(2)动态规划:01背包、完全背包、多重背包,源代码由C++实现
文章目录
- 1. 01背包问题
- 1.1 问题描述与算法分析
- 1.2 核心代码
- 1.3 测试代码
- 1.4 示例输入输出
- 2. 完全背包问题
- 2.1 问题描述与算法分析
- 2.2 核心代码
- 2.3 测试代码
- 2.4 示例输入输出
- 3. 多重背包问题
- 3.1 问题描述与算法分析
- 3.2 核心代码
- 3.3 测试代码
- 3.4 示例输入输出
背包问题是动态规划算法的一个典型实例。
1. 01背包问题
1.1 问题描述与算法分析
01背包问题描述:有编号分别为a,b,c,d,e的五件物品,它们的重量分别是2,2,6,5,4,它们的价值分别是6,3,5,4,6,每件物品数量只有一个,现在给你个承重为10的背包,如何让背包里装入的物品具有最大的价值总和?
动态规划的基本思路:将该问题转换成子问题,考虑五件物品在给定承重 C 的背包下最大价值为原问题,如下表所示,即为考虑abcde,C = 10时的最大价值,假设为f[5][10],原问题的解可以分解为两种情况,第一种情况是不考虑放入a只考虑放入bcde承重为C时的最大价值f[4][C],第二种情况是考虑放入a时的最大价值,即value[a]+f[4][10-weight[a]]。 原问题的解f[5][10]取上述两种情况中的最大值,即f[5][10] = max{f[4][10], (f[4][10-weight[a]+value[a]))}。 由此可以看出里面涉及到需要计算f[4][10]和f[4][10-weight[a]]即f[4][4]等子问题。 以此类推,自顶向下的分析可以看出原问题需要子问题的解,我们需要先计算出子问题的解,自底向上求解。求解方式如下表所示,顺序是自底向上、从左往右,或者从左往右、自底向上都可以。注意此问题中的abcde可以包含相同的物件,它们之间的顺序也可以是任意的,不影响最终的结果。

1.2 核心代码
vector<vector<int>>& knapsack01(
vector<pair<int, int>> &goodsVec, int packageVol)
{
if (goodsVec.empty())
{
throw "Invalid arg : goodsVec empty";
}
if (packageVol < 0 || packageVol > 1000)
{
throw "Invalid arg : packageVol out of range";
}
//动态规划的二维数组
static vector<vector<int>>dpValue(
goodsVec.size(), vector<int>(packageVol + 1, 0));
for (unsigned i = 0; i < dpValue.size(); ++i)
{
for (unsigned j = 0; j < dpValue[0].size(); ++j)
{
int volume = j;
if (0 == i) //只有一种物品时
{
dpValue[i][j] = goodsVec[i].first <= volume ? goodsVec[i].second : 0;
}
else if (0 == j) //背包容量为0时
{
dpValue[i][j] = 0;
}
else //背包容量和物品种数都>=1时,使用递推公式
{
//背包容量volume不能容纳一件物品weight[i]
if (volume < goodsVec[i].first)
{
dpValue[i][j] = dpValue[i - 1][j];
}
else //背包容量volume能容纳一件物品weight[i]
{
int value = dpValue[i - 1][volume - goodsVec[i].first]
+ goodsVec[i].second;
dpValue[i][j] = max(dpValue[i - 1][j], value);
}
}
} //for 2
} //for 1
return dpValue;
}
1.3 测试代码
#include 1.4 示例输入输出
输入:
5 10 //5种物品,背包承重为10
2 6 //第一种物品,重量为2,价值为1,数目1个
2 3
6 5
5 4
4 6
输出:
0 0 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 //只放入第一种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
0 0 6 6 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 //放入第一种和第二种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
0 0 6 6 9 9 9 9 11 11 14 //放入第一种、第二种和第三种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
0 0 6 6 9 9 9 10 11 13 14 //放入前四种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
0 0 6 6 9 9 12 12 15 15 15 //放入五种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
2. 完全背包问题
2.1 问题描述与算法分析
完全背包问题描述:有编号分别为a,b,c,d的四件物品,它们的重量分别是2,3,4,7,它们的价值分别是1,3,5,9,每件物品数量无限个,现在给你个承重为10的背包,如何让背包里装入的物品具有最大的价值总和?
完全背包问题与01背包问题的区别在于每一件物品的数量都有无限个,而01背包每件物品数量只有一个。
问题解法其实和01背包问题一样,只是初始化的值和递推公式需要稍微变化一下。初始化时,当只考虑一件物品a时,f[1][j] = j/weight[a]。 递推公式计算时,f[i][y] = max{f[i-1][y], (f[i][y-weight[i]]+value[i])},注意这里当考虑放入一个物品 i 时应当考虑还可能继续放入 i,因此这里是f[i][y-weight[i]]+value[i], 而不是f[i-1][y-weight[i]]+value[i]。

2.2 核心代码
vector<vector<int>>& knapsackComplete(
vector<pair<int, int>>&goodsVec, int packageVol)
{
if (goodsVec.empty())
{
throw "Invalid arg : goodsVec empty";
}
if (packageVol < 0 || packageVol > 1000)
{
throw "Invalid arg : packageVol out of range";
}
static vector<vector<int>>dpValue(
goodsVec.size(), vector<int>(packageVol + 1, 0));
for (unsigned i = 0; i < dpValue.size(); ++i)
{
for (unsigned j = 0; j < dpValue[0].size(); ++j)
{
int volume = j;
if (0 == i)
{
dpValue[i][j] = (volume / goodsVec[i].first) * goodsVec[i].second;
}
else if (0 == j)
{
dpValue[i][j] = 0;
}
else
{
if (volume < goodsVec[i].first)
{
dpValue[i][j] = dpValue[i - 1][j];
}
else
{
int value = dpValue[i][volume - goodsVec[i].first]
+ goodsVec[i].second;
dpValue[i][j] = max(dpValue[i - 1][j], value);
}
}
} //for 2
} //for 1
return dpValue;
}
2.3 测试代码
#include 2.4 示例输入输出
输入:
4 10 //4种物品,背包承重为10
2 1 //第一种物品,重量为2,价值为1,数目不限
3 3
4 5
7 9
输出:
0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 //只放入第一种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
0 0 1 3 3 4 6 6 7 9 9 //放入第一种和第二种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
0 0 1 3 5 5 6 8 10 10 11 //放入第一种、第二种和第三种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
0 0 1 3 5 5 6 9 10 10 12 //放入四种物品,承重为0-10的最优值结果
3. 多重背包问题
3.1 问题描述与算法分析
多重背包问题描述:有编号分别为a,b,c的三件物品,它们的重量分别是1,2,2,它们的价值分别是6,10,20,他们的数目分别是10,5,2,现在给你个承重为 8 的背包,如何让背包里装入的物品具有最大的价值总和?
多重背包和01背包、完全背包的区别:多重背包中每个物品的个数都是给定的,可能不是一个,绝对不是无限个。
有两种解法,解题思路:
(1)多重背包的第一种解法:
作为一个新问题考虑,由于每个物品多了数目限制,因此初始化和递推公式都需要更改一下。初始化时,只考虑一件物品a时,f[1][j] = min{num[1], j/weight[1]}。 计算考虑i件物品承重限制为y时最大价值f[i][y]时,递推公式考虑两种情况,要么第 i 件物品一件也不放,就是f[i-1][y], 要么第 i 件物品放 k 件,其中 1 <= k <= (y/weight[i]),考虑这一共 k+1 种情况取其中的最大价值即为f[i][y]的值,即f[i][y] = max{f[i-1][y], (f[i-1][y-kweight[i]]+kvalue[i])}。 这里为什么不能像完全背包一样直接考虑f[i][y-weight[i]]+value[i]呢?因为这样不容易判断第 i 件物品的个数是否超过限制数量 num[i]。
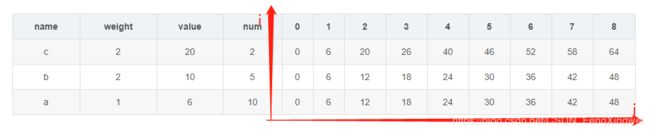
(2)多重背包的第二种解法:
由01背包的分析可知,01背包中允许放入的物品有重复,即01背包中如果考虑要放入的物品的重量和价格相同,不影响最终的结果,因为我们可以考虑把多重背包问题中限制数目的物品拆分成单独的一件件物品,作为01背包问题考虑。问题解法和01背包一致,这里不再列举出动态规划的表格了。
下面只给出第一种解法的代码实现。
3.2 核心代码
vector<vector<int>>& knapsackLimitNum(
vector<pair<pair<int, int>, int>>&goodsVec, int packageVol)
{
if (goodsVec.empty())
{
throw "Invalid arg : goodsVec empty";
}
if (packageVol < 0 || packageVol > 1000)
{
throw "Invalid arg : packageVol out of range";
}
static vector<vector<int>>dpValue(
goodsVec.size(), vector<int>(packageVol + 1, 0));
for (unsigned i = 0; i < dpValue.size(); ++i)
{
for (unsigned j = 0; j < dpValue[0].size(); ++j)
{
int volume = j;
if (0 == i)
{
int count = min(goodsVec[i].second, volume / goodsVec[i].first.first);
dpValue[i][j] = goodsVec[i].first.second * count;
}
else if (0 == j)
{
dpValue[i][j] = 0;
}
else
{
if (volume < goodsVec[i].first.first)
{
dpValue[i][j] = dpValue[i - 1][j];
}
else
{
unsigned count = min(goodsVec[i].second, volume/goodsVec[i].first.first);
for (unsigned k = 1; k <= count; ++k)
{
int value = dpValue[i - 1][volume - k * goodsVec[i].first.first]
+ k*goodsVec[i].first.second;
dpValue[i][j] = max(value, dpValue[i - 1][j]);
}
}
}
} //for 2
} //for 1
return dpValue;
}
3.3 测试代码
#include 3.4 示例输入输出
输入:
3 8 //3件物品,背包承重最大为8
1 6 10 //第一件物品, 重量为1,价值为6, 数目为10
2 10 5
2 20 2
输出:
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 //放入第一种物品,承重限制为0-8的最优值结果
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 //放入第一种和第二种物品,承重限制为0-8的最优值结果
0 6 20 26 40 46 52 58 64 //放入三种物品,承重限制为0-8的最优值结果
好了,就到这里吧。