回溯法,随机迷宫,以及更多
我在我的游戏中增加了迷宫场景,这个迷宫随机生成而且中央有一片开阔地带作为终点位置。作为挑战的一部分我希望迷宫在有一定规模的前提下不至于过难,解决方案是玩家身在迷宫中时给出某种提示(UI 或者立体声音效)将玩家引向正确的方向。
随机生成迷宫的方式不唯一,生成方式影响迷宫风格。就没有高度差距的二维迷宫而言回溯法生成的迷宫形状自然,容易得到一个完美迷宫,即联系迷宫中任意两点的路径唯一。
这个方案的效果长这样,有道路,还有两个空腔,其中一个空腔在左上角:
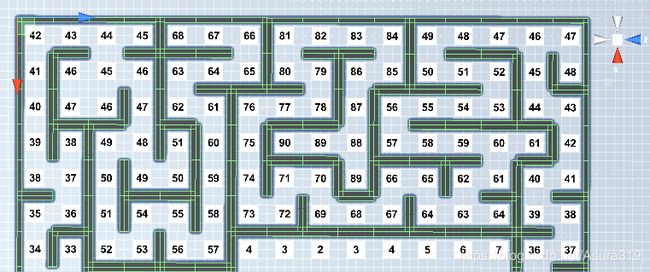
约定,原理,数据结构
首先我们做出一些约定:
- 迷宫被视为由一系列单元组成,无关具体形状。
- 单元记录从自身出发能到达的其他邻接点,在这里迷宫单元是方格,邻接点固定在上下左右四个方向,那么保存在某方向上是否有开口即可。
- 迷宫使用矩阵表示,单元位置坐标 (a, b) 表示在矩阵的第 a 行第 b 列,而 a、b 分别为迷宫在 x、z 轴上的单位长度位移增量(形如上面那张图,这样约定省略了换算,二维坐标的 xy 轴/行列可以方便地作用于 Unity 中的坐标)。
回溯法原理简单粗暴。
- 初始状态的迷宫所有单元都是全封闭的,算法将指定的起点压栈
- 观察栈顶节点,如果节点没有未访问的邻接点就出栈,出栈导致栈空则结束算法,得到有可用邻接点的单元作为当前点
- 随机选取一个当前点未访问过的邻接点,将该点压栈、打上已访问标记、连接该点和当前点,重复步骤2
使用矩阵表示迷宫,可以用数组存放所有节点。因为每个点只考虑上下左右方向是否连通,可以使用一个二进制位表示连通与否。更极端一些甚至连同访问标记和迷宫中的空洞也可以使用二进制位表示。
迷宫中的空洞要在生成迷宫前预先设置,不能与起点重叠,这里规定设置一个空洞需要空洞的左上角点坐标、横方向增量和纵方向增量(前面约定的作用体现了)。迷宫生成时算法走到空洞所在点时将此空洞的所有点打上访问标记,并且将空洞所在的点相互连接形成大的空穴。
走在迷宫里稍微有些震撼,虽然有些模型只是占位符比如那个奇怪的楼梯……

代码
复制类的内容,或者生成 dll 文件后导入可以在 Unity 中创建迷宫类实例。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace RandMaze
{
///
/// 生成四方向随机迷宫
///
public class DMaze
{
///
/// 存放迷宫单元,其大小在构造函数中决定
///
public int[] Maze { get; private set; }
///
/// 迷宫中的空洞,连接的空洞被视为一个单元
///
public bool[] Hole { get; private set; }
private bool[] visited;
///
/// 迷宫的行数,迷宫单元在x轴上的个数
///
public int XCount { get; private set; }
///
/// 迷宫的列数,迷宫单元在y轴上的个数
///
public int YCount { get; private set; }
public int Capacity { get; private set; }
public Random rand = new Random();
public int enter_x, enter_y;
public int exit_x, exit_y;
public bool enterOpen = false, exitOpen = false;
public const int up = 1;
public const int right = 1 << 1;
public const int down = 1 << 2;
public const int left = 1 << 3;
///
/// 生成 x 行 y 列的迷宫
///
/// 迷宫行数
/// 迷宫列数
public DMaze(int x, int y)
{
if (x < 0) { x = 4; }
if (y < 0) { y = 4; }
XCount = x;
YCount = y;
Capacity = x * y;
Maze = new int[Capacity];
Hole = new bool[Capacity];
visited = new bool[Capacity];
}
///
/// 清空迷宫信息
///
public void ClearMaze()
{
for (int i = 0; i < Capacity; i++)
{
Maze[i] = 0;
visited[i] = false;
}
}
///
/// 设置迷宫中的空洞
///
/// 空洞左上角 x 坐标
/// 空洞左上角 y 坐标
/// 空洞 x 方向宽度
/// 空洞 y 方向宽度
public void SetHole(int x, int y, int dx, int dy)
{
if (x + dx > XCount) { dx = XCount - x; }
if (y + dy > YCount) { dy = YCount - y; }
for (int i = 0; i < dx; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dy; j++)
{
Hole[ToPoint(x + i, y + j)] = true;
}
}
}
///
/// 清空空洞信息
///
public void ClearHole()
{
for (int i = 0; i < Capacity; i++) { Hole[i] = false; }
}
public int ToPoint(int x, int y)
{
if (x < 0 || x > XCount - 1) { x = 0; }
if (y < 0 || y > YCount - 1) { y = 0; }
return YCount * x + y;
}
bool InRange(int x, int y)
{
return x < XCount && y < YCount;
}
void Link(int p, int q)
{
int px = p / YCount, py = p % YCount;
int qx = q / YCount, qy = q % YCount;
if (px == qx) // same x
{
if (py > qy) // py > qy
{
Maze[p] |= left;
Maze[q] |= right;
}
if (py < qy) // py < qy
{
Maze[p] |= right;
Maze[q] |= left;
}
}
if (py == qy) // same y
{
if (px > qx) // px > qx
{
Maze[p] |= up;
Maze[q] |= down;
}
if (px < qx) // px < qx
{
Maze[p] |= down;
Maze[q] |= up;
}
}
}
void VisitNode(int p, bool useHole = false)
{
if (useHole && Hole[p])
{
_VisitNodeHole(p);
return;
}
visited[p] = true;
}
Queue _qVNHole;
void _VisitNodeHole(int p) // 处理遇到空洞的情形
{
if (_qVNHole == null) { _qVNHole = new Queue(); }
_qVNHole.Enqueue(p);
while (_qVNHole.Count != 0)
{
int current = _qVNHole.Dequeue();
visited[current] = true;
int cx = current / YCount;
int cy = current % YCount;
if (!Visited(cx - 1, cy) && Hole[ToPoint(cx - 1, cy)]) { _qVNHole.Enqueue(ToPoint(cx - 1, cy)); }
if (!Visited(cx, cy + 1) && Hole[ToPoint(cx, cy + 1)]) { _qVNHole.Enqueue(ToPoint(cx, cy + 1)); }
if (!Visited(cx + 1, cy) && Hole[ToPoint(cx + 1, cy)]) { _qVNHole.Enqueue(ToPoint(cx + 1, cy)); }
if (!Visited(cx, cy - 1) && Hole[ToPoint(cx, cy - 1)]) { _qVNHole.Enqueue(ToPoint(cx, cy - 1)); }
}
}
public void BuildHole() // 处理空洞,其实在生成迷宫算法结束末尾直接调用就很好
{
for (int p = 0; p < Capacity; p++)
{
int x = p / YCount, y = p % YCount;
if (Hole[p])
{
if (x > 0 && Hole[ToPoint(x - 1, y)]) { Maze[p] |= up; }
if (y < YCount - 1 && Hole[ToPoint(x, y + 1)]) { Maze[p] |= right; }
if (x < XCount - 1 && Hole[ToPoint(x + 1, y)]) { Maze[p] |= down; }
if (y > 0 && Hole[ToPoint(x, y - 1)]) { Maze[p] |= left; }
}
}
}
bool Visited(int x, int y)
{
if (x < 0 || x > XCount - 1 || y < 0 || y > YCount - 1) { return true; }
return visited[ToPoint(x, y)];
}
bool ValidDir(int x, int y, int dir) // dir = 0, 1, 2, 3
{
switch (dir)
{
case 0: // up
return !Visited(x - 1, y);
case 1: // right
return !Visited(x, y + 1);
case 2: // down
return !Visited(x + 1, y);
case 3: // left
return !Visited(x, y - 1);
default: return false;
}
}
///
/// DFS 生成迷宫
///
/// 起点 x 坐标
/// 起点 y 坐标
public void DfsBuild(int x, int y, bool useHole = false)
{
if (x < 0 || x > XCount - 1) { x = 0; }
if (y < 0 || y > YCount - 1) { y = 0; }
Stack points = new Stack();
int[] nextCache = new int[4]; // magic
points.Push(ToPoint(x, y));
VisitNode(points.Peek(), useHole);
while (true)
{
int current = points.Peek();
int cx = current / YCount;
int cy = current % YCount;
while (Visited(cx - 1, cy) && // up
Visited(cx + 1, cy) && // down
Visited(cx, cy + 1) && // right
Visited(cx, cy - 1)) // left
{
points.Pop();
if (points.Count == 0) { return; }
current = points.Peek();
cx = current / YCount;
cy = current % YCount;
} // 之后 current 一定有可用邻接点
int nextCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) // magic
{
if (ValidDir(cx, cy, i)) { nextCache[nextCount++] = i; }
}
int m_next = rand.Next(nextCount);
int nextDir = nextCache[m_next];
int pNext;
switch (nextDir)
{
case 0: // up
pNext = ToPoint(cx - 1, cy);
break;
case 1: // right
pNext = ToPoint(cx, cy + 1);
break;
case 2: // down
pNext = ToPoint(cx + 1, cy);
break;
case 3: // left
pNext = ToPoint(cx, cy - 1);
break;
default: return;
}
Link(current, pNext);
points.Push(pNext);
VisitNode(pNext, useHole);
}
}
Queue<(int, int)> bfsQ = new Queue<(int, int)>();
///
/// BFS 扫描,不分配内存
///
/// 起点 x 坐标
/// 起点 y 坐标
/// 保存扫描结果,保存对应索引的单元与起点距离
public void FindPathUnAlloc(int sx, int sy, ref int[] disGraph)
{
if (disGraph.Length != Capacity)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("disGraph", "disGraph 的长度应与 Capacity 相等。");
}
bfsQ.Enqueue((sx, sy));
disGraph[ToPoint(sx, sy)] = 0;
while (bfsQ.Count != 0)
{
(int x, int y) = bfsQ.Dequeue();
int currentDis = disGraph[ToPoint(x, y)];
if ((Maze[ToPoint(x, y)] & up) != 0 &&
currentDis + 1 < disGraph[ToPoint(x - 1, y)])
{
bfsQ.Enqueue((x - 1, y));
disGraph[ToPoint(x - 1, y)] = currentDis + 1;
}
if ((Maze[ToPoint(x, y)] & right) != 0 &&
currentDis + 1 < disGraph[ToPoint(x, y + 1)])
{
bfsQ.Enqueue((x, y + 1));
disGraph[ToPoint(x, y + 1)] = currentDis + 1;
}
if ((Maze[ToPoint(x, y)] & down) != 0 &&
currentDis + 1 < disGraph[ToPoint(x + 1, y)])
{
bfsQ.Enqueue((x + 1, y));
disGraph[ToPoint(x + 1, y)] = currentDis + 1;
}
if ((Maze[ToPoint(x, y)] & left) != 0 &&
currentDis + 1 < disGraph[ToPoint(x, y - 1)])
{
bfsQ.Enqueue((x, y - 1));
disGraph[ToPoint(x, y - 1)] = currentDis + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
在 Unity 脚本中使用的方式形如:
...
public class Maze : MonoBehaviour
{
Transform selfTransform;
public DMaze dMaze; // 迷宫类实例
public GameObject wallPrefab; // 迷宫墙体预制件
public int mazeHeight = 8; // 高度约定为 x 轴上的增量
public int mazeWidth = 8; // 宽度约定为 z 轴上的增量
public int seed = 0; // 随机数种子
public int enterPoint_x = 0, enterPoint_y = 4; // 入口坐标
public int exitPoint_x = 8, exitPoint_y = 4; // 出口坐标
int p_enter, p_exit; // 入口和出口指针
[Header("迷宫内空洞坐标及尺寸,按序号分别设置")]
public bool useHole = false;
public int[] holeXs;
public int[] holeYs;
public int[] holeDXs;
public int[] holeDYs;
[Header("迷宫终点坐标")]
public int endX = 8, endY = 8;
int[] _distGraph; // 记录对应单元与终点的距离
public int[] DistGraph { get { return _distGraph; } }
public const int infinity = int.MaxValue / 2;
private void Awake()
{
selfTransform = transform;
dMaze = new DMaze(mazeHeight, mazeWidth) { rand = new System.Random(seed) };
p_enter = dMaze.ToPoint(enterPoint_x, enterPoint_y);
p_exit = dMaze.ToPoint(exitPoint_x, exitPoint_y);
if (useHole)
{
for (int i = 0; i < holeXs.Length; i++)
{
dMaze.SetHole(holeXs[i], holeYs[i], holeDXs[i], holeDYs[i]);
}
}
dMaze.DfsBuild(enterPoint_x, enterPoint_y, useHole);
if (useHole) { dMaze.BuildHole(); }
StartCoroutine(BuildWallAsync()); // 调用生成迷宫墙体的方法
_distGraph = new int[dMaze.Capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < _distGraph.Length; i++) { _distGraph[i] = infinity; }
dMaze.FindPathUnAlloc(endX, endY, ref _distGraph);
}
...