李航《统计学习方法》——第五章 决策树模型
由于网上资料很多,这里就不再对算法原理进行推导,仅给出博主用Python实现的代码,供大家参考
适用问题:多类分类
三个步骤:特征选择、决策树的生成和决策树的剪枝
常见的决策树算法有:
- ID3:特征划分基于信息增益
- C4.5:特征划分基于信息增益比
- CART:特征划分基于基尼指数
测试数据集:train.csv
ID3算法代码:
# encoding=utf-8
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 二值化
def binaryzation(img):
cv_img = img.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.threshold(cv_img,50,1,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV,cv_img)
return cv_img
def binaryzation_features(trainset):
features = []
for img in trainset:
img = np.reshape(img,(28,28))
cv_img = img.astype(np.uint8)
img_b = binaryzation(cv_img)
# hog_feature = np.transpose(hog_feature)
features.append(img_b)
features = np.array(features)
features = np.reshape(features,(-1,feature_len))
return features
class Tree(object):
def __init__(self,node_type,Class = None, feature = None):
self.node_type = node_type # 节点类型(internal或leaf)
self.dict = {} # dict的键表示特征Ag的可能值ai,值表示根据ai得到的子树
self.Class = Class # 叶节点表示的类,若是内部节点则为none
self.feature = feature # 表示当前的树即将由第feature个特征划分(即第feature特征是使得当前树中信息增益最大的特征)
def add_tree(self,key,tree):
self.dict[key] = tree
def predict(self,features):
if self.node_type == 'leaf' or (features[self.feature] not in self.dict):
return self.Class
tree = self.dict.get(features[self.feature])
return tree.predict(features)
# 计算数据集x的经验熵H(x)
def calc_ent(x):
x_value_list = set([x[i] for i in range(x.shape[0])])
ent = 0.0
for x_value in x_value_list:
p = float(x[x == x_value].shape[0]) / x.shape[0]
logp = np.log2(p)
ent -= p * logp
return ent
# 计算条件熵H(y/x)
def calc_condition_ent(x, y):
x_value_list = set([x[i] for i in range(x.shape[0])])
ent = 0.0
for x_value in x_value_list:
sub_y = y[x == x_value]
temp_ent = calc_ent(sub_y)
ent += (float(sub_y.shape[0]) / y.shape[0]) * temp_ent
return ent
# 计算信息增益
def calc_ent_grap(x,y):
base_ent = calc_ent(y)
condition_ent = calc_condition_ent(x, y)
ent_grap = base_ent - condition_ent
return ent_grap
# ID3算法
def recurse_train(train_set,train_label,features):
LEAF = 'leaf'
INTERNAL = 'internal'
# 步骤1——如果训练集train_set中的所有实例都属于同一类Ck
label_set = set(train_label)
if len(label_set) == 1:
return Tree(LEAF,Class = label_set.pop())
# 步骤2——如果特征集features为空
class_len = [(i,len(list(filter(lambda x:x==i,train_label)))) for i in range(class_num)] # 计算每一个类出现的个数
(max_class,max_len) = max(class_len,key = lambda x:x[1])
if len(features) == 0:
return Tree(LEAF,Class = max_class)
# 步骤3——计算信息增益,并选择信息增益最大的特征
max_feature = 0
max_gda = 0
D = train_label
for feature in features:
# print(type(train_set))
A = np.array(train_set[:,feature].flat) # 选择训练集中的第feature列(即第feature个特征)
gda=calc_ent_grap(A,D)
if gda > max_gda:
max_gda,max_feature = gda,feature
# 步骤4——信息增益小于阈值
if max_gda < epsilon:
return Tree(LEAF,Class = max_class)
# 步骤5——构建非空子集
sub_features = list(filter(lambda x:x!=max_feature,features))
tree = Tree(INTERNAL,feature=max_feature)
max_feature_col = np.array(train_set[:,max_feature].flat)
feature_value_list = set([max_feature_col[i] for i in range(max_feature_col.shape[0])]) # 保存信息增益最大的特征可能的取值 (shape[0]表示计算行数)
for feature_value in feature_value_list:
index = []
for i in range(len(train_label)):
if train_set[i][max_feature] == feature_value:
index.append(i)
sub_train_set = train_set[index]
sub_train_label = train_label[index]
sub_tree = recurse_train(sub_train_set,sub_train_label,sub_features)
tree.add_tree(feature_value,sub_tree)
return tree
def train(train_set,train_label,features):
return recurse_train(train_set,train_label,features)
def predict(test_set,tree):
result = []
for features in test_set:
tmp_predict = tree.predict(features)
result.append(tmp_predict)
return np.array(result)
class_num = 10 # MINST数据集有10种labels,分别是“0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9”
feature_len = 784 # MINST数据集每个image有28*28=784个特征(pixels)
epsilon = 0.001 # 设定阈值
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("Start read data...")
time_1 = time.time()
raw_data = pd.read_csv('../data/train.csv', header=0) # 读取csv数据
data = raw_data.values
imgs = data[::, 1::]
features = binaryzation_features(imgs) # 图片二值化(很重要,不然预测准确率很低)
labels = data[::, 0]
# 避免过拟合,采用交叉验证,随机选取33%数据作为测试集,剩余为训练集
train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(features, labels, test_size=0.33, random_state=0)
time_2 = time.time()
print('read data cost %f seconds' % (time_2 - time_1))
# 通过ID3算法生成决策树
print('Start training...')
tree = train(train_features,train_labels,list(range(feature_len)))
time_3 = time.time()
print('training cost %f seconds' % (time_3 - time_2))
print('Start predicting...')
test_predict = predict(test_features,tree)
time_4 = time.time()
print('predicting cost %f seconds' % (time_4 - time_3))
# print("预测的结果为:")
# print(test_predict)
for i in range(len(test_predict)):
if test_predict[i] == None:
test_predict[i] = epsilon
score = accuracy_score(test_labels, test_predict)
print("The accruacy score is %f" % score)代码可从这里decision_tree/ID3.py获得
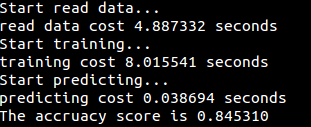
运行结果:
C4.5算法代码:
# encoding=utf-8
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 二值化
def binaryzation(img):
cv_img = img.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.threshold(cv_img,50,1,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV,cv_img)
return cv_img
def binaryzation_features(trainset):
features = []
for img in trainset:
img = np.reshape(img,(28,28))
cv_img = img.astype(np.uint8)
img_b = binaryzation(cv_img)
# hog_feature = np.transpose(hog_feature)
features.append(img_b)
features = np.array(features)
features = np.reshape(features,(-1,feature_len))
return features
class Tree(object):
def __init__(self,node_type,Class = None, feature = None):
self.node_type = node_type # 节点类型(internal或leaf)
self.dict = {} # dict的键表示特征Ag的可能值ai,值表示根据ai得到的子树
self.Class = Class # 叶节点表示的类,若是内部节点则为none
self.feature = feature # 表示当前的树即将由第feature个特征划分(即第feature特征是使得当前树中信息增益最大的特征)
def add_tree(self,key,tree):
self.dict[key] = tree
def predict(self,features):
if self.node_type == 'leaf' or (features[self.feature] not in self.dict):
return self.Class
tree = self.dict.get(features[self.feature])
return tree.predict(features)
# 计算数据集x的经验熵H(x)
def calc_ent(x):
x_value_list = set([x[i] for i in range(x.shape[0])])
ent = 0.0
for x_value in x_value_list:
p = float(x[x == x_value].shape[0]) / x.shape[0]
logp = np.log2(p)
ent -= p * logp
return ent
# 计算条件熵H(y/x)
def calc_condition_ent(x, y):
x_value_list = set([x[i] for i in range(x.shape[0])])
ent = 0.0
for x_value in x_value_list:
sub_y = y[x == x_value]
temp_ent = calc_ent(sub_y)
ent += (float(sub_y.shape[0]) / y.shape[0]) * temp_ent
return ent
# 计算信息增益
def calc_ent_grap(x,y):
base_ent = calc_ent(y)
condition_ent = calc_condition_ent(x, y)
ent_grap = base_ent - condition_ent
return ent_grap
# C4.5算法
def recurse_train(train_set,train_label,features):
LEAF = 'leaf'
INTERNAL = 'internal'
# 步骤1——如果训练集train_set中的所有实例都属于同一类Ck
label_set = set(train_label)
if len(label_set) == 1:
return Tree(LEAF,Class = label_set.pop())
# 步骤2——如果特征集features为空
class_len = [(i,len(list(filter(lambda x:x==i,train_label)))) for i in range(class_num)] # 计算每一个类出现的个数
(max_class,max_len) = max(class_len,key = lambda x:x[1])
if len(features) == 0:
return Tree(LEAF,Class = max_class)
# 步骤3——计算信息增益,并选择信息增益最大的特征
max_feature = 0
max_gda = 0
D = train_label
for feature in features:
# print(type(train_set))
A = np.array(train_set[:,feature].flat) # 选择训练集中的第feature列(即第feature个特征)
gda = calc_ent_grap(A,D)
if calc_ent(A) != 0: ####### 计算信息增益比,这是与ID3算法唯一的不同
gda /= calc_ent(A)
if gda > max_gda:
max_gda,max_feature = gda,feature
# 步骤4——信息增益小于阈值
if max_gda < epsilon:
return Tree(LEAF,Class = max_class)
# 步骤5——构建非空子集
sub_features = list(filter(lambda x:x!=max_feature,features))
tree = Tree(INTERNAL,feature=max_feature)
max_feature_col = np.array(train_set[:,max_feature].flat)
feature_value_list = set([max_feature_col[i] for i in range(max_feature_col.shape[0])]) # 保存信息增益最大的特征可能的取值 (shape[0]表示计算行数)
for feature_value in feature_value_list:
index = []
for i in range(len(train_label)):
if train_set[i][max_feature] == feature_value:
index.append(i)
sub_train_set = train_set[index]
sub_train_label = train_label[index]
sub_tree = recurse_train(sub_train_set,sub_train_label,sub_features)
tree.add_tree(feature_value,sub_tree)
return tree
def train(train_set,train_label,features):
return recurse_train(train_set,train_label,features)
def predict(test_set,tree):
result = []
for features in test_set:
tmp_predict = tree.predict(features)
result.append(tmp_predict)
return np.array(result)
class_num = 10 # MINST数据集有10种labels,分别是“0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9”
feature_len = 784 # MINST数据集每个image有28*28=784个特征(pixels)
epsilon = 0.001 # 设定阈值
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("Start read data...")
time_1 = time.time()
raw_data = pd.read_csv('../data/train.csv', header=0) # 读取csv数据
data = raw_data.values
imgs = data[::, 1::]
features = binaryzation_features(imgs) # 图片二值化(很重要,不然预测准确率很低)
labels = data[::, 0]
# 避免过拟合,采用交叉验证,随机选取33%数据作为测试集,剩余为训练集
train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(features, labels, test_size=0.33, random_state=0)
time_2 = time.time()
print('read data cost %f seconds' % (time_2 - time_1))
# 通过C4.5算法生成决策树
print('Start training...')
tree = train(train_features,train_labels,list(range(feature_len)))
time_3 = time.time()
print('training cost %f seconds' % (time_3 - time_2))
print('Start predicting...')
test_predict = predict(test_features,tree)
time_4 = time.time()
print('predicting cost %f seconds' % (time_4 - time_3))
# print("预测的结果为:")
# print(test_predict)
for i in range(len(test_predict)):
if test_predict[i] == None:
test_predict[i] = epsilon
score = accuracy_score(test_labels, test_predict)
print("The accruacy score is %f" % score)代码可从这里decision_tree/C45.py获得
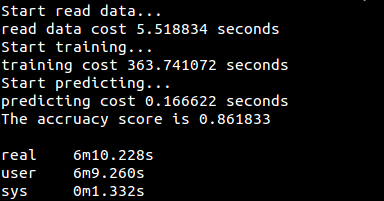
运行结果:
CART算法代码(用sklearn实现):
# encoding=utf-8
import pandas as pd
import time
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("Start read data...")
time_1 = time.time()
raw_data = pd.read_csv('../data/train.csv', header=0)
data = raw_data.values
features = data[::, 1::]
labels = data[::, 0]
# 随机选取33%数据作为测试集,剩余为训练集
train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(features, labels, test_size=0.33, random_state=0)
time_2 = time.time()
print('read data cost %f seconds' % (time_2 - time_1))
print('Start training...')
# criterion可选‘gini’, ‘entropy’,默认为gini(对应CART算法),entropy为信息增益(对应ID3算法)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini')
clf.fit(train_features,train_labels)
time_3 = time.time()
print('training cost %f seconds' % (time_3 - time_2))
print('Start predicting...')
test_predict = clf.predict(test_features)
time_4 = time.time()
print('predicting cost %f seconds' % (time_4 - time_3))
score = accuracy_score(test_labels, test_predict)
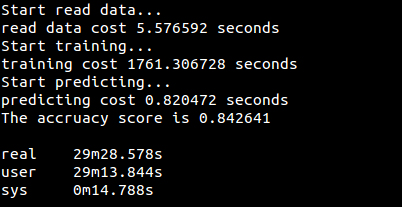
print("The accruacy score is %f" % score)