dp中滚动数组的应用:01背包、POJ 1159 Palindrome、多段图路径问题
滚动数组用于对空间复杂度的优化,并不能减少程序时间复杂度。
1.朴素的0-1背包问题:
d[i][j]表示将前i个物品放入容量为j的背包的最大价值。
首先给出一般方法:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=50,maxv=100;
int v,w,n,d[maxn][maxv],V;
/*Sample input:
5 12
2 3
4 8
1 2
3 5
5 11
Sample output:
6
*/
int main(){
while(cin>>n>>V){
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>w>>v;
for(int j=V;j>=v;j--)
d[i][j]=max(d[i-1][j],d[i-1][j-v]+w);
}
cout< 使用滚动数组后的循环体与结果输出:
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>w>>v;
for(int j=V;j>=v;j--)
d[j]=max(d[j],d[j-v]+w);
}
cout<2.POJ 1159 Palindrome
未优化(MLE):
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5010;
int N,d[maxn][maxn];
char s[maxn];
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d",&N)){
scanf("%s",s+1);
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
for(int i=N;i>=1;i--)
for(int j=i+1;j<=N;j++){
if(s[i]==s[j]) d[i][j]=d[i+1][j-1];
else d[i][j]=min(d[i+1][j],d[i][j-1])+1;
}
printf("%d\n",d[1][N]);
}
return 0;
}
使用滚动数组:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5010;
int N,d[2][maxn];
char s[maxn];
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d",&N)){
scanf("%s",s+1);
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
int cur=0;
for(int i=N;i>=1;i--){
cur^=1;
for(int j=i+1;j<=N;j++){
if(s[i]==s[j]) d[cur][j]=d[1-cur][j-1];
else d[cur][j]=min(d[1-cur][j],d[cur][j-1])+1;
}
}
printf("%d\n",d[cur][N]);
}
return 0;
}
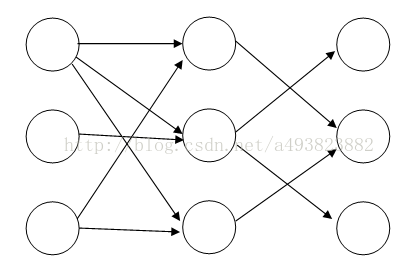
3.多段路径问题
有如图的有向图,从左到右共有n个节点,从上到下有m个节点,给出有向边,求出到达最后一列各点的路径总数。
(上图即程序中样例对应的有向图)
首先给出朴素算法:
d[i][j]:到达第i列,第j行节点的路径总数
a[i][j][k]:第i列,第j行节点所连接的第i+1列的节点的行标号
#include
using namespace std;
int m,n,d[50][50],a[50][50][50];
/*sample input:
3 3
3 1 2 3
1 2
2 1 3
1 2
2 1 3
1 2
sample answer:
(a=1) 2
(a=2) 4
(a=3) 2
*/
int main(){
while(cin>>m>>n){
// int cur=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
int cnt;
cin>>cnt;
for(int k=1;k<=cnt;k++) cin>>a[i][j][k];
a[i][j][0]=cnt;
}
cout<<"end"<>a) cout< 然后给出使用滚动数组优化的循环体与结果输出:
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) d[0][j]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
cur^=1;
memset(d[cur],0,sizeof(d[cur]));
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
for(int k=1;k<=a[i][j][0];k++)
d[cur][a[i][j][k]]+=d[1-cur][j];
}
int a;
while(cin>>a) cout<在每次对于列的枚举循环(i的for循环)中,改变当前cur值。
其中对于d数组,标号为cur的表示当前列的各节点的d值,即对应与第i+1列,标号为1-cur的表示上一列各节点d值,即第i列。
注意每次需要将当前cur的d值清空。
此问题与0-1背包不同的是,后者是一维的问题,只需要使用前一个状态的一个值,而本问题是二维的,需要计算各个j的d值,而计算它们还需用到上个状态的各j的值,若直接覆盖则会丢失数据。故需要用到标记cur保存上一个状态的信息。
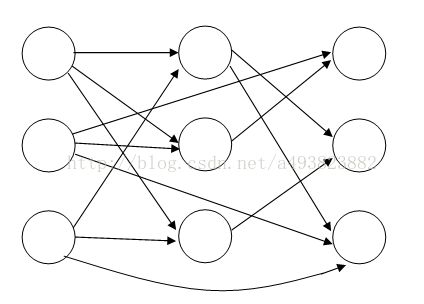
4.需要前两个状态的多段图问题
问题2的变形,即对于第i列节点,i-1、i-2列的节点均可到达。(上图为下面程序中样例对应的有向图)
a[i][j][k][t]:第i列,第j行节点所连接的列的节点的行标号,当t=0,表示连接第i+1列,当t=1表示连接第i+2列。
直接给出使用滚动数组的代码:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=55;
int n,m,a[maxn][maxn][maxn][2],d[3][maxn];
/*Sample Input:
3 3
3 1 2 3
0
1 2
2 1 3
2 1 3
1 3
2 2 3
0
1 1
0
1 2
0
Sample output:
3 (a==1)
4 (a==2)
4 (a==3)
*/
int main(){
while(cin>>n>>m){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
for(int t=0;t<2;t++){
int temp;
cin>>temp;
for(int k=1;k<=temp;k++) cin>>a[i][j][k][t];
a[i][j][0][t]=temp;
}
cout<<"end"<>a) cout< 可以看到若需要前两个状态,则需要3个cur值,cur值应不断模3增加。