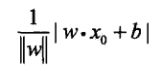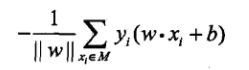统计学习-感知机算法
解决问题:二分类、线性分类(不能解决异或问题)
感知机(perceptron):有监督学习、判别模型,SVM的基础
模型:
输入:
![]()
输出:
![]()
模型 参数为w和b
策略:
数据集满足线性可分性
学习一个能将正类和负类完全正确分开的分离超平面
1)依据误分类的点数(不是参数wb的连续可导函数,不易优化)
2)误分类点到超平面S的总距离
任意一点到超平面的距离:
(推导)替换为:
因此所有误分类点到超平面距离的和:
得出感知机学习的损失函数为:
学习算法:
随机梯度下降
1)
2)对偶形式的区别是,引入了更新次数n
学习到的w和b有区别:
其中的yjxj已知,可以提前计算得出:Gram矩阵
简单形式代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class MyPerceptron:
def __init__(self):
self.w=None
self.b=0
self.l_rate=1
def fit(self,X_train,y_train):
#用样本点的特征数更新初始w,如x1=(3,3)T,有两个特征,则self.w=[0,0]
self.w=np.zeros(X_train.shape[1])#列
i=0
while iSklearn实现:
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
import numpy as np
X_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]])
y = np.array([1, 1, -1])
#perceptron=Perceptron()
perceptron=Perceptron(penalty="l2",alpha=0.01,eta0=1,tol=1e-3)
perceptron.fit(X_train,y)
print("w:",perceptron.coef_,"\n","b:",perceptron.intercept_,"\n","n_iter:",perceptron.n_iter_)
res=perceptron.score(X_train,y)
print("correct rate:{:.0%}".format(res))
X=X_train
X_new=np.array([[0], [6]])
w=perceptron.coef_
w=w.T
b=perceptron.intercept_
y_predict=(-b-(w[0]*X_new))/w[1]#W0x+w1y+b=0 则y=-b/w1-w0*x/w1
plt.plot(X[:2,0],X[:2,1],"g*",label="1")
plt.plot(X[2:,0], X[2:,1], "rx",label="-1")
#绘制分离超平面
plt.plot(X_new,y_predict,"b-")
#设置两坐标轴起止值
plt.axis([0,6,0,6])
#设置坐标轴标签
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
#显示图例
plt.legend()
#显示图像
plt.show()
X1=np.array([[2,2]])
y2=perceptron.predict(X1)
函数:
返回属性值
补充:
1)为什么不能解决异或问题?
比如 00 (1) 11(1) 01(0) 10(0) 在坐标系中表示点,无法用一条直线将它们不同的类别完全划分开
参考资料
【1】统计机器学习
【2】中文文档https://sklearn.apachecn.org/
【3】https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.Perceptron.html