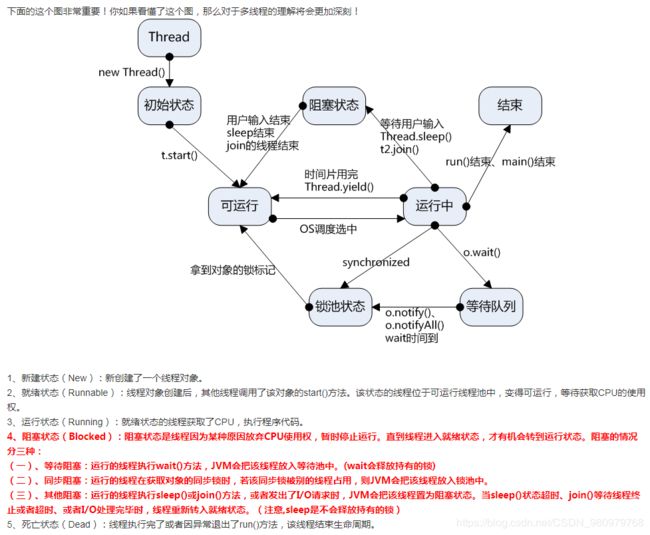
多线程的线程状态转换——与常见的函数
多线程的线程状态转换
常见的函数
① sleep():使线程静止,不会释放对象锁.
② wait():使线程释放对象锁,需与 synchronized() ,notify().
③ notify():唤醒处于 同步块 wait() 的一段线程使其运行.
①②③Demo: ↓
public class WaitThread {
public WaitThread()
{
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ThreadB b = new WaitThread().new ThreadB();
b.start();
System.out.println("b is start....");
synchronized (b) // 括号里的b是什么意思,起什么作用?
{
try
{
System.out.println("Waiting for b to complete...");
System.out.println("Completed.Now back to main thread");
b.wait(); // 这一句是什么意思,究竟让谁wait?
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
}
System.out.println("Total is :" + b.total);
}
class ThreadB extends Thread
{
int total;
public void run()
{
synchronized (this)
{
System.out.println("ThreadB is running..");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
total += i;
System.out.println("total is " + total);
}
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
notify();
}
}
}
}
④ join():等待某线程终止.
为什么要用join()方法
在很多情况下,主线程生成并起动了子线程,如果子线程里要进行大量的耗时的运算,主线程往往将于子线程之前结束,但是如果主线程处理完其他的事务后,需要用到子线程的处理结果,也就是主线程需要等待子线程执行完成之后再结束,这个时候就要用到join()方法了。
④Demo:↓
private String name;
public JoinThread(String name)
{
super(name);
this.name=name;
}
public void run()
{
synchronized (Thread.class)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程运行开始!");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
System.out.println("子线程"+name + "运行 : " + i);
try
{
sleep((long) (Math.random()*1000));
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程运行结束!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "主线程运行开始!");
JoinThread mTh1 = new JoinThread("A");
JoinThread mTh2 = new JoinThread("B");
mTh1.start();
mTh1.join();
mTh2.start();
mTh2.join();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "主线程运行结束!");
}
⑤ yield() :
yield 方法使当前线程让出 CPU 占有权,但让出的时间是不可设定的。实际上,yield()是让出去cpu的占有权,与其他的
线程竞争执行,优先级只是提高了竞争的,并不会等待优先级高的执行完毕之后才执行,而是去竞争都有可能去占有cpu去执行.
⑤ Demo:↓ 如果没有interrupt() 函数,如果遇上线程阻塞,线程不会中断,
private String name;
public JoinThread(String name)
{
super(name);
this.name=name;
}
public void run()
{
synchronized (Thread.class)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程运行开始!");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
System.out.println("子线程"+name + "运行 : " + i);
try
{
sleep((long) (Math.random()*1000));
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程运行结束!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "主线程运行开始!");
JoinThread mTh1 = new JoinThread("A");
JoinThread mTh2 = new JoinThread("B");
mTh1.start();
mTh1.join();
mTh2.start();
mTh2.join();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "主线程运行结束!");
}
⑥ interrupt():在一个线程中调用另一个线程的interrupt()方法,即会向那个线程发出信号——线程中断状态已被设置。至于那个线程何去何从,由具体的代码实现决定。
⑥ Demo:↓(如果遇上线程阻塞,线程不会终止,处于长时间的休眠状态)
public class InterruptThread implements Runnable {
private volatile static boolean on = false;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
Thread testThread = new Thread(new InterruptThread(), "InterruptionInJava");
// start thread
testThread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
InterruptThread.on = true;
//testThread.interrupt(); //
System.out.println("main end");
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!on) {
try {
System.out.println("into ....");
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("caught exception: " + e);
}
}
}
}
⑥ Demo:↓(interrupt() 遇上线程阻塞的状态,会立马抛出异常,从而中断阻塞状态)
public class InterruptThread implements Runnable {
private volatile static boolean on = false;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
Thread testThread = new Thread(new InterruptThread(), "InterruptionInJava");
// start thread
testThread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
InterruptThread.on = true;
testThread.interrupt(); // (interrupt() 遇上线程阻塞的状态,会立马抛出异常,从而中断阻塞状态)
System.out.println("main end");
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!on) {
try {
System.out.println("into ....");
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("caught exception: " + e);
}
}
}
}