Python学习笔记
在线学习:
http://www.runoob.com/python/python-tutorial.html
scipy官方文档:
https://scipy.org/docs.html
Numpy是以矩阵为基础的数学计算模块,纯数学。Scipy基于Numpy,科学计算库,有一些高阶抽象和物理模型。比方说做个傅立叶变换,这是纯数学的,用Numpy;做个滤波器,这属于信号处理模型了,在Scipy里找。Pandas提供了一套名为DataFrame的数据结构,比较契合统计分析中的表结构,并且提供了计算接口,可用Numpy或其它方式进行计算。
作者:Coldwings
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/38353562/answer/115438054
来源:知乎
1 Jupyter notebook
环境为Ubuntu 64-bit,安装了Anaconda。在终端输入jupyter notebook打开交互界面。

右上角的new可以新建一个notebook。新建一个Python notebook,在code cell中输入命令,按Shift+Enter可以执行。
加载python文件%load hello.py
执行Python文件%run hello.py
设置远程访问可参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/yangxiaolan/p/5778305.html
2 用法
2.1 注释
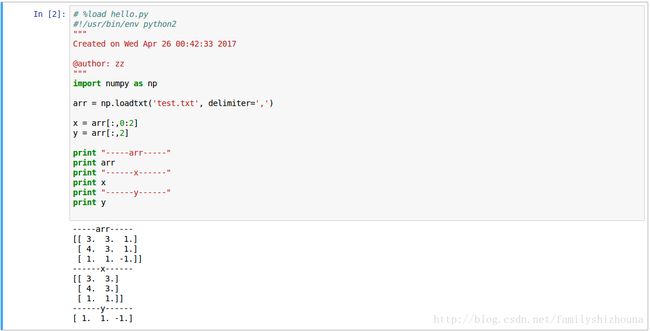
2.2读写文件和切割数组
file = open('predict.txt')
result = open('result.txt', 'w+')
for line in file:
c = new_grocery.predict(line)
result.write(str(c))
result.write(', ')
result.write(line)
result.close()参考:
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/a6JRr2Y
http://blog.csdn.net/tina_ttl/article/details/51031113
http://www.cnblogs.com/xuxn/archive/2011/07/27/read-a-file-with-python.html
2.3 None
相当于java中的null
2.4 实例变量与类变量
class AAA():
aaa = 10
obj1 = AAA()
obj2 = AAA()
print obj1.aaa, obj2.aaa, AAA.aaa
obj1.aaa += 2
print obj1.aaa, obj2.aaa, AAA.aaa
AAA.aaa += 3
print obj1.aaa, obj2.aaa, AAA.aaa代码执行结果为:
10 10 10
12 10 10
12 13 13类对象和实例对象中都会有一个变量,当还没有为实例对象中的属性赋值时,就向上查找类对象的值。如下图所示:
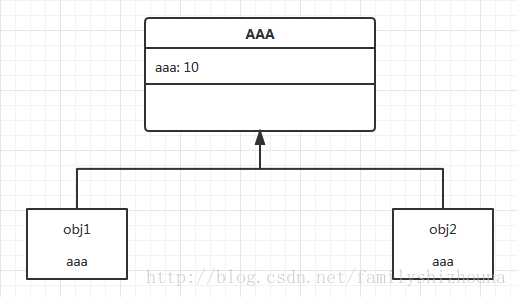
参考:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002671941
2.5 ndarray排序
train = np.array([[2,3],[5,4],[9,6],[4,7],[8,1],[7,2]])
train = train[train[:,0].argsort()] # 按照第一维排序结果:
[[2 3]
[4 7]
[5 4]
[7 2]
[8 1]
[9 6]]2.6 类
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, parent):
self.data = data
self.parent = parent
def setLChild(self, lChild):
self.lChild = lChild
def setRChild(self, rChild):
self.rChild = rChild2.7 中文
在开头加
#coding=utf-82.8 画图
官方文档:
http://www.labri.fr/perso/nrougier/teaching/matplotlib/
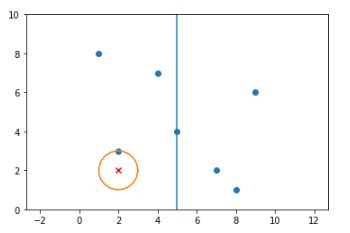
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
data = np.array([[1,8],[2,3],[5,4],[9,6],[4,7],[8,1],[7,2]])
plt.scatter(data[:,0], data[:,1]) # 画散点
plt.plot([5, 5],[0, 10]) # 画两点线
[x0,y0]=[2,2]
plt.scatter([x0],[y0],c='red',marker='x') # 画一个点
r=1
theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 20)
x = x0 + r*np.cos(theta)
y = y0 + r*np.sin(theta)
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.axis([0, 10, 0, 10])
plt.show()2.9 调试
pdb:Python debuger
break(b) 设置断点
continue(c) 继续执行程序
list(l) 查看当前行的代码段
step(s) 进入函数
return(r) 执行代码,直到从当前函数返回
exit(q) 中止并退出
next(n) 执行下一行
pp 打印变量的值
help参考:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-pythondebugger/
2.10 基本数据类型
2.10.1 字典
d = dict(key1=value1, key2=value2, ...) # dictionary
print d输出:
{'a': '1', 'b': 2}2.10.2 数组
a = [1, 3, 7, 5] # 数组
b = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} # 字典
range(5) # 数组
[None]*n #定义长度为n的数组2.11 numpy
numpy数组运算:根据布尔型数组进行过滤、标量乘法、应用数学函数。
obj[obj > 0]
obj * 2
np.exp(obj)2.12 整数变为浮点数
float(i)3 一些小知识点
3.1 集合操作
http://www.iplaypy.com/jichu/set.html
交集&,差集-,并集|
3.2 with…as用法
http://www.cnblogs.com/itcomputer/articles/4601411.html
这个语法是用来替代传统的try…finally语法的。with Expression [as VARIABLE] WITH-BLOCK
下面两端代码时等价的:
file = open('/tmp/foo.txt')
try:
data = file.read()
finally:
file.close()with open('/tmp/foo.txt') as file:
data = file.read()3.3 python list []
http://www.runoob.com/python/python-lists.html
list.count(obj) #统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数
list.append(obj) #在列表末尾添加新的对象 3.4 python内置函数 range()
http://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-range.html
Python range()函数可创建一个整数列表,一般用在for循环中。
range(start, stop[, step])参数说明:
- start:计数从start开始。默认是从0开始。例如:range(5)等价于range(0, 5)
- end:计数到end结束,但不包括end。例如:range(0, 5)是[0,1,2,3,4]没有5
- step:步长,默认为1。例如:range(0, 5)等价于range(0, 5, 1)
4 bug集合
4.1 UnicodeEncodeError: ‘ascii’ codec can’t encode characters in position
参考:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_64a3795a01018vyp.html
在开头加上
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding( "utf-8" )