SpringBoot学习笔记(3) Spring Boot 运行原理,自动配置
启动流程
我们可以先看看这段代码发生了什么事情
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);

在创建SpringApplication的时候初始化了一些ApplicationContext和ApplicationListener
主要通过getSpringFactoriesInstances方法来实现

上面的SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法看这里

下面我们可以查看下spring.factories文件,spring-boot-autoconfigure和 spring-boot的jar包中都有
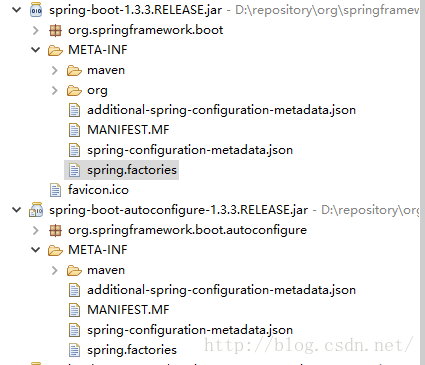
我们可以先看看Spring-boot里面的文件

当SpringApplication创建,初始化了上述的 Application Context和Application Listeners

通过spring.factories文件拿到一系列的Context和Listener之后 执行run方法
run方法会从spring.factories文件中获取到run listener,然后在spirng boot 执行到各个阶段时执行Listener事件和Context事件
所以,所谓的SpringApplicationRunListeners实际上就是在SpringApplication对象的run方法执行的不同阶段,去执行一些操作,并且这些操作是可配置的。
Spring boot总共有这些事件类型

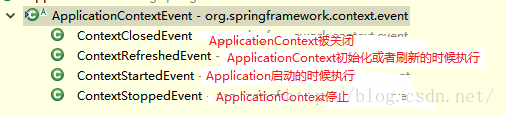
Spring 事件体系
http://blog.csdn.net/caihaijiang/article/details/7460888

看下createAndRefreshContext方法

applyInitializers方法其中
DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer读取context.initializer.classes配置,这些类都是实现了ApplicationContextInitializer接口的类,读取之后执行initialize方法,所以我们在这里可以自己扩展一些东西
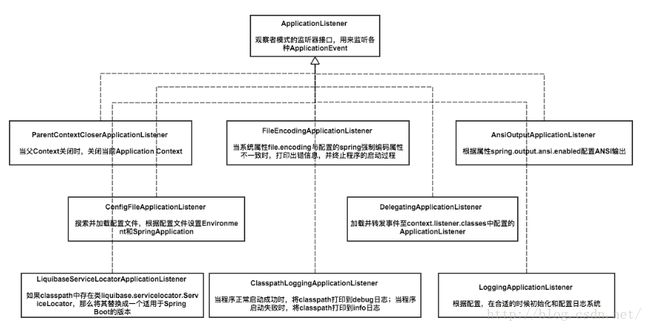
这里有一些listener和context的功能图

这里面代码看的晕乎乎的,都不知道理解的对不对,希望不会对你们产生误导
参考资料
http://blog.csdn.net/liaokailin/article/category/5765237
http://zhaox.github.io/java/2016/03/22/spring-boot-start-flow
http://blog.csdn.net/u011179993/article/details/51475732
自动配置
Spring Boot关于自动配置的源码在spring-boot-autoconfigure中.

上面的这些东西主要是靠condition包下面的注解来根据不同的条件自动创建Bean的

这些注解都是组合了@Conditional元注解,只是使用了不同的条件
我们可以查看下@ConditionalOnWebApplication这个注解

这个注解使用的条件是OnWebApplicationCondition这个类
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.StandardServletEnvironment;
/**
* {@link Condition} that checks for the presence or absence of
* {@link WebApplicationContext}.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @see ConditionalOnWebApplication
* @see ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
*/
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 20)
class OnWebApplicationCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
private static final String WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context."
+ "support.GenericWebApplicationContext";
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
boolean webApplicationRequired = metadata
.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnWebApplication.class.getName());
//判断是否是web环境,并获取结果
ConditionOutcome webApplication = isWebApplication(context, metadata);
if (webApplicationRequired && !webApplication.isMatch()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(webApplication.getMessage());
}
if (!webApplicationRequired && webApplication.isMatch()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(webApplication.getMessage());
}
return ConditionOutcome.match(webApplication.getMessage());
}
private ConditionOutcome isWebApplication(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//判断GenericWebApplicationContext是否在类路径中
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS, context.getClassLoader())) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch("web application classes not found");
}
//容器中是否有名为session的scope
if (context.getBeanFactory() != null) {
String[] scopes = context.getBeanFactory().getRegisteredScopeNames();
if (ObjectUtils.containsElement(scopes, "session")) {
return ConditionOutcome.match("found web application 'session' scope");
}
}
//当前容器的enviroment是否为StandardServletEnviroment
if (context.getEnvironment() instanceof StandardServletEnvironment) {
return ConditionOutcome
.match("found web application StandardServletEnvironment");
}
//当前容器的resourceLoader是否是WebApplicationContext
if (context.getResourceLoader() instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
return ConditionOutcome.match("found web application WebApplicationContext");
}
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch("not a web application");
}
}最终通过ConditionOutcome返回是否web项目,还有判断结果
自定义starter pom
自己实现一个简单的例子,当某个类存在的时候,自动配置这个Bean,并且可以讲这个属性在application.properties中配置
新建一个maven项目
Pom.xml
4.0.0
com.ibigsea
spring-boot-starter-hello
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
jar
spring-boot-starter-hello
http://maven.apache.org
UTF-8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-autoconfigure
1.3.3.RELEASE
Hello.java
package com.ibigsea.spring_boot_starter_hello;
/**
* 通过application.properties的hello.msg来配置,默认为world
* @author bigsea
*
*/
public class Hello {
private String msg;
public String sayHello() {
return "hello " + msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}HelloProperties.java
package com.ibigsea.spring_boot_starter_hello;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* 属性配置,Spring boot 自身的自动配置
* @author bigsea
*
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private static final String MSG = "world";
private String msg = MSG ;
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}HelloAutoConfiguration.java
package com.ibigsea.spring_boot_starter_hello;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)//开启属性注入,通过@autowired注入
@ConditionalOnClass(Hello.class)//判断这个类是否在classpath中存在
//当设置hello=enabled的情况下,如果没有设置则默认为true,即条件符合
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix="hello", value="enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class HelloAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean//使用java配置方式配置这个类
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(Hello.class)//容器中如果没有Hello这个类,那么自动配置这个Hello
public Hello hello() {
Hello hello = new Hello();
hello.setMsg(helloProperties.getMsg());
return hello;
}
}并且要添加spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.ibigsea.spring_boot_starter_hello.HelloAutoConfiguration整个项目结构

好了,到这里我们就完成了一个starter项目了,下面自己测试下
Pom.xml
4.0.0
com.ibigsea
test-starter
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
jar
test-starter
http://maven.apache.org
UTF-8
1.3.3.RELEASE
com.ibigsea
spring-boot-starter-hello
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
${boot.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
${boot.version}
test
App.java
package com.ibigsea.test_starter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.ibigsea.spring_boot_starter_hello.Hello;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class App {
@Autowired
private Hello hello;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index() {
return hello.sayHello();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}application.properties
hello.msg=bigsea运行结果

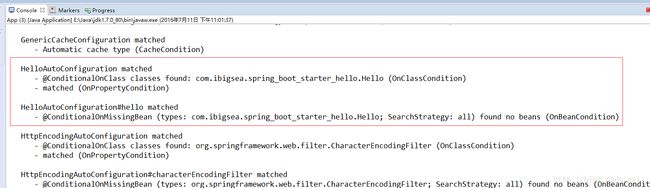
开启dubug模式 可以看到自动配置信息