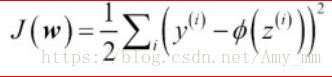Adaptive linear neurons model 线性神经元 运用梯度下降法 进行代价函数的最优化
Minimizing cost functions with gradient descent
【梯度下降法】
将平方误差的和作为代价函数J(w)( cost function )
利用梯度下降法最优化cost function
J(w)对于w求偏导:
所以 w更新为
代码中即 : self.w_[1:] += self.eta * (X.T).dot(y - output) output = X 点乘 W
权值w更新 = eta(learning rate ) * X点乘(y - X点乘W)
【python 实现 线性神经元】
源码 GIT地址:
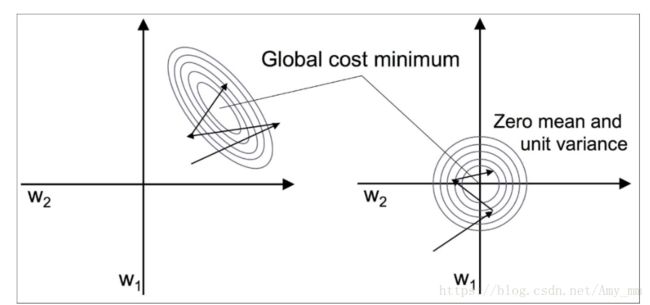
【feature scaling 改善梯度下降法】
将数据进行标准化,变形为标准正态分布,使得梯度下降收敛更快
能够用较少的步数找到最优解(成本函数的最小值)
git地址 :https://github.com/xuman-Amy/Perceptron_python/blob/master/Adaline_python.py
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = pd.read_csv("G:\Machine Learning\python machine learning\python machine learning code\code\ch02\iris.data",header = None)
# select setosa and versicolor
y = df.iloc[0:100, 4].values
y = np.where(y == 'Iris-setosa', -1, 1)
# extract sepal length and petal length
X = df.iloc[0:100, [0, 2]].values
class AdalineGD(object): #线性神经元 梯度递减
class AdalineGD(object):
"""
ADAptive LInear NEuron classifier.
------------
eta : float #学习率
Learning rate (between 0.0 and 1.0)
n_iter : int #迭代次数
Passes over the training dataset.
random_state : int #随机数生成器参数
Random number generator seed for random weight initialization.
Attributes
-----------
w_ : 1d-array #权重
Weights after fitting.
cost_ : list #平方误差
Sum-of-squares cost function value in each epoch.
"""
# 参数初始化
def __init__(self, eta=0.01, n_iter=50, random_state=1):
self.eta = eta
self.n_iter = n_iter
self.random_state = random_state
# 拟合数据 进行权值更新 计算错误率
def fit(self,X,y):
'''
""" Fit training data.
Parameters
----------
X : {array-like}, shape = [n_samples, n_features]
Training vectors, where n_samples is the number of samples and
n_features is the number of features.
X:要进行拟合的输入数据集,有n_sample个样本,每个样本有n_feature个特征值
例如 X = ([1,2,3],[4,5,6]) [1,2,3]为类别+1,[4,5,6]为类别-1
y : array-like, shape = [n_samples]
Target values.
y:输出数据分类,{+1,-1}
Returns
-------
self : object
"""
'''
rgen = np.random.RandomState(self.random_state)
#将偏置b并入到w矩阵,所以大小为X行数加1 X.shape[1]代表行数,即样本个数
self.w_ = rgen.normal(loc = 0.0, scale = 0.01, size = 1+ X.shape[1])
self.cost_ = []
for i in range(self.n_iter):
#在这个代码中activation函数可以不用,写上它只是为了代码的通用性,
#比如logistic代码中可以更改为sigmod函数
net_input = self.net_input(X)
output = self.activation(net_input)
errors = (y - output)
#更新原理见博客 https://mp.csdn.net/postedit/79668201
self.w_[1:] += self.eta * (X.T).dot(errors)
self.w_[0] += self.eta * errors.sum()
cost = (errors ** 2 ).sum() / 2 #平方误差的总和 Sum of Squred Errors
self.cost_.append(cost)
return self
# 净输入 X点乘W
def net_input(self, X):
return np.dot(X,self.w_[1:]) + self.w_[0]
#在本代码中 activation没有意义 是为了以后logistic中可以用到
def activation(self, X):
return X
#预测函数
def predict(self, X):
return np.where(self.activation(self.net_input(X)) >= 0.0,1,-1 )
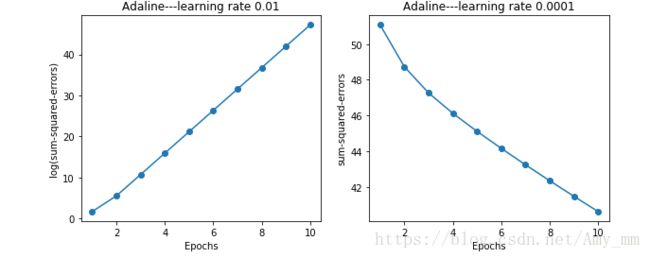
#不同的eta对应的不同迭代次数的收敛性
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows = 1,ncols = 2,figsize = (10,4))
ada1 = AdalineGD(n_iter = 10, eta = 0.1).fit(X,y)
#ax[0].plot(range(1, len(ada1.cost_) + 1),np.log10(ada1.cost_),marker = 'o')
ax[0].plot(range(1, len(ada1.cost_) + 1), np.log10(ada1.cost_), marker='o')
ax[0].set_xlabel("Epochs")
ax[0].set_ylabel("log(sum-squared-errors)")
ax[0].set_title("Adaline---learning rate 0.01")
ada2 = AdalineGD(n_iter = 10, eta = 0.0001).fit(X,y)
ax[1].plot(range(1, len(ada2.cost_) + 1),ada2.cost_, marker = 'o')
ax[1].set_xlabel("Epochs")
ax[1].set_ylabel("sum-squared-errors")
ax[1].set_title("Adaline---learning rate 0.0001")
plt.show()
【画超平面】
X_std = np.copy(X)
#进行标准正态化
X_std [:, 0] = (X_std[:, 0] - X_std[:, 0].mean()) / X[:, 0].std()
X_std [:, 1] = (X_std[:, 1] - X_std[:, 1].mean()) / X[:, 1].std()from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
#画超平面
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, resolution=0.02):
#具体函数 在博文(一)中有记录 博文地址http://blog.csdn.net/Amy_mm/article/details/79625288
markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# plot the decision surface 画分离超平面
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
#生成间隔为resolution的网格
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
#调用感知机分类函数进行预测
#np.array([xx1.ravel(),xx2.ravel()]).T 为*行两列的矩阵,对应二维平面上xx1,xx2行程的网格点
#对这些网格点进行分类为+1,-1,
#画出等高线,+1类画一种颜色,-1另一种
Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(),xx2.ravel()]).T)
Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape)
#contour()函数(一)中有记录
plt.contourf(xx1,xx2,Z,alpha = 0.3,cmap = cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(),xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(),xx2.max())
# plot class samples 画出样本点
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(x = X[y == cl, 0],
y = X[y == cl, 1],
alpha = 0.8,
c = colors[idx],
marker = markers[idx],
label = cl,
edgecolor = 'black')
ada = AdalineGD(n_iter = 15, eta = 0.01)
ada.fit(X_std,y)
plot_decision_regions(X_std,y,ada)
plt.title('Adaline - Stochastic Gradient Descent')
plt.xlabel('sepal length [standardized]')
plt.ylabel('petal length [standardized]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('images/02_15_2.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
plt.plot(range(1,len(ada.cost_) + 1),ada.cost_,marker = 'o')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Average Cost')
#
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('images/02_15_2.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
【随机梯度递减】
class AdalineSGD(object):
def __init__(self, n_iter = 10, eta = 0.1, shuffle = True, random_state = None):
self.eta = eta
self.n_iter = n_iter
self.w_initialized = False
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.random_state = random_state
def fit (self,X,y):
self._initialize_weights(X.shape[1])
self.cost_ = []
for i in range(self.n_iter):
if self.shuffle:
X, y = self._shuffle(X, y)
cost = []
for xi, target in zip(X, y):
cost.append(self._update_weights(xi, target))
avg_cost = sum(cost) / len(y)
self.cost_.append(avg_cost)
return self
# If we want to update our model, for example, in an online learning scenario with
# streaming data, we could simply call the partial_fit method on individual
# samples—for instance ada.partial_fit(X_std[0, :], y[0])
def partial_fit (self,X,y):
#
if not self.w_initialized:
self._initialize_weights(X.shape[1])
if y.ravel().shape[0] > 1 :
for xi, y in zip(X,y):
self._update_weights(xi,targey)
else:
self._update_weights(X, y)
return self
def _shuffle(self, X, y):
# permutation (x) ---> If x is an integer, randomly permute np.arange(x).
r = self.rgen.permutation(len(y))
#print('X[r]',X[r],'Y[r]',y[r])
return X[r], y[r]
def _initialize_weights(self, m):
#初始化 weight 使得w更小
self.rgen = np.random.RandomState(self.random_state)
self.w_ = self.rgen.normal(loc = 0.0, scale = 0.01, size = m + 1)
self.w_initialized = True
def _update_weights(self, xi, target):
#运用线性神经元更新w
output = self.activation(self.net_input(xi))
error = (target - output)
self.w_[1:] += self.eta * xi.dot(error)
self.w_[0] += self.eta * error
cost = error ** 2 / 2
return cost
def net_input(self, X):
"""Calculate net input"""
return np.dot(X, self.w_[1:]) + self.w_[0]
def activation(self,X):
return X
def predict(self, X):
return np.where(self.activation(self.net_input(X)) >= 0.0, 1, -1)
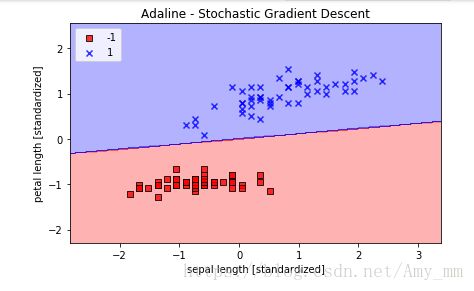
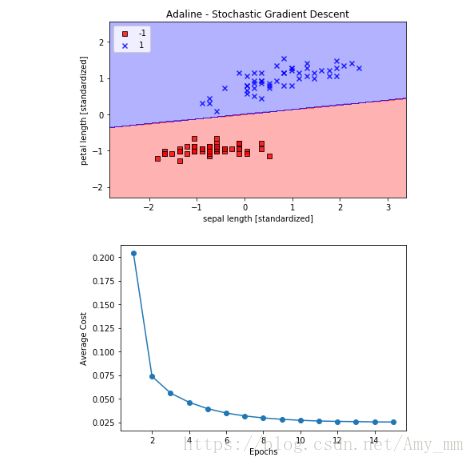
ada = AdalineSGD(n_iter=15, eta=0.01, random_state=1)
ada.fit(X_std, y)
plot_decision_regions(X_std, y, classifier=ada)
plt.title('Adaline - Stochastic Gradient Descent')
plt.xlabel('sepal length [standardized]')
plt.ylabel('petal length [standardized]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('images/02_15_1.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
plt.plot(range(1, len(ada.cost_) + 1), ada.cost_, marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Average Cost')
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('images/02_15_2.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()