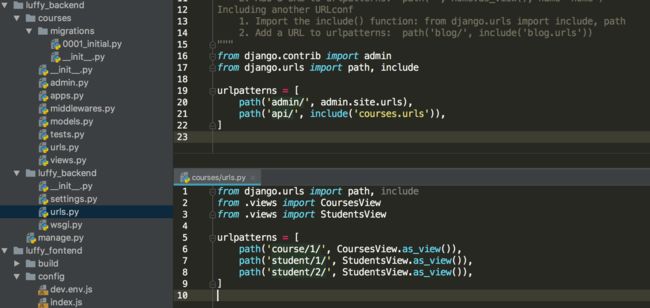
`django-admin startproject luffy_backend`创建一个courses应用
cd luffy_backend
python manage.py startapp courses在models.py中创建两个类
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Courses(models.Model):
course_name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
course_price = models.IntegerField()
course_teacher = models.CharField(max_length=16)
start_date = models.DateField(auto_now=True, null=False)
end_date = models.DateField(auto_now=True, null=False)
def __str__(self):
return self.course_name
class Students(models.Model):
student_name = models.CharField(max_length=16)
student_id = models.IntegerField()
student_phone = models.IntegerField()
student_address = models.CharField(max_length=128)插入数据
// courses_courses
insert into courses_courses(course_name, course_price, course_teacher, start_date, end_date) values('Python全栈中级开发', 12800, 'Pizza', '2018-10-01', '2018-10-02');
insert into courses_courses(course_name, course_price, course_teacher, start_date, end_date) values('Python全栈高级开发', 19800, 'Alex', '2018-10-03', '2018-10-04');
insert into courses_courses(course_name, course_price, course_teacher, start_date, end_date) values('Linux高级运维', 12800, 'Oldboy', '2018-10-05', '2018-10-06');
insert into courses_courses(course_name, course_price, course_teacher, start_date, end_date) values('高级网络工程师', 12800, 'Egon', '2018-10-07', '2018-10-08');
insert into courses_courses(course_name, course_price, course_teacher, start_date, end_date) values('Go全栈高级开发', 12800, 'Yuan', '2018-10-09', '2018-10-10');
insert into courses_courses(course_name, course_price, course_teacher, start_date, end_date) values('Vue高级开发', 12800, 'Xiaoma', '2018-10-11', '2018-10-12');
// courses_students
insert into courses_students(id, student_name, student_id, student_phone, student_address) values(1, 'Alex', 100001, 1378061875, '北京市大兴区智障一中');
insert into courses_students(id, student_name, student_id, student_phone, student_address) values(2, 'Pizza', 100002, 1378161875, '北京市朝阳区第一中学');
insert into courses_students(id, student_name, student_id, student_phone, student_address) values(2, 'Egon', 100003, 1378261875, '北京市房山智障三中');
insert into courses_students(id, student_name, student_id, student_phone, student_address) values(4, 'Oldboy', 100004, 1378361875, '北京市大兴区智障三中');
insert into courses_students(id, student_name, student_id, student_phone, student_address) values(5, 'Yuanhao', 100005, 1378460275, '北京市丰台区智障四中');
insert into courses_students(id, student_name, student_id, student_phone, student_address) values(6, 'Jinxin', 100006, 1378560875, '北京市海淀区智障五中');在views.py中写好接口
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
import json
from luffy_backend import settings
from .models import Courses
from .models import Students
# Create your views here.
class CoursesView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
print("Courses Get Methods Exec!")
courses = list()
for item in Courses.objects.all():
course = {
"course_name": item.course_name,
"course_price": item.course_price,
'course_teacher': item.course_teacher,
'start_date': str(item.start_date),
'end_date': str(item.end_date)
}
courses.append(course)
print(courses)
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(courses, ensure_ascii=False))
class StudentsView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
print("Student Get Methods Exec!")
students = list()
for item in Students.objects.all():
student = {
'student_name': item.student_name,
'student_id': item.student_id,
'student_phone': item.student_phone,
'student_address': item.student_address
}
students.append(student)
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(students, ensure_ascii=False))
def post(self, request):
print("Student Post Methods Exec!")
print(request.body.decode('utf-8'))
response = json.dumps(request.POST)
return HttpResponse(response)定义接口
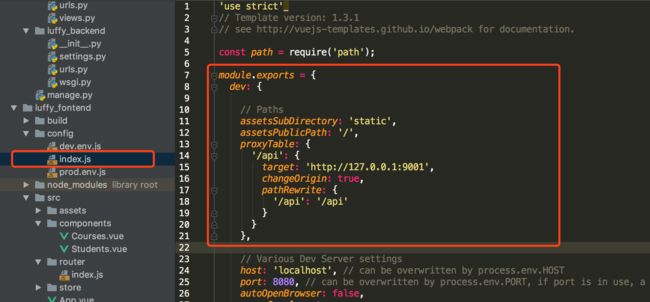
配置后台接口
注意,修改配置文件后,需要重启前端服务器。
在Vue Cli中使用axios
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
import axios from "axios"
Vue.prototype.$axios = axios;
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
template: '获取课程信息
这是课程详情页面
课程名称
课程价格
授课老师
开课日期
结课日期
{{ course.course_name }}
{{ course.course_price }}
{{ course.course_teacher }}
{{ course.start_date }}
{{ course.end_date }}
获取学生信息
这是学员信息页面
学生ID
学生姓名
学生电话
学生地址
{{ student.student_id }}
处理跨域问题
发送post请求时,需要解决跨域问题,我们采用在Django中自定义一个处理跨域问题的中间件来解决这个问题。
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
class MyCore(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_response(self, request, response):
response["Access-Control-Allow-Origin"] = '*'
if request.method == 'OPTIONS':
response["Access-Control-Allow-Headers"] = 'Content-Type'
response["Access-Control-Allow-Methods"] = 'POST, DELETE, PUT'
return response以上,就是我们通过Axios的get和post请求与后台进行数据交互的全过程。