spring boot学习笔记(三):controller用法及数据库操作
一、controller用法
1、@controller和@RestController注解的区别
@controller处理http请求,页面展示需要配合thymeleaf模板使用。
示例:
a、首先,在pom文件添加thymeleaf模板依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>b、新建GirConerllr:
package com.springboot.gril.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.springboot.gril.entity.Girl;
import com.springboot.gril.repository.GirlRepository;
@Controller
public class GirlController {
@Autowired
private GirlRepository girlRepository;
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test(){
return "index";
}
}
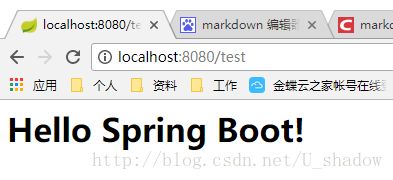
c、在resource/templates下创建index.html文件,这里的html文件名必须跟controller的方法返回的的名称一致:
index.html:
<h1>
Hello Spring Boot!
h1>d、启动项目,测试效果:
这里thymeleaf模板的使用我也不是很熟练,也不是本篇文章的重点内容,我就不做详细的介绍,想做深入了解的可以查看官方文档。另外,现在项目趋向于前后端分离,后端一般给前端提供接口,返回json串,因此这里推荐使用下面介绍的@RestController注解。
2、@RestController注解
@RestController注解实际上是一个组合注解,相当于@controller和@ResponseBody配合使用。后面的内容都是使用的@RestController注解,在这里就不单独举例子讲解。
3、多个路径指向同一个方法
实现多个路径指向同一个方法,只需在@RequestMapping的value中以集合的方式:
package com.springboot.gril.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springboot.gril.entity.Girl;
import com.springboot.gril.repository.GirlRepository;
@RestController
public class GirlController {
@Autowired
private GirlRepository girlRepository;
@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello", "/hi"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello(){
ren "Hello Spring Boot";
}
}
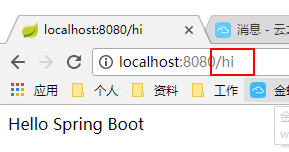
启动项目测试:
在项目启动的时候我们就可以看到两个地址映射到同一个方法上:
![]()
通过浏览器访问:

4、获取url中参数
- @PathVariable注解方式获取
- @RequestParam注解方式获取
package com.springboot.gril.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springboot.gril.entity.Girl;
import com.springboot.gril.repository.GirlRepository;
@RestController
public class GirlController {
@Autowired
private GirlRepository girlRepository;
@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello", "/hi"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello(){
return "Hello Spring Boot";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/getParamOne/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getParamOne(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return "方式一——传入参数为:" + id;
}
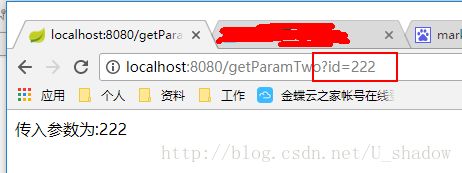
@RequestMapping(value = "/getParamTwo", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getParamTwo(@RequestParam("id") Integer myId){
return "方式二——传入参数为:" + myId;
}
}
那么这两种方式有什么区别呢?
首先我们介绍一下我们@RequestParam这种方式。我们一般习惯在url后通过”?+参数名称 + = + 参数名称”的方式传递参数,@RequestParam就是获取这种方式传递的参数。
这里需要注意一点是,url后面的参数名称必须跟java代码中@RequestParam(“id”)后面括号中的名称保持一致。
相信有人会注意到,用这种方式时,如果不传入id,访问该方法就会报错,或者不给id值,后台就会是null。那么,如果我们希望我们在没有传入参数的时候可以不用传入id的值,并且给id一个默认值要怎么做呢?这里只需修改@RequestParam内容既可。
@RequestMapping(value = "/getParamTwo", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getParamTwo(@RequestParam(value = "id", required = false, defaultValue = "0")
Integer myId){
return "方式二——传入参数为:" + myId;
}至于@PathVariable方式获取参数则比较简洁一些,我们不需要在url后加上参数名、参数值,只需按照方法上的注解方式输入,例如上面的为@RequestMapping(value = “/getParamOne/{id}”, method = RequestMethod.GET)
,那么我们在地址中输入http://localhost:8080/getParamOne/111,后台就可以后台就可们传到我们传入的111
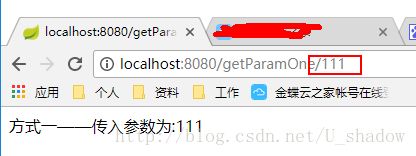
这里要注意的是,在Java代码中@RequestMapping和@PathVariable注解中的参数名称必须一致。
另外,地址栏输入访问方法跟参数顺序需同java注解中保持一致,比如,如果在java中注解方式是@RequestMapping(value = “/{id}/getParamOne”, method = RequestMethod.GET),则地址栏中输入需要是http://localhost:8080/111/getParamOne。
二、数据库操作
spring boot对数据库的操作比较简单,下面开始简单介绍一下通过spring boot操作数据库,以mysql数据库为例。
首先,需在pom文件中引入相关依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>在application.yml文件中添加连接数据库的相关配置
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dbgirl
username: root
password: root
jpa:
show-sql: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create然后,新建一个Girl实体
package com.springboot.gril.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Girl {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Integer id;
private String cupSize;
private Integer age;
public Girl() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCupSize() {
return cupSize;
}
public void setCupSize(String cupSize) {
this.cupSize = cupSize;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@Entity注解标明该类是一个实体类,对应数据库中的一个表
@Id
声明主键id
@GeneratedValue id自增
另外,在实体类中需要添加无参的构造方法,否则在操作数据库是会出问题。
在数据库中创建对应的数据库,我这里是dbgirl,启动项目,我们会发现在数据库中自动帮我们创建了一个girl的表,字段跟我们创建的实体对应。原因是因为applicatio.yml中的配置

这句话的意思是,我们在每次启动项目时,都会自动帮我们创建对应的表,如果这个表存在的会先删除它,然后重新创建(表中有数据也会删除),所以,我们常用的配置是把create改成update。update表明,项目第一次启动时,也会创建相应的表,但是后面启动时不会删除表。
这里还有其它的几个配置属性:
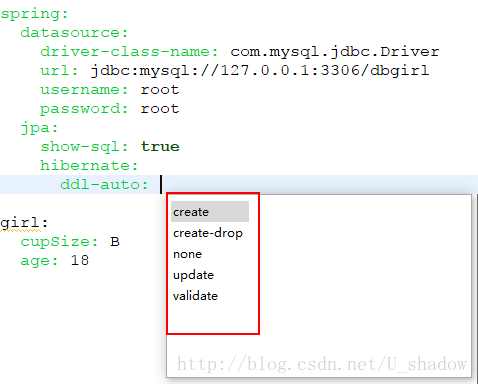
create-drop:应用停掉的时候会删除表;
none:不做任何操作;
validate:会验证类跟表中的属性是否一致,不一致会报错;
有兴趣的朋友可以修改各个属性实际测试一下。
下面,我们来看一下如何操作数据库里面的数据:
新建一个GirlRepository接口,继承JpaRepository接口
package com.springboot.gril.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springboot.gril.entity.Girl;
public interface GirlRepository extends JpaRepository<Girl, Integer>{
}
这里可以看到,我并没有在GirlRepository 中写任何的方法。
然后在controller中引用GirlRepository :
@Autowired
private GirlRepository girlRepository;这里由于逻辑很简单,所以我并没有新建server,实际开发中我们是会建一个server层的,我这里就省去了。
a、查询所有数据
在controller中创建对应方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/girlList", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List findAll(){
return girlRepository.findAll();
} 启动项目,测试效果:
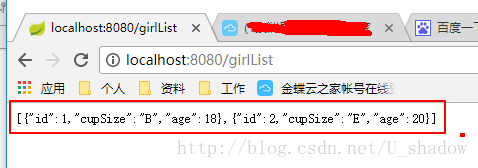
前面有说过,@RestController方式,返回的是json串,这里也验证了这一点。
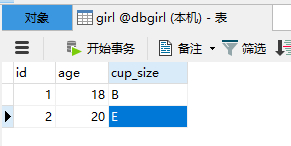
然后我们看一下数据库的数据:
b、根据id查询
在controller中创建对应方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/findGirlByID/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Girl findGirlByID(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return girlRepository.findOne(id);
}测试验证:
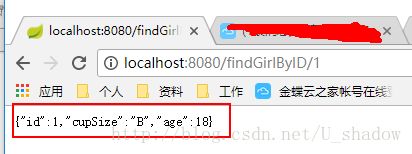
c、删除操作
在controller中创建对应方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/delGirlByID/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void delGirlByID(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
girlRepository.delete(id);
}delete方法没有返回值,执行后查看数据库数据:
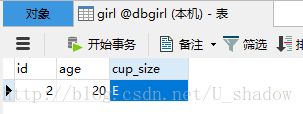
可以看到,id为1的数据已经被删除了。
c、新增操作
在controller中创建对应方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/addGirl", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Girl addGirl(){
Girl girl = new Girl();
girl.setCupSize("F");
girl.setAge(26);
return girlRepository.save(girl);
}测试结果:
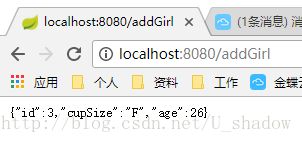

可以看到,数据已经插入到数据库中了。
e、修改操作
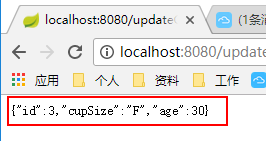
我们现在将id为3的数据年龄修改为30.
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateGirl/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Girl updateGirl(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
Girl girl = new Girl();
girl.setId(id);
girl.setAge(30);
girl.setCupSize("F");
return girlRepository.save(girl);
}这里介绍了spring boot对数据库的简单操作,下一篇将会介绍一些稍复杂的操作。
最后,我也是初学spring boot,如果各位发现哪里有问题,希望大家给我留言指出,谢谢!