react-native 之fetch从网络超时到放弃
react-native 之fetch从网络超时到放弃
Fetch是它是React Native中的网络库,是XMLHttpRequest之上的网络封装。它反映了WHATWG fetch规范,可以在whatwg/fetch中找到。
但是Fetch有两个问题
- 无法通过外部中断
- 不支持 timeout
react-native设置网络超时网上有现成的方案:
- 使用
Promise.race()将fetch和一个setTimeout的Promise包装在了一起,新的Promise和fetch谁先返回就把该Promise实例返回值传递给下面的.then()或者是.catch()。 - react-native-fetch-polyfill 暴露一些无法通过whatwg-fetch访问的Native的XMLHttpRequest的响应选项,比如timeout。
这两种方式都可以解决问题,但是react-native的调用网络归根结底是使用android和iOS中的原生网络框架,比如在android中react-native使用的是OKHTTP作为网络请求框架,那可不可以通过直接修改底层代码设置全局的网络超时?
按照这个思路进行下去,以android为例:
react-native通过OkHttpClientProvider获取OKHTTP,通过调试发现任何模块获取OkHttpClient都需要调用OkHttpClientProvider中的createClient()方法:
public static OkHttpClient createClient() {
if (sFactory != null) {
return sFactory.createNewNetworkModuleClient();
}
return createClientBuilder().build();
}那么我们只需要设置一个sFactory就可以替换OkHttpClient,狸猫换太子:
OkHttpClientProvider.setOkHttpClientFactory(new OkHttpClientFactory() {
@Override public OkHttpClient createNewNetworkModuleClient() {
OkHttpClient.Builder client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(CONNECT_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(READ_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.writeTimeout(WRITE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.cookieJar(new ReactCookieJarContainer());
return OkHttpClientProvider.enableTls12OnPreLollipop(client).build();
}
});如上面代码,设置了新的超时时间,但是测试后发现除了连接超时,并没有起到网络超时的作用,这是为何?通过调试发现以下蛛丝马迹:
通过调试可发现react-native最终通过Handler调用android原生方法,执行调用任务的是NativeRunnable:
/**
* A Runnable that has a native run implementation.
*/
@DoNotStrip
public class NativeRunnable implements Runnable {
private final HybridData mHybridData;
@DoNotStrip
private NativeRunnable(HybridData hybridData) {
mHybridData = hybridData;
}
public native void run();
}HybridData 是react-native和android之间数据传递的对象,其中mNativePointer是react-native在内存中保存数据的指针地址,所以react-native和原生APP交互并没有产生内存copy:
@DoNotStrip
public class HybridData {
static {
SoLoader.loadLibrary("fb");
}
@DoNotStrip
private Destructor mDestructor = new Destructor(this);
/**
* To explicitly delete the instance, call resetNative(). If the C++
* instance is referenced after this is called, a NullPointerException will
* be thrown. resetNative() may be called multiple times safely. Because
* the {@link DestructorThread} also calls resetNative, the instance will not leak if this is
* not called, but timing of deletion and the thread the C++ dtor is called
* on will be at the whim of the Java GC. If you want to control the thread
* and timing of the destructor, you should call resetNative() explicitly.
*/
public synchronized void resetNative() {
mDestructor.destruct();
}
/**
* N.B. Thread safety.
* If you call isValid from a different thread than {@link #resetNative()} then be sure to
* do so while synchronizing on the hybrid. For example:
*
* synchronized(hybrid) {
* if (hybrid.isValid) {
* // Do stuff.
* }
* }
*
*/
public boolean isValid() {
return mDestructor.mNativePointer != 0;
}
public static class Destructor extends DestructorThread.Destructor {
// Private C++ instance
@DoNotStrip
private long mNativePointer;
Destructor(Object referent) {
super(referent);
}
@Override
void destruct() {
// When invoked from the DestructorThread instead of resetNative,
// the DestructorThread has exclusive ownership of the HybridData
// so synchronization is not necessary.
deleteNative(mNativePointer);
mNativePointer = 0;
}
static native void deleteNative(long pointer);
}
}最终Hander会执行JavaModuleWrapper中的invoke方法,invoke会针对NativeModule的具体方法进行调用:
@DoNotStrip
public class JavaModuleWrapper {
...
@DoNotStrip
public void invoke(int methodId, ReadableNativeArray parameters) {
if (mMethods == null || methodId >= mMethods.size()) {
return;
}
mMethods.get(methodId).invoke(mJSInstance, parameters);
}
}JavaMethodWrapper 则通过反射调用java真实方法:
public class JavaMethodWrapper implements NativeModule.NativeMethod {
...
@Override
public void invoke(JSInstance jsInstance, ReadableNativeArray parameters) {
...
mMethod.invoke(mModuleWrapper.getModule(), mArguments);
}
}一个网络请求最终调用的参数如下:
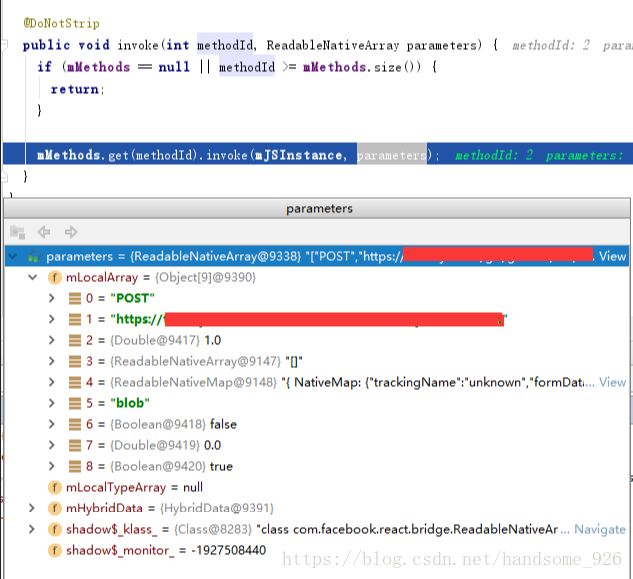
这里要留意mLocalArray中第八个参数是Double类型,且值为0。
网络请求调用的方法:
@ReactMethod
/**
* @param timeout value of 0 results in no timeout
*/
public void sendRequest(
String method,
String url,
final int requestId,
ReadableArray headers,
ReadableMap data,
final String responseType,
final boolean useIncrementalUpdates,
int timeout,
boolean withCredentials) {
...
OkHttpClient.Builder clientBuilder = mClient.newBuilder();
...
// If the current timeout does not equal the passed in timeout, we need to clone the existing
// client and set the timeout explicitly on the clone. This is cheap as everything else is
// shared under the hood.
// See https://github.com/square/okhttp/wiki/Recipes#per-call-configuration for more information
if (timeout != mClient.connectTimeoutMillis()) {
clientBuilder.readTimeout(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
OkHttpClient client = clientBuilder.build();
...
}==! 上面的注释已经说明白了,方法中的第八个参数timeout(每次请求默认为0)如果和全局readTimeout不一致,就会重新设置一个新的,原因在okhttp官网指出了https://github.com/square/okhttp/wiki/Recipes#per-call-configuration,所以通过给react-native原生网络模块设置全局网络超时不可行,当然,我们可以将NetworkingModule.java文件copy出来重新修改并替换,但这样做有违初衷。
react-native网络请求如何回调:
public class ResponseUtil {
...
public static void onRequestSuccess(RCTDeviceEventEmitter eventEmitter, int requestId) {
WritableArray args = Arguments.createArray();
args.pushInt(requestId);
args.pushNull();
eventEmitter.emit("didCompleteNetworkResponse", args);
}
public static void onResponseReceived(
RCTDeviceEventEmitter eventEmitter,
int requestId,
int statusCode,
WritableMap headers,
String url) {
WritableArray args = Arguments.createArray();
args.pushInt(requestId);
args.pushInt(statusCode);
args.pushMap(headers);
args.pushString(url);
eventEmitter.emit("didReceiveNetworkResponse", args);
}
}可以看到react-native使用fetch和react-native调用原生方法无异。
结论:如果react-native作为原生APP中的一个RN模块,为什么不直接用原生网络封装的接口,这样还可以做到维护同一套网络协议结构和加解密流程。如果是纯RN项目可以考虑fetch-polyfill替代fetch,等待Facebook最终解决网络访问超时的问题。
如果有更好的解决方案,希望不吝赐教,感谢!