leetcode 三角形
1.Triangle 三角形
Given a triangle, find the minimum path sum from top to bottom. Each step you may move to adjacent numbers on the row below.
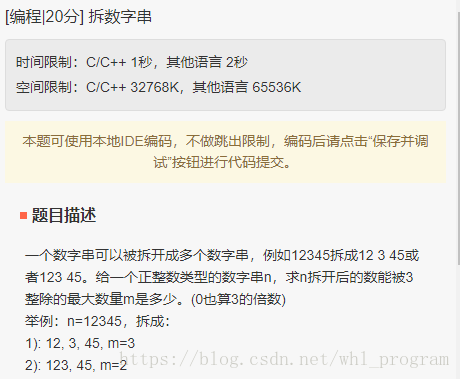
For example, given the following triangle
[
[2],
[3,4],
[6,5,7],
[4,1,8,3]
]
The minimum path sum from top to bottom is 11 (i.e., 2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11).
Note:
Bonus point if you are able to do this using only O(n) extra space, where n is the total number of rows in the triangle.
解决代码,自底向上
解决思路
因为上一层的每个点到下一层都有两种方式,通过反推,由最后一层一直推到第一层。
有递推式
minPath[i] = 当前点值 + min(上一层的左边点值, 上一层的右边点值)
class Solution {
public:
int minimumTotal(vector > &triangle)
{
vector minPath= triangle[triangle.size()-1];
for ( int i = triangle.size() - 2; i>= 0 ; --i )
for ( int j = 0; j < triangle[i].size() ; ++ j )
minPath[j] = triangle[i][j] + min(minPath[j],minPath[j+1]);
return minPath[0];
}
};
2.Decode Ways 解码方法
A message containing letters from A-Z is being encoded to numbers using the following mapping:
'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26
Given an encoded message containing digits, determine the total number of ways to decode it.
For example,
Given encoded message "12", it could be decoded as "AB" (1 2) or "L" (12).
The number of ways decoding "12" is 2.
需要用动态规划Dynamci Programming来解。建立一位dp数组,长度比输入数组长多2,全部初始化为1,因为斐波那契数列的前两项也为1,然后从第三个数开始更新,对应数组的第一个数。对每个数组首先判断其是否为0,若是将改为dp赋0,若不是,赋上一个dp值,此时相当如加上了dp[i - 1], 然后看数组前一位是否存在,如果存在且满足前一位不是0,且和当前为一起组成的两位数不大于26,则当前dp值加上dp[i - 2], 至此可以看出来跟斐波那契数组的递推式一样,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
if (s.empty()) return 0;
vector dp(s.size() + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < dp.size(); ++i) {
if (s[i - 1] != '0') dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
if (i >= 2 && s.substr(i - 2, 2) <= "26" && s.substr(i - 2, 2) >= "10") {
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
return dp.back();
}
}; 3、Restore IP Addresses 复原IP地址
Given a string containing only digits, restore it by returning all possible valid IP address combinations.
Example:
Input: "25525511135"
Output: ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"]
这道题要求是复原IP地址,IP地址对我们并不陌生,就算我们不是学CS的,只要我们是广大网友之一,就应该对其并不陌生。IP地址由32位二进制数组成,为便于使用,常以XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX形式表现,每组XXX代表小于或等于255的10进制数。所以说IP地址总共有四段,每一段可能有一位,两位或者三位,范围是[0, 255],题目明确指出输入字符串只含有数字,所以当某段是三位时,我们要判断其是否越界(>255),还有一点很重要的是,当只有一位时,0可以成某一段,如果有两位或三位时,像 00, 01, 001, 011, 000等都是不合法的,所以我们还是需要有一个判定函数来判断某个字符串是否合法。这道题其实也可以看做是字符串的分段问题,在输入字符串中加入三个点,将字符串分为四段,每一段必须合法,求所有可能的情况。根据目前刷了这么多题,得出了两个经验,一是只要遇到字符串的子序列或配准问题首先考虑动态规划DP,二是只要遇到需要求出所有可能情况首先考虑用递归。这道题并非是求字符串的子序列或配准问题,更符合第二种情况,所以我们要用递归来解。我们用k来表示当前还需要分的段数,如果k = 0,则表示三个点已经加入完成,四段已经形成,若这时字符串刚好为空,则将当前分好的结果保存。若k != 0, 则对于每一段,我们分别用一位,两位,三位来尝试,分别判断其合不合法,如果合法,则调用递归继续分剩下的字符串,最终和求出所有合法组合,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector restoreIpAddresses(string s) {
vector res;
restore(s, 4, "", res);
return res;
}
void restore(string s, int k, string out, vector &res) {
if (k == 0) {
if (s.empty()) res.push_back(out);
}
else {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) {
if (s.size() >= i && isValid(s.substr(0, i))) {
if (k == 1) restore(s.substr(i), k - 1, out + s.substr(0, i), res);
else restore(s.substr(i), k - 1, out + s.substr(0, i) + ".", res);
}
}
}
}
bool isValid(string s) {
if (s.empty() || s.size() > 3 || (s.size() > 1 && s[0] == '0')) return false;
int res = atoi(s.c_str());
return res <= 255 && res >= 0;
}
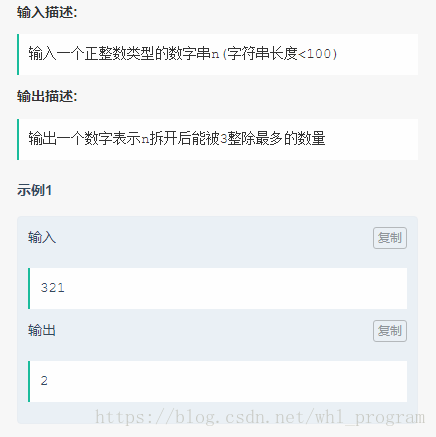
}; 4.
1. 遍历求字符和sum,遍历过程之中碰到3的倍数,最终结果res+1,sum重新计数
2. 单个字符如果是3的倍数(包括0),res+1,然后立刻sum重新计数
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector arr;
string str;
int res=0, sum=0;
cin >> str;
for(int i=0; i'9')
return 0;
int temp = str[i]-'0';
arr.push_back(temp);
}
for(int i=0; i