spring resteasy单元测试
mock框架在web项目中进行单元测试非常方便,resteasy作为一个优秀的rest框架,也为我们提供了mock测试工具,但是并没有替我们集成spring,因此我们编写的Resource类无法完成bean的注入,进行单元测试时比较麻烦。我们希望像springmvc那样非常方便地进行单元测试(http://blog.csdn.net/dwade_mia/article/details/77451605),为了解决该问题,笔者扩展了spring test的代码,完成spring test与resteasy mock的集成。
spring test源码解读
SpringJUnit4ClassRunner
SpringJUnit4ClassRunner集成junit测试入口
TestContextManager由SpringJUnit4ClassRunner创建,负责创建TestContext上下文
下面是一个常用的Mock测试类
@WebAppConfiguration(value="src/main/webapp")
@ContextConfiguration( locations={"classpath*:spring-config/applicationContext.xml"} )
@RunWith( SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class )
public class BaseApiTest extends AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests {
// ......
}其中RunWith指定SpringJUnit4ClassRunner,而SpringJUnit4ClassRunner重写了createTest方法,在junit启动的时候,会调用createTest方法,包括创建Spring容器,对Test测试类进行属性注入等,下图是方法调用的关系图

SpringJunit4ClassRunner.java
//初始化的时候会创建TestContextManager,用于获取测试基类的信息,比如注解等,由TestContextManager创建
public SpringJUnit4ClassRunner(Class clazz) throws InitializationError {
super(clazz);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SpringJUnit4ClassRunner constructor called with [" + clazz + "]");
}
ensureSpringRulesAreNotPresent(clazz);
this.testContextManager = createTestContextManager(clazz);
}
protected TestContextManager createTestContextManager(Class clazz) {
return new TestContextManager(clazz);
}
//重写junit实例化对象的方法
protected Object createTest() throws Exception {
Object testInstance = super.createTest();
getTestContextManager().prepareTestInstance(testInstance);
return testInstance;
}TestExecutionListener
以下是spring自带的TestExecutionListener,比如测试类的属性注入,其中DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener用于对测试类进行注入属性注入,当然我们也可以在测试类上面添加自定义的监听器

在创建测试类实例的时候,需要对测试类进行处理,最终调用TextContextManager的prepareTestInstance方法执行监听器的处理操作,默认包括ServletTestExecutionListener, DirtiesContextBeforeModesTestExecutionListener, DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener, DirtiesContextTestExecutionListener,如果是继承了AbstractTransactionalJUnit4SpringContextTests的时候,还会添加TransactionTestExecutionListener这个Listener
SpringJunit4ClassRunner.java
protected Object createTest() throws Exception {
Object testInstance = super.createTest();
getTestContextManager().prepareTestInstance(testInstance);
return testInstance;
}TestContextManager.java
@Override
public void prepareTestInstance(TestContext testContext) throws Exception {
setUpRequestContextIfNecessary(testContext);
}
private void setUpRequestContextIfNecessary(TestContext testContext) {
if (!isActivated(testContext) || alreadyPopulatedRequestContextHolder(testContext)) {
return;
}
//获取Spring容器,如果没有的话,由测试类设置的@ContextConfiguration信息创建容器
ApplicationContext context = testContext.getApplicationContext();
if (context instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
WebApplicationContext wac = (WebApplicationContext) context;
ServletContext servletContext = wac.getServletContext();
// other code......
MockServletContext mockServletContext = (MockServletContext) servletContext;
MockHttpServletRequest request = new MockHttpServletRequest(mockServletContext);
request.setAttribute(CREATED_BY_THE_TESTCONTEXT_FRAMEWORK, Boolean.TRUE);
MockHttpServletResponse response = new MockHttpServletResponse();
ServletWebRequest servletWebRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(servletWebRequest);
testContext.setAttribute(POPULATED_REQUEST_CONTEXT_HOLDER_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
testContext.setAttribute(RESET_REQUEST_CONTEXT_HOLDER_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) wac;
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf = configurableApplicationContext.getBeanFactory();
//我们可以在测试类上面注入以下request、response对象
bf.registerResolvableDependency(MockHttpServletResponse.class, response);
bf.registerResolvableDependency(ServletWebRequest.class, servletWebRequest);
}
}
}下图是一个调用栈,ServerletTestExecutionListner会调用getApplicationContext(),如果当前上下文中没有Spring容器的话,会由cacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate.loadContext(this.mergedContextConfiguration)方法创建Spring容器,如果我们想自己创建Spring容器的话,需要注入一个自定义的cacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate,并重写loadContext方法。

这个CacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate接口默认只有一个实现DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate,我们看下调用逻辑,原来默认是由DefaultTestContext调用的,而DefaultTestContext是由TestContextManager创建的,我们找到TestContextManager
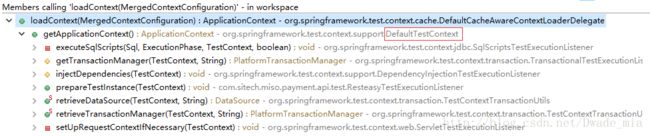

咱们看下这个TestContextManager的注释,如果我们在测试类上面定义了@BootstrapWith,就使用自定义的,否则会使用默认的DefaultTestContextBootstrapper,如果我们使用了@WebAppConfiguration则会使用WebTestContextBootstrapper,跟进BootstrapUtils.resoveTestContextBootstrapper方法便知这个逻辑处理

public TestContextManager(Class testClass) {
this(BootstrapUtils.resolveTestContextBootstrapper(BootstrapUtils.createBootstrapContext(testClass)));
}BootstrapUtils.java
private static Class resolveDefaultTestContextBootstrapper(Class testClass) throws Exception {
ClassLoader classLoader = BootstrapUtils.class.getClassLoader();
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes(testClass,
WEB_APP_CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_CLASS_NAME, false, false);
if (attributes != null) {
return ClassUtils.forName(DEFAULT_WEB_TEST_CONTEXT_BOOTSTRAPPER_CLASS_NAME, classLoader);
}
return ClassUtils.forName(DEFAULT_TEST_CONTEXT_BOOTSTRAPPER_CLASS_NAME, classLoader);
}spring test源码扩展,集成resteasy
首先,看一下TestContextBootstrapper的类图,因为是Web容器,所以我们继承WebTestContextBootstrapper,重写getCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate()方法,返回我们自定义的CacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate实现类

public class ResteasyTestContextBootstrapper extends WebTestContextBootstrapper {
@Override
protected CacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate getCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate() {
return new ResteasyCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate();
}
}/**
* 参考AbstractGenericWebContextLoader.loadContext的方法,使用MockServletContext
* 创建Listener
* @author huangxf
* @date 2017年4月30日
*/
public class ResteasyCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate extends
DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate {
private ServletContext servletContext;
@Override
protected ApplicationContext loadContextInternal(
MergedContextConfiguration mergedConfig)
throws Exception {
if (!(mergedConfig instanceof WebMergedContextConfiguration)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"Cannot load WebApplicationContext from non-web merged context configuration %s. "
+ "Consider annotating your test class with @WebAppConfiguration.", mergedConfig));
}
WebMergedContextConfiguration webMergedConfig = (WebMergedContextConfiguration) mergedConfig;
String resourceBasePath = webMergedConfig.getResourceBasePath();
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = resourceBasePath.startsWith(ResourceLoader.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX) ? new DefaultResourceLoader()
: new FileSystemResourceLoader();
this.servletContext = new MockServletContext( resourceBasePath, resourceLoader );
StringBuilder locations = new StringBuilder();
for ( String location : webMergedConfig.getLocations() ) {
locations.append( location ).append( "," );
}
locations.deleteCharAt( locations.length() - 1 );
servletContext.setInitParameter( "contextConfigLocation", locations.toString() );
//初始化ServletListener
ServletContextListener bootstrapListener = new SpringResteasyBootstrap();
ServletContextEvent event = new ServletContextEvent( servletContext );
bootstrapListener.contextInitialized( event );
//存放在上下文中
servletContext.setAttribute( SpringResteasyBootstrap.class.getName(), bootstrapListener );
return WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext( servletContext );
}
@Override
public void closeContext(
MergedContextConfiguration mergedContextConfiguration,
HierarchyMode hierarchyMode) {
ServletContextListener listener = (ServletContextListener)servletContext.getAttribute( SpringResteasyBootstrap.class.getName() );
listener.contextDestroyed( new ServletContextEvent( servletContext ) );
super.closeContext(mergedContextConfiguration, hierarchyMode);
}
}于是我们的Test测试类变成这样:
@WebAppConfiguration(value="src/main/webapp")
@ContextConfiguration( locations={"classpath*:spring-config/applicationContext.xml"} )
@RunWith( SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class )
@BootstrapWith( value=ResteasyTestContextBootstrapper.class )
public class BaseResteasyTest extends AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests {
protected Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger( this.getClass() );
@Resource
protected WebApplicationContext wac;
protected HttpServletDispatcher dispatcher;
@Before
public void beforeTest() throws ServletException {
ServletContext servletContext = wac.getServletContext();
MockServletConfig config = new MockServletConfig( servletContext );
this.dispatcher = new HttpServletDispatcher();
dispatcher.init( config );
}
protected void logResponse( MockHttpResponse response ) {
logger.info( "status:{}", response.getStatus() );
logger.info( "Response content:{}", response.getContentAsString() );
}
}我们由@BootstrapWith指定ResteasyCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate,由它负责创建相关的ServletListener,由于项目里面集成了Resteasy和Spring,因此创建Resteasy和Spring的监听器,该逻辑与web容器的启动逻辑相同
这样便初始化了Spring和Resteasy的ServletListener,还需要初始化Resteasy的HttpServletDispatcher,我们可以在测试类中可以注入WebapplicationContext,这样便可以获取ServletContext,在@BeforeTest方法中直接new出HttpServletDispatcher实例再调用init方法即可。
那么,如何使用呢?在servlet容器中是根据我们设置的url-pattern去寻找对应的Servlet,从而调用service方法即可,我们也可以用调用HttpServletDispatcher提供的getDispatcher().invoke()方法,只不过是传入的参数不同而已。
public class PaymentApiTest extends BaseResteasyTest {
@Test
public void testPayOff() throws Exception {
GatewayPayOffReq req = new GatewayPayOffReq();
req.setPartnerId( "10000" );
String json = "{\"data\":" + JsonUtils.toJson( req ) + "}";
MockHttpRequest httpRequest = MockHttpRequest.post( "/pay/payoff" )
.contentType( MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON ).accept( MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON )
.content( json.getBytes( "UTF-8" ) );
MockHttpResponse httpResponse = new MockHttpResponse();
//请求
dispatcher.getDispatcher().invoke( httpRequest, httpResponse );
//打印响应结果
logResponse( httpResponse );
}Springmvc MockMvc
另外,我们再来研究下Spring的MockMvc测试类,看下Spring是怎么做的,最终发现逻辑上是一致的,只不过提供了很多功能。
/**
* 使用mock测试web服务
* @author huangxf
* @date 2017年4月12日
*/
@WebAppConfiguration(value="src/main/webapp")
@ContextConfiguration( locations={"classpath*:spring-config/core/application-consumer.xml",
"classpath*:spring-config/core/springmvc-servlet.xml"} )
@RunWith( SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class )
public class BaseControllerTest extends AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests {
@Resource
protected WebApplicationContext wac;
protected MockMvc mockMvc;
@Before
public void beforeTest() {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup( wac ).build();
}
}而在这个里面又调用了父类的createMockMvc方法,在这个里面对TestDispatcherServlet(DispatcherServlet的子类)进行初始化,最终返回持有TestDispatcherServlet、Filter实例的MockMvc对象
MockMvcBuilderSupport.java
protected final MockMvc createMockMvc(Filter[] filters, MockServletConfig servletConfig,
WebApplicationContext webAppContext, RequestBuilder defaultRequestBuilder,
List globalResultMatchers, List globalResultHandlers,
List dispatcherServletCustomizers) {
ServletContext servletContext = webAppContext.getServletContext();
TestDispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new TestDispatcherServlet(webAppContext);
if (dispatcherServletCustomizers != null) {
for (DispatcherServletCustomizer customizers : dispatcherServletCustomizers) {
customizers.customize(dispatcherServlet);
}
}
try {
dispatcherServlet.init(servletConfig);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
// should never happen..
throw new MockMvcBuildException("Failed to initialize TestDispatcherServlet", ex);
}
//创建对象,并持有TestDispatcherServlet和Filter实例
mockMvc.setDefaultRequest(defaultRequestBuilder);
mockMvc.setGlobalResultMatchers(globalResultMatchers);
mockMvc.setGlobalResultHandlers(globalResultHandlers);
return mockMvc;
} 在我们调用MockMvc的perform方法发起请求时,在这个方法内部会创建FilterChain的Mock实例MockFilterChain,然后挨个调用Filter的doFilter方法,和真实的Servlet容器一样。在MockFilterChain的构造方法里面,会把dispatcherServlet包装成一个Filter,调用最后一个Filter的doFilter方法时,会调用dispatcherServlet的service()方法,这样和web的流程就相同了。
public ResultActions perform(RequestBuilder requestBuilder) throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequest request = requestBuilder.buildRequest(this.servletContext);
MockHttpServletResponse response = new MockHttpServletResponse();
if (requestBuilder instanceof SmartRequestBuilder) {
request = ((SmartRequestBuilder) requestBuilder).postProcessRequest(request);
}
final MvcResult mvcResult = new DefaultMvcResult(request, response);
request.setAttribute(MVC_RESULT_ATTRIBUTE, mvcResult);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(new ServletRequestAttributes(request, response));
//在MockFilterChain的构造方法里面,会把dispatcherServlet包装成一个Filter,调用最后一个Filter的doFilter方法时,会调用dispatcherServlet的service()方法
MockFilterChain filterChain = new MockFilterChain(this.servlet, this.filters);
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
//......
return new ResultActions() {
//......
};
}相关的代码在net.dwade.plugins.resteasy.mock这个包下面,github地址:https://github.com/huangxfchn/dwade/tree/master/framework-plugins