CS224d Assignment Word2Vec
Word2Vec 练习题


y o ^ = P ( o ∣ c ) = e x p ( u o T v c ) ∑ w = 1 V e x p ( u w T v c ) \widehat{y_o}=P(o|c)=\frac{exp(u_o^Tv_c)}{\sum^V_{w=1}exp(u_w^Tv_c)} yo =P(o∣c)=∑w=1Vexp(uwTvc)exp(uoTvc)
o o o:输出词汇索引
c c c:中心词汇索引
v c v_c vc:中心词汇向量
u o u_o uo:输出词汇向量

设d为词向量维度,由图可知:
θ = U T v c ∈ W × 1 \theta=U^Tv_c\in{W\times1} θ=UTvc∈W×1
y o ^ = P ( o ∣ c ) = e x p ( u o T v c ) ∑ w = 1 V e x p ( u w T v c ) = s o f t m a x ( θ ) o \widehat{y_o}=P(o|c)=\frac{exp(u_o^Tv_c)}{\sum^V_{w=1}exp(u_w^Tv_c)}=softmax(\theta)_o yo =P(o∣c)=∑w=1Vexp(uwTvc)exp(uoTvc)=softmax(θ)o
按提示:

![]()
对所有的w对 u w u_w uw求导数,即对U求导数。

由题损失函数为:


为更便于做题,先画一个简单的图进行CBOW模型和Skipgram模型的对比:
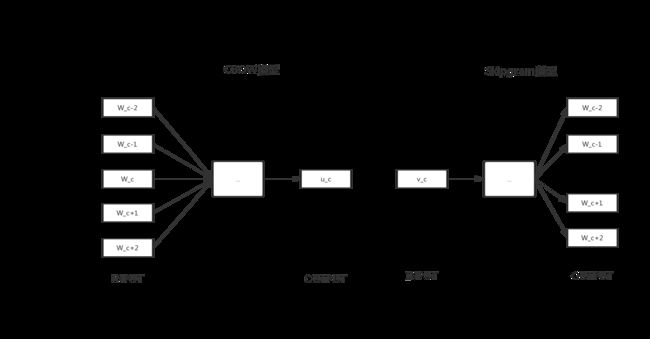
在skipgram模型中:

∂ J ∂ v c = ∑ − m ≤ j ≤ m , j ≠ 0 ∂ F ( w c + j , v c ) ∂ v c \frac{\partial{J}}{\partial{v_c}}=\sum_{-m\le{j}\le{m},j\neq{0}}\frac{\partial{F(w_{c+j},v_c)}}{\partial{v_c}} ∂vc∂J=−m≤j≤m,j̸=0∑∂vc∂F(wc+j,vc)
∂ J ∂ v j 为 零 向 量 , j ≠ c \frac{\partial{J}}{\partial{v_j}}为零向量,j\neq{c} ∂vj∂J为零向量,j̸=c
在CBOW模型中:
有上述对比图可知,CBOW模型由多个上下文词预测中心词,

∂ J ∂ v c = ∂ F ( w c , v ^ ) ∂ v c 为 零 向 量 \frac{\partial{J}}{\partial{v_c}}=\frac{\partial{F(w_c,\widehat{v})}}{\partial{v_c}}为零向量 ∂vc∂J=∂vc∂F(wc,v )为零向量
∂ J ∂ v j = ∂ F ( w c , v ^ ) ∂ v ^ ⋅ ∂ v ^ v j = ∂ F ( w c , v ^ ) v j \frac{\partial{J}}{\partial{v_j}}=\frac{\partial{F(w_c,\widehat{v})}}{\partial{\widehat{v}}}\cdot{\frac{\partial{\widehat{v}}}{v_j}}=\frac{\partial{F(w_c,\widehat{v})}}{v_j} ∂vj∂J=∂v ∂F(wc,v )⋅vj∂v =vj∂F(wc,v )
import numpy as np
import random
from q1_softmax import softmax
from q2_gradcheck import gradcheck_naive
from q2_sigmoid import sigmoid, sigmoid_grad
def normalizeRows(x):
"""
行归一化
"""
N = x.shape[0]
x /= np.sqrt(np.sum(x**2, axis=1)).reshape((N,1)) + 1e-30
return x
def test_normalize_rows():
print("Testing normalizeRows...")
x = normalizeRows(np.array([[3.0,4.0],[1, 2]]))
# result should be [[0.6, 0.8], [0.4472, 0.8944]]
print(x)
assert (np.amax(np.fabs(x - np.array([[0.6,0.8],[0.4472136,0.89442719]]))) <= 1e-6)
def softmaxCostAndGradient(predicted, target, outputVectors, dataset):
"""
word2vec的Softmax损失函数
"""
# 输入:
# - predicted: 预测词向量的numpy数组
# - target: 目标词的下标
# - outputVectors: 所有token的"output"向量(行形式)
# - dataset: 用来做负例采样
# 输出:
# - cost: 输出的互熵损失
# - gradPred: the gradient with respect to the predicted word
# vector
# - grad: the gradient with respect to all the other word
# vectors
probabilities = softmax(predicted.dot(outputVectors.T))
cost = -np.log(probabilities[target])
delta = probabilities
delta[target] -= 1
N = delta.shape[0]
D = predicted.shape[0]
grad = delta.reshape((N,1)) * predicted.reshape((1,D))
gradPred = (delta.reshape((1,N)).dot(outputVectors)).flatten()
return cost, gradPred, grad
def negSamplingCostAndGradient(predicted, target, outputVectors, dataset,
K=10):
"""
Word2vec模型负例采样后的损失函数和梯度
"""
grad = np.zeros(outputVectors.shape)
gradPred = np.zeros(predicted.shape)
indices = [target]
for k in xrange(K):
newidx = dataset.sampleTokenIdx()
while newidx == target:
newidx = dataset.sampleTokenIdx()
indices += [newidx]
labels = np.array([1] + [-1 for k in xrange(K)])
vecs = outputVectors[indices,:]
t = sigmoid(vecs.dot(predicted) * labels)
cost = -np.sum(np.log(t))
delta = labels * (t - 1)
gradPred = delta.reshape((1,K+1)).dot(vecs).flatten()
gradtemp = delta.reshape((K+1,1)).dot(predicted.reshape(
(1,predicted.shape[0])))
for k in xrange(K+1):
grad[indices[k]] += gradtemp[k,:]
t = sigmoid(predicted.dot(outputVectors[target,:]))
cost = -np.log(t)
delta = t - 1
gradPred += delta * outputVectors[target, :]
grad[target, :] += delta * predicted
for k in xrange(K):
idx = dataset.sampleTokenIdx()
t = sigmoid(-predicted.dot(outputVectors[idx,:]))
cost += -np.log(t)
delta = 1 - t
gradPred += delta * outputVectors[idx, :]
grad[idx, :] += delta * predicted
return cost, gradPred, grad
def skipgram(currentWord, C, contextWords, tokens, inputVectors, outputVectors,
dataset, word2vecCostAndGradient = softmaxCostAndGradient):
""" Skip-gram model in word2vec """
# skip-gram模型的实现
# 输入:
# - currrentWord: 当前中心词所对应的串
# - C: 上下文大小(词窗大小)
# - contextWords: 最多2*C个词
# - tokens: 对应词向量中词下标的字典
# - inputVectors: "input" word vectors (as rows) for all tokens
# - outputVectors: "output" word vectors (as rows) for all tokens
# - word2vecCostAndGradient: the cost and gradient function for a prediction vector given the target word vectors, could be one of the two cost functions you implemented above
# 输出:
# - cost: skip-gram模型算得的损失值
# - grad: 词向量对应的梯度
currentI = tokens[currentWord]
predicted = inputVectors[currentI, :]
cost = 0.0
gradIn = np.zeros(inputVectors.shape)
gradOut = np.zeros(outputVectors.shape)
for cwd in contextWords:
idx = tokens[cwd]
cc, gp, gg = word2vecCostAndGradient(predicted, idx, outputVectors, dataset)
cost += cc
gradOut += gg
gradIn[currentI, :] += gp
return cost, gradIn, gradOut
def word2vec_sgd_wrapper(word2vecModel, tokens, wordVectors, dataset, C, word2vecCostAndGradient = softmaxCostAndGradient):
batchsize = 50
cost = 0.0
grad = np.zeros(wordVectors.shape)
N = wordVectors.shape[0]
inputVectors = wordVectors[:N/2,:]
outputVectors = wordVectors[N/2:,:]
for i in xrange(batchsize):
C1 = random.randint(1,C)
centerword, context = dataset.getRandomContext(C1)
if word2vecModel == skipgram:
denom = 1
else:
denom = 1
c, gin, gout = word2vecModel(centerword, C1, context, tokens, inputVectors, outputVectors, dataset, word2vecCostAndGradient)
cost += c / batchsize / denom
grad[:N/2, :] += gin / batchsize / denom
grad[N/2:, :] += gout / batchsize / denom
return cost, grad
def test_word2vec():
# Interface to the dataset for negative sampling
dataset = type('dummy', (), {})()
def dummySampleTokenIdx():
return random.randint(0, 4)
def getRandomContext(C):
tokens = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"]
return tokens[random.randint(0,4)], [tokens[random.randint(0,4)] \
for i in xrange(2*C)]
dataset.sampleTokenIdx = dummySampleTokenIdx
dataset.getRandomContext = getRandomContext
random.seed(31415)
np.random.seed(9265)
dummy_vectors = normalizeRows(np.random.randn(10,3))
dummy_tokens = dict([("a",0), ("b",1), ("c",2),("d",3),("e",4)])
print("==== Gradient check for skip-gram ====")
gradcheck_naive(lambda vec: word2vec_sgd_wrapper(skipgram, dummy_tokens, vec, dataset, 5), dummy_vectors)
gradcheck_naive(lambda vec: word2vec_sgd_wrapper(skipgram, dummy_tokens, vec, dataset, 5, negSamplingCostAndGradient), dummy_vectors)
print("\n==== Gradient check for CBOW ====")
gradcheck_naive(lambda vec: word2vec_sgd_wrapper(cbow, dummy_tokens, vec, dataset, 5), dummy_vectors)
gradcheck_naive(lambda vec: word2vec_sgd_wrapper(cbow, dummy_tokens, vec, dataset, 5, negSamplingCostAndGradient), dummy_vectors)
print("\n=== Results ===")
print(skipgram("c", 3, ["a", "b", "e", "d", "b", "c"], dummy_tokens, dummy_vectors[:5,:], dummy_vectors[5:,:], dataset))
print(skipgram("c", 1, ["a", "b"], dummy_tokens, dummy_vectors[:5,:], dummy_vectors[5:,:], dataset, negSamplingCostAndGradient))
# print(cbow("a", 2, ["a", "b", "c", "a"], dummy_tokens, dummy_vectors[:5,:], dummy_vectors[5:,:], dataset))
#print(cbow("a", 2, ["a", "b", "a", "c"], dummy_tokens, dummy_vectors[:5,:], dummy_vectors[5:,:], dataset, negSamplingCostAndGradient))
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_normalize_rows()
test_word2vec()
import glob
import random
import numpy as np
import os.path as op
import _pickle as pickle
def load_saved_params():
""" A helper function that loads previously saved parameters and resets iteration start """
st = 0
for f in glob.glob("saved_params_*.npy"):
iter = int(op.splitext(op.basename(f))[0].split("_")[2])
if (iter > st):
st = iter
if st > 0:
with open("saved_params_%d.npy" % st, "r") as f:
params = pickle.load(f)
state = pickle.load(f)
return st, params, state
else:
return st, None, None
def save_params(iter, params):
with open("saved_params_%d.npy" % iter, "w") as f:
pickle.dump(params, f)
pickle.dump(random.getstate(), f)
def sgd(f, x0, step, iterations, postprocessing = None, useSaved = False, PRINT_EVERY=10):
""" Stochastic Gradient Descent """
# Implement the stochastic gradient descent method in this
# function.
# Inputs:
# - f: the function to optimize, it should take a single
# argument and yield two outputs, a cost and the gradient
# with respect to the arguments
# - x0: the initial point to start SGD from
# - step: the step size for SGD
# - iterations: total iterations to run SGD for
# - postprocessing: postprocessing function for the parameters
# if necessary. In the case of word2vec we will need to
# normalize the word vectors to have unit length.
# - PRINT_EVERY: specifies every how many iterations to output
# Output:
# - x: the parameter value after SGD finishes
# Anneal learning rate every several iterations
ANNEAL_EVERY = 20000
if useSaved:
start_iter, oldx, state = load_saved_params()
if start_iter > 0:
x0 = oldx;
step *= 0.5 ** (start_iter / ANNEAL_EVERY)
if state:
random.setstate(state)
else:
start_iter = 0
x = x0
if not postprocessing:
postprocessing = lambda x: x
expcost = None
for iter in range(start_iter + 1, iterations + 1):
### Don't forget to apply the postprocessing after every iteration!
### You might want to print the progress every few iterations.
cost = None
### YOUR CODE HERE
cost, f_grad = f(x)
# 根据梯度来更新x,也就是下降x
x -= step * f_grad
x = postprocessing(x)
### END YOUR CODE
if iter % PRINT_EVERY == 0:
if not expcost:
expcost = cost
else:
expcost = .95 * expcost + .05 * cost
print("iter %d: %f" % (iter, expcost))
if iter % SAVE_PARAMS_EVERY == 0 and useSaved:
save_params(iter, x)
if iter % ANNEAL_EVERY == 0:
step *= 0.5
return x
def sanity_check():
quad = lambda x: (np.sum(x ** 2), x * 2)
print("Running sanity checks...")
t1 = sgd(quad, 0.5, 0.01, 1000, PRINT_EVERY=100)
print("test 1 result:", t1)
assert abs(t1) <= 1e-6
t2 = sgd(quad, 0.0, 0.01, 1000, PRINT_EVERY=100)
print("test 2 result:", t2)
assert abs(t2) <= 1e-6
t3 = sgd(quad, -1.5, 0.01, 1000, PRINT_EVERY=100)
print("test 3 result:", t3)
assert abs(t3) <= 1e-6
#print ""
if __name__ == "__main__":
sanity_check();
# your_sanity_checks();
