计算方法:列主元消去法,LU分解法, 雅可比迭代法,高斯塞德尔迭代法 解线性方程(C++)
Matrix.h包括矩阵类Matrix的定义,Matrix.cpp包括该类成员函数的实现,LinearEqu.h包括线性方程类LinearEqu的定义,继承自Matrix类,其中solve()方法为列主元消去法的具体步骤,LU()方法为LU分解法的具体步骤。
Matrix.h(矩阵类头文件):
//矩阵
class Matrix
{
public:
Matrix(int size = 2);
virtual ~Matrix();
void setMatrix(const double* values); //矩阵赋初值
void displayMatrix() const; //输出矩阵
int getSize() const {return size;} //矩阵大小
double &element(int i, int j) {return elements[i * size + j];}
double element(int i, int j) const {return elements[i * size + j];}
private:
int size;
double* elements;
};
Matrix.cpp(矩阵类方法实现):
#include "Matrix.h"
#include
using namespace std;
Matrix::Matrix(int size) : size(size){
elements = new double[size * size];
}
Matrix::~Matrix(){
delete[] elements;
}
//设置矩阵
void Matrix::setMatrix(const double* values)
{
for(int i = 0; i < size * size; i++)
elements[i] = values[i]; //矩阵元素赋值
}
//显示矩阵
void Matrix::displayMatrix() const{
cout << "The matrix is:" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++)
cout << element(i, j) << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
}
LinearEqu.h(线性方程类头文件):
#include "Matrix.h"
//线性方程
class LinearEqu : public Matrix
{
public:
LinearEqu(int size = 2);
virtual ~LinearEqu();
void setLinearEqu(const double* a, const double* b); //方程赋值
bool solve(); //列主元消去法
bool LU(); //LU分解法
void displayLinearEqu() const; //显示方程
void displaySolution() const; //显示方程的解
private:
double* sums; //方程右端
double* solution; //方程的解s
};
LinearEqu.cpp(线性方程类方法实现):
// LinearEqu.cpp: implementation of the LinearEqu class.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "LinearEqu.h"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Construction/Destruction
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
LinearEqu::LinearEqu(int size) : Matrix(size)
{
sums = new double[size];
solution = new double[size];
}
LinearEqu::~LinearEqu()
{
delete[] sums;
delete[] solution;
}
void LinearEqu::setLinearEqu(const double* a, const double* b){
setMatrix(a);
for(int i = 0; i < this->getSize(); i++)
sums[i] = b[i];
}
void LinearEqu::displayLinearEqu() const{
cout << "The Linear equation is:" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < this->getSize(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < this->getSize(); j++)
cout << element(i, j) << "\t";
cout << sums[i] << endl;
}
}
void LinearEqu::displaySolution() const{
cout << "The Result is:" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < this->getSize(); i++)
cout << "x[" << i << "] = " << solution[i] << endl;
}
//交换
inline void swap(double &v1, double &v2){
double temp = v1;
v1 = v2;
v2 = temp;
}
//列主元消去法
bool LinearEqu::solve(){
int n = this->getSize();
for(int k = 0; k < n - 1; k++){
int is;
double max = 0;
for(int i = k, j = k; i < n; i++){
double t = fabs(element(i, j));
if(t > max){
max = t;
is = i;
}
}
if(max == 0){
return false;
}
//交换行
else{
if(is != k){
for(int j = k; j < n; j++)
swap(element(k, j), element(is, j));
swap(sums[k], sums[is]);
}
}
//消去
double major = element(k, k);
for(i = k + 1; i < n; i++){
double m = element(i, k) / major;
for(int j = k; j < n; j++){
element(i, j) -= element(k, j) * m;
}
sums[i] -= sums[k] * m;
}
}
//判断剩下的一个元素是否为0
double d = element(n - 1, n - 1);
if(fabs(d) < 1e-15){
return false;
}
//回代过程
solution[n - 1] = sums[n - 1] / d;
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--){
double t = 0.0;
for(int j = i + 1; j <= n - 1; j++)
t += element(i, j) * solution[j];
solution[i] = (sums[i] - t)/element(i, i);
}
return true;
}
//LU分解法
bool LinearEqu::LU(){
int n = this->getSize();
vector > L(n ,vector(n));
vector > U(n ,vector(n));
//U第一行赋值
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
U[0][i] = element(0, i);
//L第一列赋值
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
L[j][0] = element(j, 0) / U[0][0];
//剩余赋值
for(i = 1; i < n; i++){
for(j = i; j < n; j++){
double sum1 = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < i; k++)
sum1 += L[i][k] * U[k][j];
U[i][j] = element(i, j) - sum1;
}
for(j = i+1; j < n; j++){
double sum2 = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < i; k++)
sum2 += L[j][k] * U[k][i];
L[j][i] = (element(j, i) - sum2) / U[i][i];
}
}
vector Y(n);
Y[0] = sums[0];
for (i = 1; i= 0; i--)
{
double sum4 = 0;
for (int k = i + 1; kgetSize();
int i,j;
vector x1(n);
vector x2(n);
vector b(n);
vector > a(n ,vector(n));
double sum, max=INT_MAX, eps=1e-5, count=0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
b[i] = sums[i] / element(i, i);
for(j = 0; j < n; j++){
a[i][j] = - element(i, j) / element(i, i);
}
a[i][i] = 0;
}
while(max > eps){
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
sum = 0;
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum += a[i][j] * x1[j];
x2[i] = sum + b[i];
solution[i] = x2[i];
}
max = fabs(x1[0] - x2[0]);
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
if(max < fabs(x1[i] - x2[i]))
max = fabs(x1[i] - x2[i]);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
x1[i] = x2[i];
}
count++;
}
cout << "经过" << count << "次迭代" << endl;
return true;
}
//高斯塞德尔迭代法
bool LinearEqu::GS()
{
int n = this->getSize();
int i,j,k;
vector x1(n);
vector x2(n);
vector b(n);
vector > a(n ,vector(n));
double sum, max=INT_MAX, eps=1e-5, count=0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
b[i] = sums[i] / element(i, i);
for(j = 0; j < n; j++){
a[i][j] = - element(i, j) / element(i, i);
}
a[i][i] = 0;
}
while(max > eps){
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
sum = 0;
for(j = 0; j < i; j++){
sum += a[i][j] * x2[j];
}
for(k = j; k < n; k++){
sum += a[i][k] * x1[k];
}
x2[i] = sum + b[i];
solution[i] = x2[i];
}
max = fabs(x1[0] - x2[0]);
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
if(max < fabs(x1[i] - x2[i]))
max = fabs(x1[i] - x2[i]);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
x1[i] = x2[i];
}
count++;
}
cout << "经过" << count << "次迭代" << endl;
return true;
}
Main.cpp(主函数):
// 列主元消去.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "LinearEqu.h"
#include
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
double a[] = {
12, -3, 3,
-18, 3, -1,
1, 1, 1};
double b[] = {15, -15, 6}; //方程右端
LinearEqu equ(3);
equ.setLinearEqu(a,b);
equ.displayLinearEqu();
cout << endl;
//列主元消去法:
cout << "列主元消去法:" << endl;
if(equ.solve())
equ.displaySolution();
else
cout << "Fail" << endl;
cout << endl;
//LU分解法
cout << "LU分解法:" << endl;
if(equ.LU())
equ.displaySolution();
else
cout << "Fail" << endl;
cout << endl;
double c[] = {
10, -1, -2,
-1, 10, -2,
-1, -1, 5};
double d[] = {72, 83, 42};
LinearEqu equ2(3);
equ2.setLinearEqu(c,d);
equ2.displayLinearEqu();
cout << endl;
//雅可比迭代法
cout << "雅可比迭代法:" << endl;
if(equ2.Jacobi())
equ2.displaySolution();
else
cout << "Fail" << endl;
cout << endl;
//高斯塞德尔迭代法
cout << "高斯塞德尔迭代法:" << endl;
if(equ2.GS())
equ2.displaySolution();
else
cout << "Fail" << endl;
return 0;
}
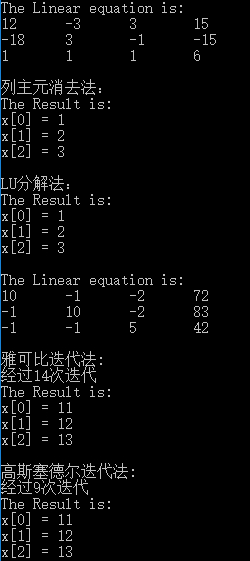
运行结果: