R语言画韦恩图
1.安装和导入的包
install.packages("VennDiagram")
library(grid)
library(futile.logger)
library(VennDiagram)2.两个数据集
- 可以根据数据量的大小来确定圆的大小
# A simple two-set diagram (根据数据量多少而确定圆的大小)前提是知道数据集的大小和交叉个数
venn.plot <- draw.pairwise.venn(100, 70, 30, c("First", "Second"));
grid.draw(venn.plot);
grid.newpage();
grid.newpage(); #清空画板,开始画新图venn.plot <- draw.pairwise.venn(
area1 = 100, #区域1的数
area2 = 70, #区域2的数
cross.area = 30, #交叉数
category = c("First", "Second"),#分类名称
fill = c("blue", "red"),#区域填充颜色
lty = "blank", #区域边框线类型
cex = 2, #区域内部数字的字体大小
cat.cex = 2, #分类名称字体大小
cat.pos = c(285, 105), #分类名称在圆的位置,默认正上方,通过角度进行调整
cat.dist = 0.09, #分类名称距离边的距离(可以为负数)
cat.just = list(c(-1, -1), c(1, 1)), #分类名称的位置
ext.pos = 30, #线的角度 默认是正上方12点位置
ext.dist = -0.05, #外部线的距离
ext.length = 0.85, #外部线长度
ext.line.lwd = 2, #外部线的宽度
ext.line.lty = "dashed" #外部线为虚线
);
grid.draw(venn.plot); #显示图形示例:
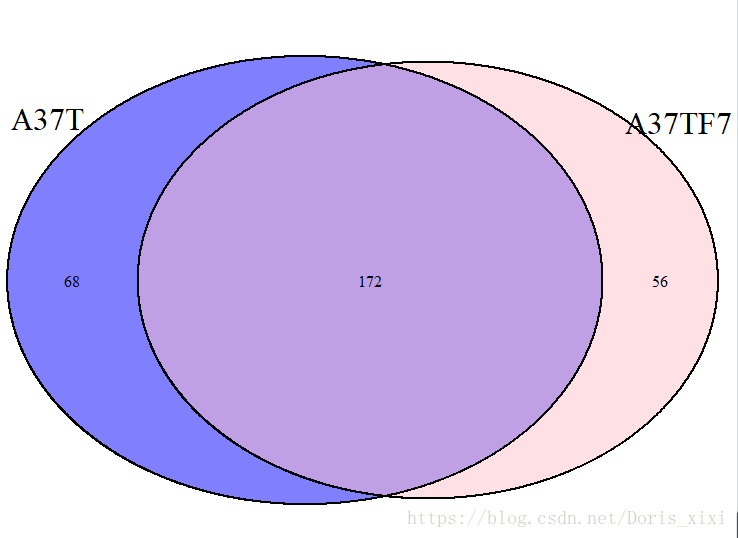
A37_venn.plot<-draw.pairwise.venn(240, 228, 172, c("A37T", "A37TF7"), fill = c("blue", "pink"),cat.cex=2);
- 不能根据数据集大小来改变圆的大小
# Same diagram as above, but without scaling(不会根据数据的多少而自动适应圆的大小)
venn.plot <- draw.pairwise.venn(100, 70, 30, c("First", "Second"), scaled = FALSE);
grid.draw(venn.plot);
grid.newpage(); #清空画板,开始画新图3.三个数据集
# A more complicated diagram
venn.plot <- draw.triple.venn(
area1 = 65,
area2 = 75,
area3 = 85,
n12 = 35,
n23 = 15,
n13 = 25,
n123 = 5,
category = c("First", "Second", "Third"),
fill = c("blue", "red", "green"),
lty = "blank",
cex = 2,
cat.cex = 2,
cat.col = c("blue", "red", "green")
);
grid.draw(venn.plot);#画图展示
# Writing to file
tiff(filename = "Triple_Venn_diagram.tiff", compression = "lzw"); #保存图片
dev.off(); #退出画图
示例:
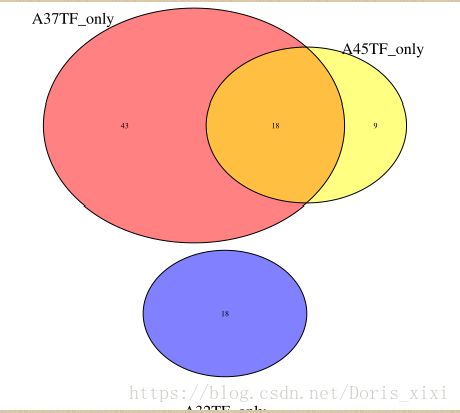
Tumor_venn.plot<- draw.triple.venn(area1 = 169,area2 = 61,area3 =44 ,n12 = 0,n23 = 0,n13 = 16,n123 =0,category = c("A32T_only", "A37T_only", "A45T_only"), fill = c("blue", "red","yellow"),cat.cex=2)
grid.newpage();4.四个数据集
# Reference four-set diagram
venn.plot <- draw.quad.venn(
area1 = 72,
area2 = 86,
area3 = 50,
area4 = 52,
n12 = 44,
n13 = 27,
n14 = 32,
n23 = 38,
n24 = 32,
n34 = 20,
n123 = 18,
n124 = 17,
n134 = 11,
n234 = 13,
n1234 = 6,
category = c("First", "Second", "Third", "Fourth"),
fill = c("orange", "red", "green", "blue"),
lty = "dashed",
cex = 2,
cat.cex = 2,
cat.col = c("orange", "red", "green", "blue")
);
grid.draw(venn.plot);#画图展示5.通过数据列表进行制作图
- 两个数据集
# a more elaborate two-set Venn diagram with title and subtitle
venn.plot <- venn.diagram(
x = list( "A" = 1:100,"B" = 96:140),
filename = "c:/Venn_22set_complex.tiff",
col = "transparent",
fill = c("red", "green"),
cex = 2.5,
cat.cex = 2.5,
rotation.degree = 0,
main = "Complex Venn Diagram",
main.cex = 2,
sub.cex = 1,
alpha = 0.50
); # x为向量示例:
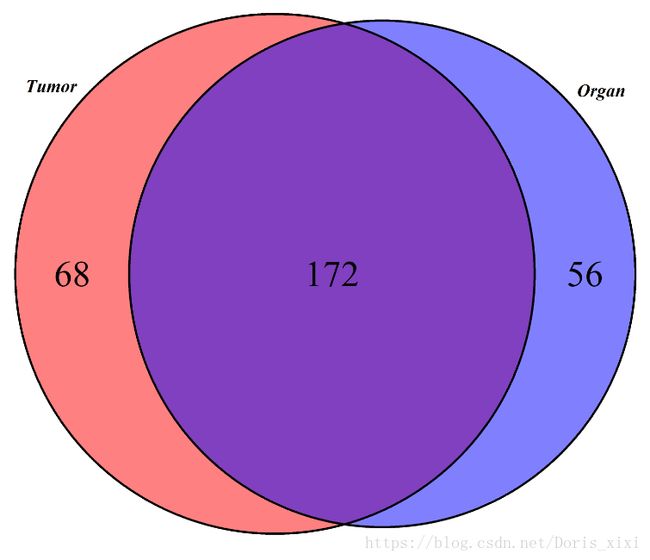
venn.diagram(x=list(Tumor=test_A37T[,2],Organ=test_A37TF7[,2]),filename="A37.tif",euler.d = TRUE,scaled = TRUE,fill=c("red","blue"), alpha=c(0.5,0.5), cex=2, cat.fontface=4);会把结果输出到当前目录,结果如下:
- 三个数据集
A <- sample(1:1000, 400, replace = FALSE);
B <- sample(1:1000, 600, replace = FALSE);
C <- sample(1:1000, 350, replace = FALSE);
venn.plot <- venn.diagram(
#数据列表
x = list(
A = A,
B = B,
C = C
),
filename ="C:\\1.tiff", #保存路径
height = 450,
width = 450,
resolution =300,
#imagetype="png",
col = "transparent", #指定图形的圆周边缘颜色 transparent 透明
fill = c("cornflowerblue", "green", "darkorchid1"), #填充颜色
alpha = 0.50, #透明度
label.col = c("orange", "white", "darkorchid4", "white",
"white", "darkgreen", "white"),
cex = 0.45, #每个区域label名称的大小
fontfamily = "serif", #字体
fontface = "bold", #字体格式
cat.col = c("darkblue", "darkgreen", "darkorchid4"), #分类颜色
cat.cex = 0.45, #每个分类名称大小
cat.pos = c(100, 260, 0), #
cat.dist = c(0.07, 0.07, 0.05), #
cat.fontfamily = "serif", #分类字体
rotation.degree =180, #旋转角度
margin = 0.2 #在网格单元中给出图周围空白量的编号
);
可以不保存查看图片,但是效果不佳(命令如下,但是需要首先把filename设置为(filename=NULL))
grid.draw(venn.plot);
dev.off();- 四个 数据集
#sample为抽样函数,首先指定抽样范围,然后制定抽样个数,最后指定是否允许同样的抽样值
A <- sample(1:1000, 400, replace = FALSE);
B <- sample(1:1000, 600, replace = FALSE);
C <- sample(1:1000, 350, replace = FALSE);
D <- sample(1:1000, 550, replace = FALSE);
E <- sample(1:1000, 375, replace = FALSE);
venn.plot <- venn.diagram(
#数据列表
x = list(
A = A,
D = D,
B = B,
C = C
),
filename = "Venn_4set_pretty.tiff", #保存路径
col = "transparent", #指定图形的圆周边缘颜色 transparent 透明
fill = c("cornflowerblue", "green", "yellow", "darkorchid1"), #填充颜色
alpha = 0.50, #透明度
label.col = c("orange", "white", "darkorchid4", "white",
"white", "white", "white", "white", "darkblue", "white",
"white", "white", "white", "darkgreen", "white"),
cex = 1.5, #每个区域label名称的大小
fontfamily = "serif", #字体
fontface = "bold", #字体格式
cat.col = c("darkblue", "darkgreen", "orange", "darkorchid4"), #分类颜色
cat.cex = 1.5, #每个分类名称大小
cat.pos = 0, #
cat.dist = 0.07, #
cat.fontfamily = "serif", #分类字体
rotation.degree = 270, #旋转角度
margin = 0.2 #在网格单元中给出图周围空白量的编号
);参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u011808596/article/details/80974250