Java基础之注解186 什么是Annotation187 自定义Annotation188反射读取注解信息与定义注解的注解
目录
1、认识Annotation
2、系统定义的Annotation
3、自定义Annotation
4、Retention和RetentionPolicy
5、反射与Annotation
6、@Documented注解
7、@Target注解
8、@Inherited注解
1、认识Annotation
JDK1.5开始,Java增加了对元数据(即类的组成单元数据)的支持,也就是(Annotation)注解,他是代码里做的特殊标记,这些标记可以在编译,类加载,运行时在不改变原有逻辑的情况下,被读取,并执行相应的处理,通过使用Annotation,程序员可以在源文件中嵌入一些补充的信息。代码分析工具,开发工具和部署工具可以通过这些补充信息进行验证或者进行部署。Annotation类似于修饰符一样被使用,可以用于包,类,构造方法,方法,成员变量,参数,局部变量的声明。
注意:
Annotation是一个接口
java.lang.Annotation接口.
2、系统定义的Annotation
在JDK 1.5之后,在系统中提供了三个Annotation,分别是:
@Override、@Deprecated、@SuppressWarnings。
- @Override
表示当前的方法定义将覆盖超类中的方法。如果你不小心拼写错误,或者方法签名对不上被覆盖的方法,编译器就会发出错误提示。 - @Deprecated
表示的是一个类或方法已经不再建议继续使用了,标记为已过时。 - @SuppressWarnings
表示关闭不当的编译器警告信息。
- @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)//未检查的转化,如集合没有指定类型
- @SuppressWarnings(“unused”) //未使用的变量
- @SuppressWarnings(“resource”) //有泛型未指定类型
- @SuppressWarnings(“path”) //在类路径,原文件路径中有不存在的路径
- @SuppressWarnings(“deprecation”) //使用了某些不赞成使用的类和方法
- @SuppressWarnings(“fallthrough”) //switch语句执行到底没有break关键字
- @SuppressWarnings(“serial”)//某类实现Serializable 但是没有定义serialVersionUID 这个需要但是不必须的字段
- @SuppressWarnings(“rawtypes”) //没有传递带有泛型的参数
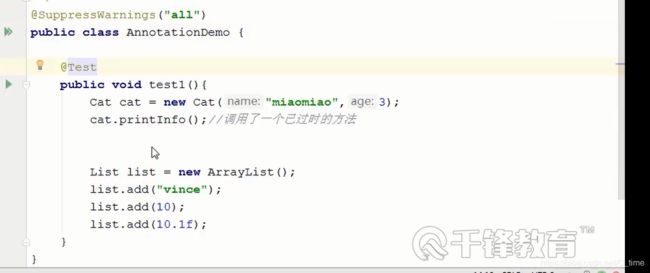
- @SuppressWarnings(“all”) //全部类型的警告
最右边有黄色的警告
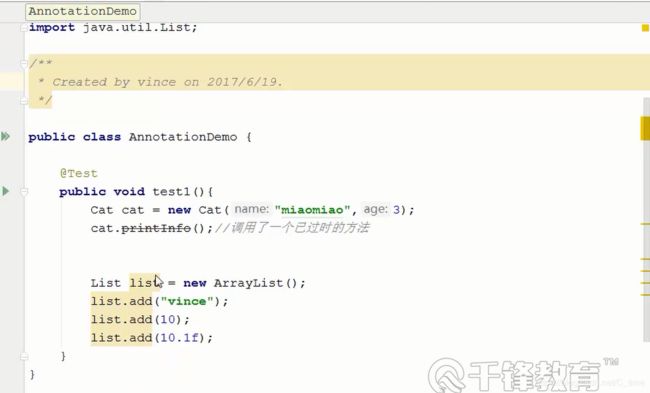
加上 @SuppressWarnings(“all”)就全没了
消除警告信息的意思
3、自定义Annotation
注解应用需要三个步骤:
(1)编写注解
(2)在类上应用注解
(3)对应用了注解的类进行反射操作的类
自定义Annotation的语法如下:
访问控制权限 @interface Annotation名称{}
例如:
public @interface MyAnnotation {}
1.在Annotation中定义变量
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public String name();
public String info();
}
2.1定义变量后,在调用此Annotation时必须设置变量值。
@MyAnnotation(name = “vince", info = “hello")
public class Demo {
}
2.2通过default指定变量默认值,
有了默认值在使用时可以不设值
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public String name() default “vince";
public String info() default “hello";
}
1.定义一个变量的数组,接收一组参数
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public String[] name();
}
2.使用时指定数组值
@MyAnnotation(name = { “jack", “vince" })
public class Demo {
}
使用枚举限制变量取值范围
public enum Color {
RED, GREEN, BLUE
}
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public Color color();
}
4、Retention和RetentionPolicy
Annotation要想决定其作用的范围,通过@Retention指定,而Retention指定的范围由RetentiontPolicy决定,RetentionPolicy指定了三种范围:

示列:
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public String name();
}
5、反射与Annotation
一个Annotation真正起作用,必须结合反射机制,在反射中提供了以下的操作方法:java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject

示例:
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(“com.vince.annotation.Test");
Method met = cls.getMethod(“setName"); // 找到setName()方法
if (met.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)) {
MyAnnotation my = (MyAnnotation) met
.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
String name = my.name();
String info = my.info();
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("info = " + info);
}
通过反射 获取注解的值去使用
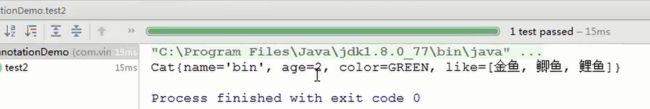
6、@Documented注解
此注解表示的是文档化,可以在生成doc文档的时候添加注解。
@Documented
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public String name();
public String info();
}
可以增加一些DOC注释。
/**
- 这个方法是从Object类中覆写而来的
*/
@MyAnnotation(name = “vince", info = “teacher")
public String toString() {
return "hello";
}
7、@Target注解
@Target注解表示的是一个Annotation的使用范围,例如:之前定义的MyAnnotation可以在任意的位置上使用。

8、@Inherited注解
@Inherited表示一个Annotation是否允许被其子类继承下来。
示例
@Inherited
@Target(value = ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public String name();
public String info();
}
使用时允许被其子类所继承。
Cat
package com.vince;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by vince on 2017/6/19.
*/
@MyAnnotation(name = "bin",like = {"金鱼","鲫鱼","鲤鱼"},color = Color.GREEN)
public class Cat {
private String name;
private int age;
private Color color;
private String[] like;
public String[] getLike() {
return like;
}
public void setLike(String[] like) {
this.like = like;
}
public Color getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(Color color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//用于验证方法是否覆盖父类中的方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", color=" + color +
", like=" + Arrays.toString(like) +
'}';
}
//用于标记方法已过时,不建议使用
@Deprecated
public String printInfo(){
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Cat() {
}
public Cat(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.vince;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by vince on 2017/6/19.
*/
//消除警告信息
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class AnnotationDemo {
//反射来处理注解
@Test
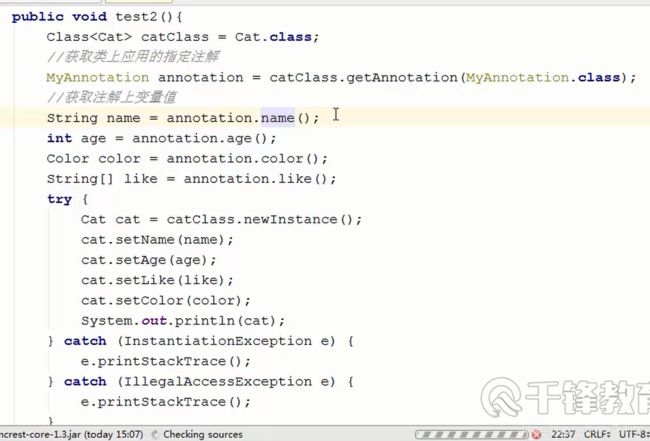
public void test2(){
Class<Cat> catClass = Cat.class;
//获取类上应用的指定注解
MyAnnotation annotation = catClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
//获取注解上变量值
String name = annotation.name();
int age = annotation.age();
Color color = annotation.color();
String[] like = annotation.like();
try {
Cat cat = catClass.newInstance();
cat.setName(name);
cat.setAge(age);
cat.setLike(like);
cat.setColor(color);
System.out.println(cat);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void test1(){
Cat cat = new Cat("miaomiao",3);
cat.printInfo();//调用了一个已过时的方法
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("vince");
list.add(10);
list.add(10.1f);
}
}
自定义注解
package com.vince;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* Created by vince on 2017/6/19.
* 自定义注解
*/
//用于生成文档
@Documented
//表示该注解的作用范围在运行时存在
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//用于表示注解的应用范围(类型,方法,属性,构造器,参数,局部变量,包,Annotation)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Inherited
public @interface MyAnnotation {
//定义变量
public String name();
public int age() default 2; //给变量设置默认值
public String[] like();//定义一个数组变量
public Color color();//定义一个枚举类型的变量
}
定义枚举
package com.vince;
/**
* Created by vince on 2017/6/19.
*/
public enum Color {
RED,GREEN,YELLOW;
}