Java静态代理与动态代理,JDKProxy和CGLIB
代理模式
代理模式就是隐藏真实对象,而暴露代理对象,而由代理对象去调用真实对象的行为。
静态代理
public interface Subject {
/**
* 处理方法
*/
void process();
}
代理类
Subject realSubject;
public Proxy(Subject realSubject){
this.realSubject=realSubject;
}
/**
* 处理方法
*/
@Override
public void process() {
System.out.println("before");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
try {
realSubject.process();
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("after Throwing");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}finally {
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("after");
}
}
真实类
public class RealSubject implements Subject {
/**
* 处理方法
*/
@Override
public void process() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
Main
public class app {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subject subject=new Proxy(new RealSubject());
subject.process();
}
}
结果
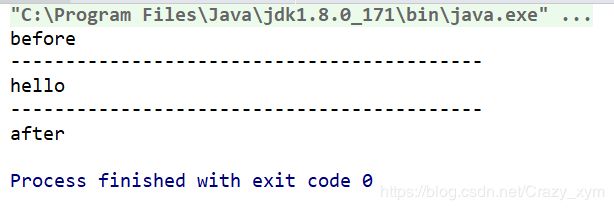
可以看见在执行打印Hello之前和执行之后多了两行打印文字,这就是代理带来的功能,在执行业务操作之前和之后能够额外的添加其他操作。
那么在实际中有什么用途呢?
在web项目中,一般需要对请求和返回进行记录,同时需要对异常进行记录,这时如果把Logger放在业务类中,则每个方法都需要写一大段重复代码,于是代理类的出现解决了这个问题。
但是想一想,静态代理如果有100个类需要进行代理也就意味着要给100个类写上
implement Subject,这是不现实的。于是动态代理应运而生。
动态代理
相信大家在学习Spring的过程中都使用过AOP,其中各种Advice注解能够方便的让我们做切面编程,
回到刚才了例子,如果使用AOP来操作会是怎样的呢?
@Around(value = "log()")
public Object log(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
for (Object arg:joinPoint.getArgs()){
logger.info("请求值:"+arg.toString());
}
Object result=null;
try {
result = joinPoint.proceed();
}catch (Throwable e){
logger.error("error",e);
}
logger.info("返回值"+result.toString());
return result;
}
可以看见已经非常简洁了。那么它底层是如何实现的呢?这里就要引出主角了,JDKProxy和CGLIB
JDKProxy
使用java.lang.reflec.Proxy.newInstance进行生成代理类
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h)
里面的Class<> interfaces就是真实类实现的接口
public class app {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将生成的代理类保存
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles","true");
Subject proxySubject= (Subject) Proxy.newProxyInstance(app.class.getClassLoader(),RealSubject.class.getInterfaces(),new SubjectInvocationHandler(new RealSubject()));
proxySubject.process();
}
}
需要实现InvocationHandler
public class SubjectInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
Subject subject;
public SubjectInvocationHandler(Subject realSubject){
subject=realSubject;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before");
System.out.println("----------------------------");
Object result=null;
try {
System.out.println("开启事务");
result=method.invoke(subject,args);
System.out.println("事务提交");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("事务发现异常进行回滚");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}finally {
System.out.println("----------------------------");
System.out.println("after");
}
return result;
}
}
生成的代理类代码
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Subject {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m0;
private static Method m3;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws {
super(var1);
}
public final void process() throws {
try {
super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString");
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode");
m3 = Class.forName("staticproxy.Subject").getMethod("process");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());
}
}
}
运行结果

可以看到生成的代理类实现了Subject接口,同时持有实现的SubjectInvocationHandler,那么执行process的时候就是执行SubjectInvocationHandler的invoke方法。
CGLIB
cglib采用asm动态生成字节码技术
实际上CGLIB是使用拦截器,把方法的执行过程拦截,给方法做代理
public class SubjectInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before");
System.out.println("------------------------------");
Object result=null;
try {
result=methodProxy.invokeSuper(o,objects);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}finally {
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("after");
}
return result;
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "D:\\class");
Enhancer enhancer=new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(RealSubject.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new SubjectInterceptor());
Subject proxySubject= (Subject) enhancer.create();
proxySubject.process();
}
}
查看CGLIB生成的代理类,可以看见MethodInterceptor对象var10000调用了intercept方法。
public class RealSubject$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$13c51f84 extends RealSubject implements Factory {
public final void process() {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (var10000 != null) {
var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$process$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$process$0$Proxy);
} else {
super.process();
}
}
}
JDKProxy和CGLIB的区别
JDKProxy里面只能对实现interface的类进行代理,而CGLIB是基于继承,从而没有接口限制。
Spring中
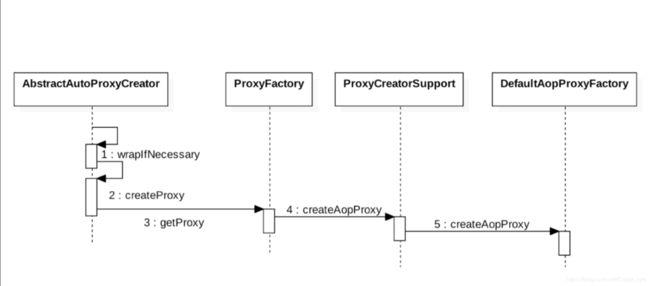
DefaultAopProxyFactory源码
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (!config.isOptimize() && !config.isProxyTargetClass() && !this.hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
} else {
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
} else {
return (AopProxy)(!targetClass.isInterface() && !Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) ? new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config) : new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config));
}
}
}
对于Spring来说,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy中proxyTargetClass默认为false,
如果proxyTargetClass为false则很可能使用JDKProxy。