caffe 速览笔记
Caffe Tutorial
Caffe 模型的最基本要素: Blob, Layers, Nets
Blob 传送数据的基本单元
Blob与tensorflow中的tensor类似,都是用来在节点之间传递数据所用,接口也类似,常规的dimension是 数据量N x 通道K x 高度H x 宽度W
Blob内部存有data和diff两大块。前者是传递的数据,后者是计算的梯度。
由于blob同时存在CPU和GPU,所以有两种方式来访问他们:
- const (don`t change the values)
- mutable (changes the values)
const Dtype* cpu_data() const;
Dtype* mutable_cpu_data();要使用合适的方式来访问blob变量,主要是因为blob具有cpu和gpu同步功能,会进行cpu和gpu的通信。所以如果不想更改值的话,最好使用const来调用,以减小通信开销。并且blob的指针不要存在自己的对象中,而使用函数来获取指针,因为syncedmem需要函数的调用来确定什么时候复制数据。
cpu 和 gpu 之间的转换?
Layer 计算与连接的单元
Layer是模型的本质与计算的基本单元。包括卷积、池化、内积、sigmoid等。
每个Layer包括了三个重要的计算:设置、前向传输、后向传输(setup, forward, backward)
- Setup: 初始化layer与连接
- Forward: 根据来自底部的数据进行计算,传到顶部
- Backward:根据顶部传来的梯度进行梯度计算,然后传到底部。具有参数的layer会将梯度进行存储应用
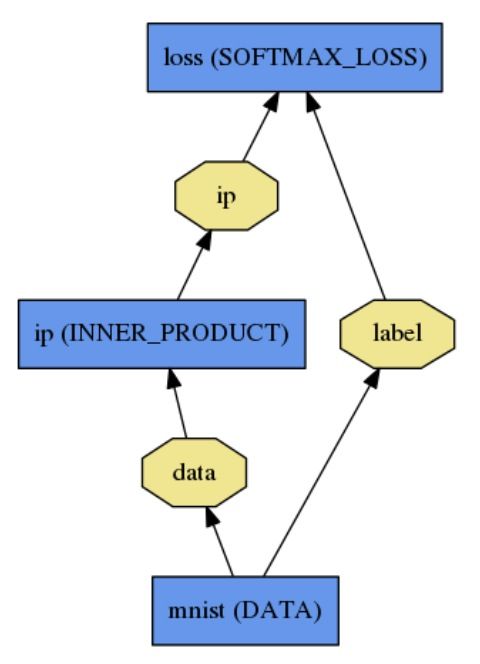
Net 定义和操作
这样进行定义:
name: "LogReg"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
data_param {
source: "input_leveldb"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "ip"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "data"
top: "ip"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}Forward 与 Backward
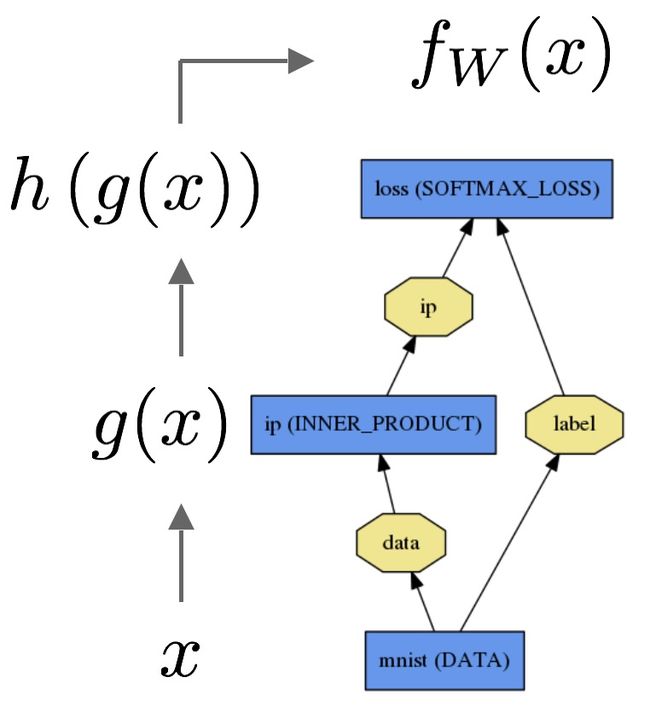
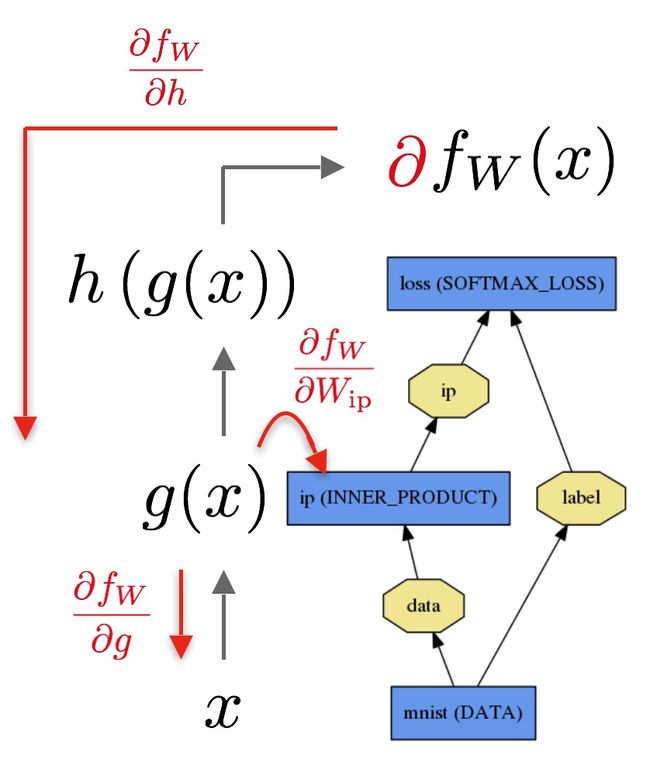
Forward 与 Backward 的传输是Net的重要计算。
Forward计算:
Loss
普通:
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "pred"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}loss weight:
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "pred"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
loss_weight: 1
}最后可根据所有loss进行加权相加计算:
loss := 0
for layer in layers:
for top, loss_weight in layer.tops, layer.loss_weights:
loss += loss_weight * sum(top)Slover
各种用于计算梯度与loss的方法。
//todo
Layers
数据层
可利用设置TransformationParameter来进行输入的预处理(mean subtraction, scaling, random cropping, and mirroring)
当TransformationParameter失效时,可利用 bias, scale, and crop层进行处理。
有以下几种data layers:
- Image Data - read raw images.
- Database - read data from LEVELDB or LMDB.
- HDF5 Input - read HDF5 data, allows data of arbitrary dimensions.
- HDF5 Output - write data as HDF5.
- Input - typically used for networks that are being deployed.
- Window Data - read window data file.
- Memory Data - read data directly from memory.
- Dummy Data - for static data and debugging.
Vison Layers
以images为输入,以images为输出。
有以下几种Vision Layers:
- 卷积层
- 池化层
- Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP)
- Crop 裁剪操作
- Deconvolution Layer 逆卷积层
Recurrent Layers
- Recurrent
- RNN
- Long-short Term Memory
Common Layers
- Inner Product
- Dropout
- Embed
Normalization Layers
- Local Response Normalization
- Mean Variance Normalization
- Batch Normalization
Activation / Neuron Layers
- ReLU / Rectified-Linear and Leaky-ReLU - ReLU and Leaky-ReLU rectification.
- PReLU - parametric ReLU.
- ELU - exponential linear rectification.
- Sigmoid
- TanH
- Absolute Value
- Power - f(x) = (shift + scale * x) ^ power.
- Exp - f(x) = base ^ (shift + scale * x).
- Log - f(x) = log(x).
- BNLL - f(x) = log(1 + exp(x)).
- Threshold - performs step function at user defined threshold.
- Bias - adds a bias to a blob that can either be learned or fixed.
- Scale - scales a blob by an amount that can either be learned or fixed.
Utility Layers
- Flatten
- Reshape
Batch Reindex
Split
- Concat
- Slicing
- Eltwise - element-wise operations such as product or sum between two blobs.
- Filter / Mask - mask or select output using last blob.
- Parameter - enable parameters to be shared between layers.
- Reduction - reduce input blob to scalar blob using operations such as sum or mean.
Silence - prevent top-level blobs from being printed during training.
ArgMax
Softmax
Python - allows custom Python layers.
Loss Layers
- Multinomial Logistic Loss
- Infogain Loss - a generalization of MultinomialLogisticLossLayer.
- Softmax with Loss - computes the multinomial logistic loss of the softmax of its inputs. It’s conceptually identical to a softmax layer followed by a multinomial logistic loss layer, but provides a more numerically stable gradient.
- Sum-of-Squares / Euclidean - computes the sum of squares of differences of its two inputs
- Hinge / Margin - The hinge loss layer computes a one-vs-all hinge (L1) or squared hinge loss (L2).
- Sigmoid Cross-Entropy Loss - computes the cross-entropy (logistic) loss, often used for predicting targets interpreted as probabilities.
- Accuracy / Top-k layer - scores the output as an accuracy with respect to target – it is not actually a loss and has no backward step.
- Contrastive Loss
Data inputs and outputs
in:
layer {
name: "mnist"
# Data layer loads leveldb or lmdb storage DBs for high-throughput.
type: "Data"
# the 1st top is the data itself: the name is only convention
top: "data"
# the 2nd top is the ground truth: the name is only convention
top: "label"
# the Data layer configuration
data_param {
# path to the DB
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
# type of DB: LEVELDB or LMDB (LMDB supports concurrent reads)
backend: LMDB
# batch processing improves efficiency.
batch_size: 64
}
# common data transformations
transform_param {
# feature scaling coefficient: this maps the [0, 255] MNIST data to [0, 1]
scale: 0.00390625
}
}out:
layer {
name: "data"
type: "Data"
[...]
transform_param {
scale: 0.1
mean_file_size: mean.binaryproto
# for images in particular horizontal mirroring and random cropping
# can be done as simple data augmentations.
mirror: 1 # 1 = on, 0 = off
# crop a `crop_size` x `crop_size` patch:
# - at random during training
# - from the center during testing
crop_size: 227
}
}