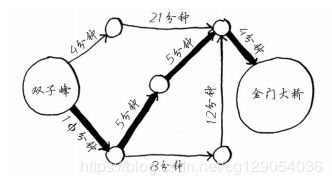
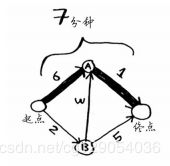
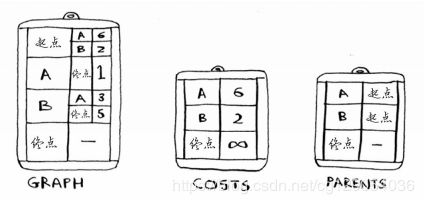
- C++ 11 Lambda表达式和min_element()与max_element()的使用_c++ lamda函数 min_element((1)
2401_84976182
程序员c语言c++学习
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上CC++开发知识点,真正体系化!由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新如果你需要这些资料,可以戳这里获取#include#include#includeusingnamespacestd;boolcmp(int
- 算法学习笔记:17.蒙特卡洛算法 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
在计算机科学和数学领域,蒙特卡洛算法(MonteCarloAlgorithm)以其独特的随机抽样思想,成为解决复杂问题的有力工具。从圆周率的计算到金融风险评估,从物理模拟到人工智能,蒙特卡洛算法都发挥着不可替代的作用。本文将深入剖析蒙特卡洛算法的思想、解题思路,结合实际应用场景与Java代码实现,并融入考研408的相关考点,穿插图片辅助理解,帮助你全面掌握这一重要算法。蒙特卡洛算法的基本概念蒙特卡
- 分布式学习笔记_04_复制模型
NzuCRAS
分布式学习笔记架构后端
常见复制模型使用复制的目的在分布式系统中,数据通常需要被分布在多台机器上,主要为了达到:拓展性:数据量因读写负载巨大,一台机器无法承载,数据分散在多台机器上仍然可以有效地进行负载均衡,达到灵活的横向拓展高容错&高可用:在分布式系统中单机故障是常态,在单机故障的情况下希望整体系统仍然能够正常工作,这时候就需要数据在多台机器上做冗余,在遇到单机故障时能够让其他机器接管统一的用户体验:如果系统客户端分布
- 算法学习笔记:15.二分查找 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
呆呆企鹅仔
算法学习算法学习笔记考研二分查找
在计算机科学的查找算法中,二分查找以其高效性占据着重要地位。它利用数据的有序性,通过不断缩小查找范围,将原本需要线性时间的查找过程优化为对数时间,成为处理大规模有序数据查找问题的首选算法。二分查找的基本概念二分查找(BinarySearch),又称折半查找,是一种在有序数据集合中查找特定元素的高效算法。其核心原理是:通过不断将查找范围减半,快速定位目标元素。与线性查找逐个遍历元素不同,二分查找依赖
- OKHttp3源码分析——学习笔记
Sincerity_
源码相关Okhttp源码解析读书笔记httpclientcache
文章目录1.HttpClient与HttpUrlConnection的区别2.OKHttp源码分析使用步骤:dispatcher任务调度器,(后面有详细说明)Request请求RealCallAsyncCall3.OKHttp架构分析1.异步请求线程池,Dispather2.连接池清理线程池-ConnectionPool3.缓存整理线程池DisLruCache4.Http2异步事务线程池,http
- Python学习笔记5|条件语句和循环语句
iamecho9
Python从0到1学习笔记python学习笔记
一、条件语句条件语句用于根据不同的条件执行不同的代码块。1、if语句基本语法:if布尔型语句1:代码块#语句1为True时执行的代码示例:age=int(input("请输入你的年龄:"))ifage>=18:print("你已成年")2、if-else语句如果if条件不成立,则执行else代码块:if布尔型语句1:代码块#语句1为True时执行的代码else:代码块#语句1为False时执行的代
- 5G标准学习笔记14 - CSI--RS概述
刘孬孬沉迷学习
5G学习笔记信息与通信
5G标准学习笔记14-CSI–RS概述大家好~,这里是刘孬孬,今天带着大家一起学习一下5GNR中一个非常非常重要的参考信号------------------CSI-RS信号,CSI-RS不是持续发送,UE只能在网络明确配置了CSI-RS的情况下才能使用其进行信道测量。前言对于CSI-RS,肯定还离不开前面所说的CSI(channelstateinformation),前面也讲过CSI对于MIMO
- 5G标准学习笔记06-基于AI/ML波束管理
刘孬孬沉迷学习
5G学习笔记
5G标准学习笔记06-基于AI/ML波束管理前言前面对于孬孬学习了波束管理的概述,下面要进一步来看一下传统波束管理和现在3GPP中推动的AL/ML波束管理之前的区别联系。一、传统波束管理方法流程传统BM流程主要包括以下步骤:波束扫描(BeamSweeping):gNB通过顺序发送多个窄波束(SSB或CSI-RS),覆盖整个服务区域,UE测量每个波束的信号质量(如L1-RSRP或L1-SINR)。波
- 5G标准学习笔记03- CSI 反馈增强概述
刘孬孬沉迷学习
5G笔记学习
5G标准学习笔记03-CSI反馈增强概述大家好,最近在研究AI/ML3gpp标准NR空口的有关内容,后面可能会给大家介绍一下对应的有关内容AI/ML在3GPP标准中的研究进展在AI/ML在NR空口的应用中,对应标准主要聚焦了3个case进行讨论研究分别是:CSI反馈增强;波束管理;定位精度增强;这三个内容可能比较涉及RAN1/2的具体内容,后面会基于这个进行一定的介绍。今天主要是主要介绍CSI反馈
- 学习笔记(33):matplotlib绘制简单图表-绘制混淆矩阵热图
宁儿数据安全
#机器学习学习笔记matplotlib
学习笔记(33):matplotlib绘制简单图表-绘制混淆矩阵热图一、绘制混淆矩阵热图代码解析1.1、导入必要的库importmatplotlib.pyplotaspltfromsklearn.metricsimportconfusion_matriximportseabornassnsmatplotlib.pyplot:Python中最常用的绘图库,用于创建各种图表confusion_matr
- LLaMA 学习笔记
AI算法网奇
深度学习基础人工智能深度学习
目录LLaMA模型结构:模型微调手册:推理示例:指定位置加载模型测试ok:模型下载:llama-stack下载modelscope下载LLaMA优化技术RMSNormSwiGLU激活函数旋转位置编码(RoPE)LLaMA模型结构:llama3结构详解-CSDN博客模型微调手册:大模型微调LLaMA详细指南(准备环境、数据、配置微调参数+微调过程)_llama微调-CSDN博客显存占用:FP16/B
- BOOT_KEY按键(学习笔记)
小高Baby@
学习笔记
先来让我们了解一下GPIO是什么吧,它在单片机中也有很重要的作用,接下来我们来看看吧。esp32C3是QFN32封装(一种集成电路(IC)封装类型),GPIO引脚一共有22个,从GPIO-0到GPIO-21。从理论上来说,所有的IO引脚都可以复用为任何外设功能,但有些引脚用作连接芯片内部FLASH或者外部FLASH功能时,官方不建议用作其它用途。esp32c3的GPIO,可以用作输入、输出,可以配
- 【机器学习笔记Ⅰ】9 特征缩放
巴伦是只猫
机器学习机器学习笔记人工智能
特征缩放(FeatureScaling)详解特征缩放是机器学习数据预处理的关键步骤,旨在将不同特征的数值范围统一到相近的尺度,从而加速模型训练、提升性能并避免某些特征主导模型。1.为什么需要特征缩放?(1)问题背景量纲不一致:例如:特征1:年龄(范围0-100)特征2:收入(范围0-1,000,000)梯度下降的困境:量纲大的特征(如收入)会导致梯度更新方向偏离最优路径,收敛缓慢。量纲小的特征(如
- Kotlin学习笔记
qq_26907861
1.Val和Varval:用于声明不可变量,不可变是指引用不可变;var:用于声明可变的变量;packagehello//可选的包头funmain(args:Array){//包级可见的函数,接受一个字符串数组作为参数vala="不可变的变量"//不可变的变量varn=2//可变println(a)println(n)}2.fun函数Kotlin中的函数可以这样声明:fun函数名(参数列表):返回
- WPF学习笔记(2)——x名称空间详解 上
幽冥宇少
WPFC#WPF学习笔记初学者C#VS2013
先说一些基本的,.NET的模块称为程序集(Assembly)。一般情况下,用VS创建的是解决方案(Solution),一个解决方案就是一个完整的程序。解决方案中包含若干个项目(Project),每个项目是可以独立编译的,他的编译结果是一个程序集。常见的程序集是以.exe为扩展名的可执行程序或者是以.dll为扩展名的动态链接库,大多数情况下,我们说“引用其他程序集”的时候,说的是动态链接库。因为.N
- 初学者的指针学习笔记(1)
近津薪荼
学习笔记
1.内存和地址1.1内存像学生宿舍一样,被分成许多个房间,每个房间都有自己的房号,每个房间能住8个学生内存被分成许多个单元(小为1Byte),每个单元都有自己的编号,每个单元里能住8个小比特(bite)c语言中,指针就是该单元内存的编号也就是地址,我们可以通过指针快速找到我们要访问的内存1.2编址计算机中的内存编址,是通过硬件设计来完成的,也就是说他被做出来的时候各个内存单元的地址就已经确定了。计
- 初学者关于自定义类型结构体的学习笔记
近津薪荼
学习笔记数据结构
1.结构的特殊声明//匿名结构体类型struct{inta;charb;floatc;}x;struct{inta;charb;floatc;}a[20],*p;p=&x;不可取,本质上是两个不同类型的结构体上述代码的声明方式,该结构体类型,如果不重命名的话,只能用一次(声明时顺便创建变量)2.结构体的自引用structNode{intdata;structNodenext;};上述代码,结构体中
- Xilinx系FPGA学习笔记(三)Vivado的仿真及ILA使用
贾saisai
FPGA学习fpga开发学习笔记
系列文章目录文章目录系列文章目录前言仿真验证(类似modelsim)ILA在线调试工具添加ILAILA的例化ILA的使用前言接着学习vivado的使用方法仿真验证(类似modelsim)首先类似添加.v文件的方法,在File-AddSource中选择Addorcreatesimulationsources或者直接在Sources里面选就行然后就编写testbench,类似之前介绍的modelsim
- 学习笔记day1
Linux基础Linux到底是什么?Linux主要指的是内核(主机中的CPU),它也是我们系统的大脑Ubuntu跟Linux的关系:Ubuntu是Linux系统的一个分支。为什么要选⽤Linux?开源的,用户可以根据自己的喜好和需求来定制系统。性免费,企业可以减少开发成本。安全性可移植性高Linux跟我们⽇常使⽤的windows的区别?操作习惯不⼀样:windows是以图形交互为主;Linux操作
- 【机器学习|学习笔记】用 Python 结合 graphviz 生成 ID3、C4.5、CART 三种决策树的结构示意图。
【机器学习|学习笔记】用Python结合graphviz生成ID3、C4.5、CART三种决策树的结构示意图【机器学习|学习笔记】用Python结合graphviz生成ID3、C4.5、CART三种决策树的结构示意图文章目录【机器学习|学习笔记】用Python结合graphviz生成ID3、C4.5、CART三种决策树的结构示意图用Python结合graphviz生成ID3、C4.5、CART三种
- Text2Reward学习笔记
1.提示词请问,“glew”是一个RL工程师常用的工具库吗?请问,thiscodebase主要是做什么用的呀?1.1解释代码是否可以请您根据thiscodebase的主要功能,参考PyTorch的文档格式和文档风格,使用Markdown格式为选中的代码行编写一段相应的文档说明呢?2.项目环境配置2.1新建环境[official]2.1.1Featurizecondacreate-p~/work/d
- pandas学习笔记
kara_486
pandas学习笔记
pandas是python中一个性能强大的数据处理库,能进行复杂的数据处理。pandas的数据结构分为三种类型,分别为series,DataFrame和index,对于初学者而言,series和DataFrame这两种结构最为重要。下面作者将重点介绍series和DataFrame这两部分。series的介绍series按照作者的目前的理解是pandas库中最基础的组成部分,seriers是由索引
- 英语学习笔记2.0
飞升不如收破烂~
学习笔记
✅正确表达:“HowlonghaveyoubeenteachingEnglish?”或者更简单地问:“HowlongdoyouteachEnglish?”(这个句子语法对,但用在现在习惯性的行为上)用法说明:如果你想问:️“你教英语多久了?”✅用现在完成时(表示一段持续的时间):HowlonghaveyoubeenteachingEnglish?️你可以这样试试新的句子:Howlonghaveyo
- C语言笔记
学习笔记仅供参考基础介绍程序就是一组计算机能识别的指令,计算机的一切操作都是由程序控制的。人和计算机都能识别的语言就是就是计算机语言,计算机工作是基于二进制的。计算机能直接识别的二进制代码就是机器指令,机器指令的集合就是机器语言。机器语言与人们习惯使用的语言差别太大,所以人们创造出了符号语言,计算机不能直接识别符号语言的指令,需要汇编程序软件将符号语言指令转成机器指令(二进制代码)。机器语言与汇编
- 黑马程序员_学习笔记2——wpf计算器
马林雷
- WPF学习笔记(27)科学计算器
三千道应用题
C#实例WPF学习笔记wpf
科学计算器1.前端界面2.功能代码1.前端界面2.功能代码usingSystem;usingSystem.Collections.Generic;usingSystem.Linq;usingSystem.Text;usingSystem.Threading.Tasks;usingSystem.Windows;usingSystem.Windows.Controls;usingSystem.Wind
- 【机器学习笔记Ⅰ】10 特征工程
特征工程(FeatureEngineering)详解特征工程是机器学习和数据科学中的核心环节,旨在通过对原始数据的转换、组合和提取,构建更适合模型的高质量特征。其质量直接决定模型性能上限(“数据和特征决定了模型的上限,而算法只是逼近这个上限”)。1.特征工程的核心目标提升模型性能:增强特征与目标变量的相关性。降低计算成本:减少冗余特征,加速训练。改善泛化能力:避免过拟合,提高鲁棒性。2.特征工程的
- Java基础学习笔记2
qichi333
学习笔记javaeclipse
今天是Java基础学习第二天,加油!!!下面是我今天记的一些笔记。(有点懒惰了,爬虫今天没学,因为赖床了(bushi),但我会勤奋起来的^_^,一定一定!明天不能偷懒了天!!)一、运算符例子:inta=10;intb=20;intc=a+b;其中,“+”是运算符,且是算术运算符;“a+b”是表达式,且是算术表达式。1.算术运算符例1:publicclassdemo3{publicstaticvoi
- SystemVerilog LRM 学习笔记 -- clocking块
1clocking...endclocking块clocking块是SV新feature,主要是为了更好解决testbench和DUT之间的timing和同步建模的问题,可以使user基于clockcycle在更高的抽象层次上写testbench(如“##3”,表示三个clock)。clocking只能在module/interface/checker/program中声明,不能在function
- JavaWeb(苍穹外卖)--学习笔记03(登录生成令牌)
老虎0627
JavaWeb(苍穹外卖)学习笔记java
前言本片文章是学习B站黑马程序员苍穹外卖的学习笔记。在Day01(如果学到登录界面这里卡住了,可以看看这篇文章),登陆界面的后端实现大致可以分为两部分登录功能和登录校验,其中登陆校验的实现是基于令牌JWT技术来实现会话追踪(校验部分还有拦截器Interceptor这个我没太学懂视频也没提,以后在更)JWT令牌基本概念JWT是一种在Web应用程序,简单且安全地处理用户身份验证和信息交换的技术,首先我
- 深入浅出Java Annotation(元注解和自定义注解)
Josh_Persistence
Java Annotation元注解自定义注解
一、基本概述
Annontation是Java5开始引入的新特征。中文名称一般叫注解。它提供了一种安全的类似注释的机制,用来将任何的信息或元数据(metadata)与程序元素(类、方法、成员变量等)进行关联。
更通俗的意思是为程序的元素(类、方法、成员变量)加上更直观更明了的说明,这些说明信息是与程序的业务逻辑无关,并且是供指定的工具或
- mysql优化特定类型的查询
annan211
java工作mysql
本节所介绍的查询优化的技巧都是和特定版本相关的,所以对于未来mysql的版本未必适用。
1 优化count查询
对于count这个函数的网上的大部分资料都是错误的或者是理解的都是一知半解的。在做优化之前我们先来看看
真正的count()函数的作用到底是什么。
count()是一个特殊的函数,有两种非常不同的作用,他可以统计某个列值的数量,也可以统计行数。
在统
- MAC下安装多版本JDK和切换几种方式
棋子chessman
jdk
环境:
MAC AIR,OS X 10.10,64位
历史:
过去 Mac 上的 Java 都是由 Apple 自己提供,只支持到 Java 6,并且OS X 10.7 开始系统并不自带(而是可选安装)(原自带的是1.6)。
后来 Apple 加入 OpenJDK 继续支持 Java 6,而 Java 7 将由 Oracle 负责提供。
在终端中输入jav
- javaScript (1)
Array_06
JavaScriptjava浏览器
JavaScript
1、运算符
运算符就是完成操作的一系列符号,它有七类: 赋值运算符(=,+=,-=,*=,/=,%=,<<=,>>=,|=,&=)、算术运算符(+,-,*,/,++,--,%)、比较运算符(>,<,<=,>=,==,===,!=,!==)、逻辑运算符(||,&&,!)、条件运算(?:)、位
- 国内顶级代码分享网站
袁潇含
javajdkoracle.netPHP
现在国内很多开源网站感觉都是为了利益而做的
当然利益是肯定的,否则谁也不会免费的去做网站
&
- Elasticsearch、MongoDB和Hadoop比较
随意而生
mongodbhadoop搜索引擎
IT界在过去几年中出现了一个有趣的现象。很多新的技术出现并立即拥抱了“大数据”。稍微老一点的技术也会将大数据添进自己的特性,避免落大部队太远,我们看到了不同技术之间的边际的模糊化。假如你有诸如Elasticsearch或者Solr这样的搜索引擎,它们存储着JSON文档,MongoDB存着JSON文档,或者一堆JSON文档存放在一个Hadoop集群的HDFS中。你可以使用这三种配
- mac os 系统科研软件总结
张亚雄
mac os
1.1 Microsoft Office for Mac 2011
大客户版,自行搜索。
1.2 Latex (MacTex):
系统环境:https://tug.org/mactex/
&nb
- Maven实战(四)生命周期
AdyZhang
maven
1. 三套生命周期 Maven拥有三套相互独立的生命周期,它们分别为clean,default和site。 每个生命周期包含一些阶段,这些阶段是有顺序的,并且后面的阶段依赖于前面的阶段,用户和Maven最直接的交互方式就是调用这些生命周期阶段。 以clean生命周期为例,它包含的阶段有pre-clean, clean 和 post
- Linux下Jenkins迁移
aijuans
Jenkins
1. 将Jenkins程序目录copy过去 源程序在/export/data/tomcatRoot/ofctest-jenkins.jd.com下面 tar -cvzf jenkins.tar.gz ofctest-jenkins.jd.com &
- request.getInputStream()只能获取一次的问题
ayaoxinchao
requestInputstream
问题:在使用HTTP协议实现应用间接口通信时,服务端读取客户端请求过来的数据,会用到request.getInputStream(),第一次读取的时候可以读取到数据,但是接下来的读取操作都读取不到数据
原因: 1. 一个InputStream对象在被读取完成后,将无法被再次读取,始终返回-1; 2. InputStream并没有实现reset方法(可以重
- 数据库SQL优化大总结之 百万级数据库优化方案
BigBird2012
SQL优化
网上关于SQL优化的教程很多,但是比较杂乱。近日有空整理了一下,写出来跟大家分享一下,其中有错误和不足的地方,还请大家纠正补充。
这篇文章我花费了大量的时间查找资料、修改、排版,希望大家阅读之后,感觉好的话推荐给更多的人,让更多的人看到、纠正以及补充。
1.对查询进行优化,要尽量避免全表扫描,首先应考虑在 where 及 order by 涉及的列上建立索引。
2.应尽量避免在 where
- jsonObject的使用
bijian1013
javajson
在项目中难免会用java处理json格式的数据,因此封装了一个JSONUtil工具类。
JSONUtil.java
package com.bijian.json.study;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
- [Zookeeper学习笔记之六]Zookeeper源代码分析之Zookeeper.WatchRegistration
bit1129
zookeeper
Zookeeper类是Zookeeper提供给用户访问Zookeeper service的主要API,它包含了如下几个内部类
首先分析它的内部类,从WatchRegistration开始,为指定的znode path注册一个Watcher,
/**
* Register a watcher for a particular p
- 【Scala十三】Scala核心七:部分应用函数
bit1129
scala
何为部分应用函数?
Partially applied function: A function that’s used in an expression and that misses some of its arguments.For instance, if function f has type Int => Int => Int, then f and f(1) are p
- Tomcat Error listenerStart 终极大法
ronin47
tomcat
Tomcat报的错太含糊了,什么错都没报出来,只提示了Error listenerStart。为了调试,我们要获得更详细的日志。可以在WEB-INF/classes目录下新建一个文件叫logging.properties,内容如下
Java代码
handlers = org.apache.juli.FileHandler, java.util.logging.ConsoleHa
- 不用加减符号实现加减法
BrokenDreams
实现
今天有群友发了一个问题,要求不用加减符号(包括负号)来实现加减法。
分析一下,先看最简单的情况,假设1+1,按二进制算的话结果是10,可以看到从右往左的第一位变为0,第二位由于进位变为1。
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-状态模式-State
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/*
当一个对象的内在状态改变时允许改变其行为,这个对象看起来像是改变了其类
状态模式主要解决的是当控制一个对象状态的条件表达式过于复杂时的情况
把状态的判断逻辑转移到表示不同状态的一系列类中,可以把复杂的判断逻辑简化
如果在
- CUDA程序block和thread超出硬件允许值时的异常
cherishLC
CUDA
调用CUDA的核函数时指定block 和 thread大小,该大小可以是dim3类型的(三维数组),只用一维时可以是usigned int型的。
以下程序验证了当block或thread大小超出硬件允许值时会产生异常!!!GPU根本不会执行运算!!!
所以验证结果的正确性很重要!!!
在VS中创建CUDA项目会有一个模板,里面有更详细的状态验证。
以下程序在K5000GPU上跑的。
- 诡异的超长时间GC问题定位
chenchao051
jvmcmsGChbaseswap
HBase的GC策略采用PawNew+CMS, 这是大众化的配置,ParNew经常会出现停顿时间特别长的情况,有时候甚至长到令人发指的地步,例如请看如下日志:
2012-10-17T05:54:54.293+0800: 739594.224: [GC 739606.508: [ParNew: 996800K->110720K(996800K), 178.8826900 secs] 3700
- maven环境快速搭建
daizj
安装mavne环境配置
一 下载maven
安装maven之前,要先安装jdk及配置JAVA_HOME环境变量。这个安装和配置java环境不用多说。
maven下载地址:http://maven.apache.org/download.html,目前最新的是这个apache-maven-3.2.5-bin.zip,然后解压在任意位置,最好地址中不要带中文字符,这个做java 的都知道,地址中出现中文会出现很多
- PHP网站安全,避免PHP网站受到攻击的方法
dcj3sjt126com
PHP
对于PHP网站安全主要存在这样几种攻击方式:1、命令注入(Command Injection)2、eval注入(Eval Injection)3、客户端脚本攻击(Script Insertion)4、跨网站脚本攻击(Cross Site Scripting, XSS)5、SQL注入攻击(SQL injection)6、跨网站请求伪造攻击(Cross Site Request Forgerie
- yii中给CGridView设置默认的排序根据时间倒序的方法
dcj3sjt126com
GridView
public function searchWithRelated() {
$criteria = new CDbCriteria;
$criteria->together = true; //without th
- Java集合对象和数组对象的转换
dyy_gusi
java集合
在开发中,我们经常需要将集合对象(List,Set)转换为数组对象,或者将数组对象转换为集合对象。Java提供了相互转换的工具,但是我们使用的时候需要注意,不能乱用滥用。
1、数组对象转换为集合对象
最暴力的方式是new一个集合对象,然后遍历数组,依次将数组中的元素放入到新的集合中,但是这样做显然过
- nginx同一主机部署多个应用
geeksun
nginx
近日有一需求,需要在一台主机上用nginx部署2个php应用,分别是wordpress和wiki,探索了半天,终于部署好了,下面把过程记录下来。
1. 在nginx下创建vhosts目录,用以放置vhost文件。
mkdir vhosts
2. 修改nginx.conf的配置, 在http节点增加下面内容设置,用来包含vhosts里的配置文件
#
- ubuntu添加admin权限的用户账号
hongtoushizi
ubuntuuseradd
ubuntu创建账号的方式通常用到两种:useradd 和adduser . 本人尝试了useradd方法,步骤如下:
1:useradd
使用useradd时,如果后面不加任何参数的话,如:sudo useradd sysadm 创建出来的用户将是默认的三无用户:无home directory ,无密码,无系统shell。
顾应该如下操作:
- 第五章 常用Lua开发库2-JSON库、编码转换、字符串处理
jinnianshilongnian
nginxlua
JSON库
在进行数据传输时JSON格式目前应用广泛,因此从Lua对象与JSON字符串之间相互转换是一个非常常见的功能;目前Lua也有几个JSON库,本人用过cjson、dkjson。其中cjson的语法严格(比如unicode \u0020\u7eaf),要求符合规范否则会解析失败(如\u002),而dkjson相对宽松,当然也可以通过修改cjson的源码来完成
- Spring定时器配置的两种实现方式OpenSymphony Quartz和java Timer详解
yaerfeng1989
timerquartz定时器
原创整理不易,转载请注明出处:Spring定时器配置的两种实现方式OpenSymphony Quartz和java Timer详解
代码下载地址:http://www.zuidaima.com/share/1772648445103104.htm
有两种流行Spring定时器配置:Java的Timer类和OpenSymphony的Quartz。
1.Java Timer定时
首先继承jav
- Linux下df与du两个命令的差别?
pda158
linux
一、df显示文件系统的使用情况,与du比較,就是更全盘化。 最经常使用的就是 df -T,显示文件系统的使用情况并显示文件系统的类型。 举比例如以下: [root@localhost ~]# df -T Filesystem Type &n
- [转]SQLite的工具类 ---- 通过反射把Cursor封装到VO对象
ctfzh
VOandroidsqlite反射Cursor
在写DAO层时,觉得从Cursor里一个一个的取出字段值再装到VO(值对象)里太麻烦了,就写了一个工具类,用到了反射,可以把查询记录的值装到对应的VO里,也可以生成该VO的List。
使用时需要注意:
考虑到Android的性能问题,VO没有使用Setter和Getter,而是直接用public的属性。
表中的字段名需要和VO的属性名一样,要是不一样就得在查询的SQL中
- 该学习笔记用到的Employee表
vipbooks
oraclesql工作
这是我在学习Oracle是用到的Employee表,在该笔记中用到的就是这张表,大家可以用它来学习和练习。
drop table Employee;
-- 员工信息表
create table Employee(
-- 员工编号
EmpNo number(3) primary key,
-- 姓