使用Vagrant快速搭建Linux环境
什么是Vagrant
我们知道,如果要在Windows系统下搭建Linux开发环境的话,一种选择是安装虚拟机软件,通过其虚拟出想要的系统。而Vagrant就是用来管理这种虚拟系统的第三方工具,通过简单的几句命令行,就可以快速的安装系统,同时,通过配置文件还可以管理网络、共享文件夹等内容。
更为重要的是,当配置好这个系统之后,还可以将这个系统进行打包,分享给他人使用。
准备工作
要使用Vagrant这个工具,首先需要安装一个虚拟机软件,常见的虚拟机软件包括了virtualbox和VMware,但后者是要收费的,不建议使用,优选选择virtualbox。
关于virtulbox和Vagrant的安装工具,这里就不具体介绍,注意在安装完之后,为了方便使用,需要将vagrant添加到“Path”环境变量中。
使用Vagrant
添加box
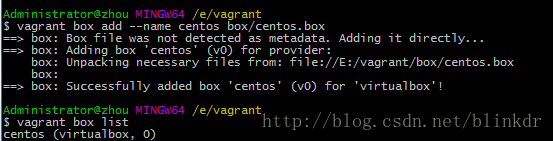
首先,安装Linux系统必不可少的是它的系统文件,而这个文件最好从网上下载到本地,可以从box镜像源进行选择下载。由于某种原因,最好使用科学上网的方法,不然会下载不动的。
在E盘下(根据自己情况)新建”vagrant”文件夹,在其目录下新建”box”文件夹,并将下载好的box文件”centos.box”放在”box”文件夹。
cd vagrant //进到vagrant文件夹
vagrant box add --name centos box\centos.box
//--name指定box的系统名称,在Vagrant的配置文件中将会使用到
而使用命令
vagrant box list
配置Vagrantfile
在系统启动之前,需要进行配置,使用命令
vagrant init centos
对”centos”进行初始,在”vagrant”目录下会生成Vagrantfile文件,文件的内容如下
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
# All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure
# configures the configuration version (we support older styles for
# backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what
# you're doing.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
# boxes at https://atlas.hashicorp.com/search.
config.vm.box = "centos"
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
# using a specific IP.
# config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
# your network.
# config.vm.network "public_network"
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
# argument is a set of non-required options.
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
# Provider-specific configuration so you can fine-tune various
# backing providers for Vagrant. These expose provider-specific options.
# Example for VirtualBox:
#
# config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
# vb.gui = true
#
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
# vb.memory = "1024"
# end
#
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
# information on available options.
# Define a Vagrant Push strategy for pushing to Atlas. Other push strategies
# such as FTP and Heroku are also available. See the documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com/v2/push/atlas.html for more information.
# config.push.define "atlas" do |push|
# push.app = "YOUR_ATLAS_USERNAME/YOUR_APPLICATION_NAME"
# end
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
# Puppet, Chef, Ansible, Salt, and Docker are also available. Please see the
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
# apt-get update
# apt-get install -y apache2
# SHELL
end可以看到对于常用的配置,这个文件都有列出,并进行了解释。这里对某些配置做简单介绍。
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| # 配置开始
config.vm.box = "centos" # 对系统'centos'的配置
# 网络设置
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# 这里是进行端口转发,host: 8080 --> guest: 80
config.vm.network "public_network"
# 配置成公共网络,就像实际存在的物理电脑一致,IP地址将有网络中的路由器分配
# 同步共享文件夹
config.vm.synced_folder "./data", "/home/vagrant"
# 这里配置两个文件夹,前一个是本地文件夹,后一个是centos系统下的文件夹
# 因此需要在"vagrant"目录下新建"data"文件夹
# 显示和内存设置
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb| # 这里指定虚拟机软件virtualbox
vb.gui = false # 是否显示gui
vb.memory = "1024" # 虚拟机内存设置
end
end # 配置结束
以上就是单个虚拟机的配置,使用命令
vagrant up
同样,Vagrantfile可以配置多虚拟机启动,其大致机构如下
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# 虚拟机centos
config.vm.define :centos do |centos|
centos.vm.box="centos"
centos.vm.network "public_network"
end
# 虚拟机ubuntu
config.vm.define :ubuntu do |ubuntu|
ubuntu.vm.box="ubuntu"
end
end
这样的话在启动时,可以指定虚拟机启动,比如
vagrant up centos
可以只启动centos系统,不指定的话,会启动全部的虚拟机。
更多的配置选项,可以参考中文文档进行更多的配置学习。
登录系统
在成功系统之后,输入命令
vagrant ssh
user: vagrant
passwd: vagrant //管理员密码也是这个
使用命令
ip addr
获取虚拟机的IP地址,如图
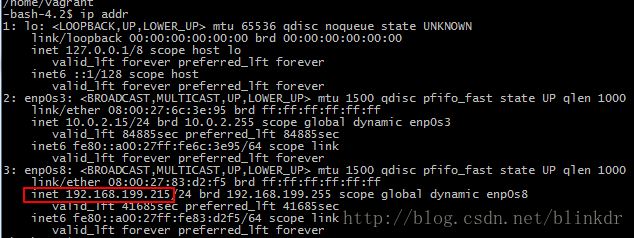
可以看到虚拟在局域网中的地址为”192.168.199.215”,使用该地址,我们也可以从局域网中的其他电脑进行登录,如图
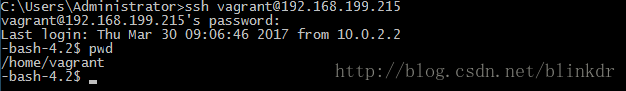
关于文件共享就更简单了,之前我们配置了
config.vm.synced_folder "./data", "/home/vagrant"
在登录之后,进行一下测试
cd ~
pwd
touch guset.txt
因此,我们可以在Windows系统下选用自己喜欢的编辑器对文件进行编辑,而且能够快速地部署到Linux系统下。
系统打包
如果想要分享你配置好了的Linux系统,这时需要将该系统进行打包,打包前需要将虚拟机关闭,使用命令
vagrant halt
将虚拟机关机。使用命令
vagrant package
对系统进行打包,如图
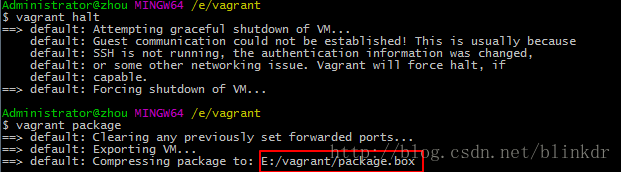
在”vagrant”目录下多了一个.box文件,如图

总结
使用Vagrant可以方便管理和配置虚拟机系统,关于更多的用法可以参考Vagrant官网文档或者中文文档。
还有,关于Vagrantfile文件最好使用git进行管理,方便学习使用。