机器学习实战笔记——线性回归
一 线性归回拟合
回归的目的是预测数值型的目标值,相当于自变量和因变量的关系,最直接的预测方法就是数学公式。如果自变量和因变量满足线性关系,那么他们的关系可以用线性方程y=wx+b 表示w和b就是回归系数。在知道x和y 的前提下,目标是找到使误差(预测值和实际值之间的距离)最小的w。
对一维向量:有n个点(x1,y1),…(xi,yi),…(xn,yn)
对w求导令其为0,可以得到w的估计值。
y=wx+b推广到多维:
假设满足Y=XTw
平方误差:
用矩阵乘法表示:
![]()
对w求导令其为0:
![]()
解得,
![]()
两个数据集得到相同的结果。比较相关性发现,数据集1的相关性比数据集2高。说明这个线性模型更适合数据集1
二 局部加权线性回归
线性回归为了满足方差最小,会出现欠拟合,特别是在自变量和因变量没有明显线性关系时。
改进算法:每个点对平方误差的影响具有不同权值,改进后误差公式为
代码from numpy import *
def loadDataSet(fileName): #general function to parse tab -delimited floats
numFeat = len(open(fileName).readline().split('\t')) - 1 #get number of fields
dataMat = []; labelMat = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr =[]
curLine = line.strip().split('\t')
for i in range(numFeat):
lineArr.append(float(curLine[i]))
dataMat.append(lineArr)
labelMat.append(float(curLine[-1]))
return dataMat,labelMat
def standRegres(xArr,yArr):
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat = mat(yArr).T
xTx = xMat.T*xMat
if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0:
print ("This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse")
return
ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T*yMat)
return ws
def lwlr(testPoint,xArr,yArr,k=1.0):
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat = mat(yArr).T
m = shape(xMat)[0]
weights = mat(eye((m)))
for j in range(m): #next 2 lines create weights matrix
diffMat = testPoint - xMat[j,:] #
weights[j,j] = exp(diffMat*diffMat.T/(-2.0*k**2))
xTx = xMat.T * (weights * xMat)
if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0:
print ("This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse")
return
ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T * (weights * yMat))
return testPoint * ws
def lwlrTest(testArr,xArr,yArr,k=1.0): #loops over all the data points and applies lwlr to each one
m = shape(testArr)[0]
yHat = zeros(m)
for i in range(m):
yHat[i] = lwlr(testArr[i],xArr,yArr,k)
return yHat
def lwlrTestPlot(xArr,yArr,k=1.0): #same thing as lwlrTest except it sorts X first
yHat = zeros(shape(yArr)) #easier for plotting
xCopy = mat(xArr)
xCopy.sort(0)
for i in range(shape(xArr)[0]):
yHat[i] = lwlr(xCopy[i],xArr,yArr,k)
return yHat,xCopy
def rssError(yArr,yHatArr): #yArr and yHatArr both need to be arrays
return ((yArr-yHatArr)**2).sum()
def ridgeRegres(xMat,yMat,lam=0.2):
xTx = xMat.T*xMat
denom = xTx + eye(shape(xMat)[1])*lam
if linalg.det(denom) == 0.0:
print ("This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse")
return
ws = denom.I * (xMat.T*yMat)
return ws
def ridgeTest(xArr,yArr):
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat=mat(yArr).T
yMean = mean(yMat,0)
yMat = yMat - yMean #to eliminate X0 take mean off of Y
#regularize X's
xMeans = mean(xMat,0) #calc mean then subtract it off
xVar = var(xMat,0) #calc variance of Xi then divide by it
xMat = (xMat - xMeans)/xVar
numTestPts = 30
wMat = zeros((numTestPts,shape(xMat)[1]))
for i in range(numTestPts):
ws = ridgeRegres(xMat,yMat,exp(i-10))
wMat[i,:]=ws.T
return wMat
def regularize(xMat):#regularize by columns
inMat = xMat.copy()
inMeans = mean(inMat,0) #calc mean then subtract it off
inVar = var(inMat,0) #calc variance of Xi then divide by it
inMat = (inMat - inMeans)/inVar
return inMat
def stageWise(xArr,yArr,eps=0.01,numIt=100):
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat=mat(yArr).T
yMean = mean(yMat,0)
yMat = yMat - yMean #can also regularize ys but will get smaller coef
xMat = regularize(xMat)
m,n=shape(xMat)
#returnMat = zeros((numIt,n)) #testing code remove
ws = zeros((n,1)); wsTest = ws.copy(); wsMax = ws.copy()
for i in range(numIt):
print (ws.T)
lowestError = inf;
for j in range(n):
for sign in [-1,1]:
wsTest = ws.copy()
wsTest[j] += eps*sign
yTest = xMat*wsTest
rssE = rssError(yMat.A,yTest.A)
if rssE < lowestError:
lowestError = rssE
wsMax = wsTest
ws = wsMax.copy()
#returnMat[i,:]=ws.T
#return returnMat
#def scrapePage(inFile,outFile,yr,numPce,origPrc):
# from BeautifulSoup import BeautifulSoup
# fr = open(inFile); fw=open(outFile,'a') #a is append mode writing
# soup = BeautifulSoup(fr.read())
# i=1
# currentRow = soup.findAll('table', r="%d" % i)
# while(len(currentRow)!=0):
# title = currentRow[0].findAll('a')[1].text
# lwrTitle = title.lower()
# if (lwrTitle.find('new') > -1) or (lwrTitle.find('nisb') > -1):
# newFlag = 1.0
# else:
# newFlag = 0.0
# soldUnicde = currentRow[0].findAll('td')[3].findAll('span')
# if len(soldUnicde)==0:
# print "item #%d did not sell" % i
# else:
# soldPrice = currentRow[0].findAll('td')[4]
# priceStr = soldPrice.text
# priceStr = priceStr.replace('$','') #strips out $
# priceStr = priceStr.replace(',','') #strips out ,
# if len(soldPrice)>1:
# priceStr = priceStr.replace('Free shipping', '') #strips out Free Shipping
# print "%s\t%d\t%s" % (priceStr,newFlag,title)
# fw.write("%d\t%d\t%d\t%f\t%s\n" % (yr,numPce,newFlag,origPrc,priceStr))
# i += 1
# currentRow = soup.findAll('table', r="%d" % i)
# fw.close()
from time import sleep
import json
import urllib.request
def searchForSet(retX, retY, setNum, yr, numPce, origPrc):
sleep(10)
myAPIstr = 'AIzaSyD2cR2KFyx12hXu6PFU-wrWot3NXvko8vY'
searchURL = 'https://www.googleapis.com/shopping/search/v1/public/products?key=%s&country=US&q=lego+%d&alt=json' % (myAPIstr, setNum)
pg = urllib.request.urlopen(searchURL)
retDict = json.loads(pg.read())
for i in range(len(retDict['items'])):
try:
currItem = retDict['items'][i]
if currItem['product']['condition'] == 'new':
newFlag = 1
else: newFlag = 0
listOfInv = currItem['product']['inventories']
for item in listOfInv:
sellingPrice = item['price']
if sellingPrice > origPrc * 0.5:
print ("%d\t%d\t%d\t%f\t%f" % (yr,numPce,newFlag,origPrc, sellingPrice))
retX.append([yr, numPce, newFlag, origPrc])
retY.append(sellingPrice)
except: print ('problem with item %d' % i)
def setDataCollect(retX, retY):
searchForSet(retX, retY, 8288, 2006, 800, 49.99)
searchForSet(retX, retY, 10030, 2002, 3096, 269.99)
searchForSet(retX, retY, 10179, 2007, 5195, 499.99)
searchForSet(retX, retY, 10181, 2007, 3428, 199.99)
searchForSet(retX, retY, 10189, 2008, 5922, 299.99)
searchForSet(retX, retY, 10196, 2009, 3263, 249.99)
def crossValidation(xArr,yArr,numVal=10):
m = len(yArr)
indexList = range(m)
errorMat = zeros((numVal,30))#create error mat 30columns numVal rows
for i in range(numVal):
trainX=[]; trainY=[]
testX = []; testY = []
random.shuffle(indexList)
for j in range(m):#create training set based on first 90% of values in indexList
if j < m*0.9:
trainX.append(xArr[indexList[j]])
trainY.append(yArr[indexList[j]])
else:
testX.append(xArr[indexList[j]])
testY.append(yArr[indexList[j]])
wMat = ridgeTest(trainX,trainY) #get 30 weight vectors from ridge
for k in range(30):#loop over all of the ridge estimates
matTestX = mat(testX); matTrainX=mat(trainX)
meanTrain = mean(matTrainX,0)
varTrain = var(matTrainX,0)
matTestX = (matTestX-meanTrain)/varTrain #regularize test with training params
yEst = matTestX * mat(wMat[k,:]).T + mean(trainY)#test ridge results and store
errorMat[i,k]=rssError(yEst.T.A,array(testY))
#print errorMat[i,k]
meanErrors = mean(errorMat,0)#calc avg performance of the different ridge weight vectors
minMean = float(min(meanErrors))
bestWeights = wMat[nonzero(meanErrors==minMean)]
#can unregularize to get model
#when we regularized we wrote Xreg = (x-meanX)/var(x)
#we can now write in terms of x not Xreg: x*w/var(x) - meanX/var(x) +meanY
xMat = mat(xArr); yMat=mat(yArr).T
meanX = mean(xMat,0); varX = var(xMat,0)
unReg = bestWeights/varX
print ("the best model from Ridge Regression is:\n",unReg)
print ("with constant term: ",-1*sum(multiply(meanX,unReg)) + mean(yMat))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
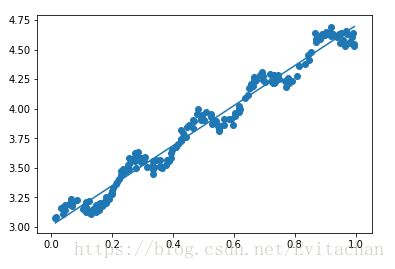
def test1():
xArr,yArr=loadDataSet('ex1.txt')
ws = standRegres(xArr,yArr)
xMat=mat(xArr)
yMat=mat(yArr)
yHat = xMat*ws
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0], yMat.T[:,0].flatten().A[0])
xCopy=xMat.copy()
xCopy.sort(0)
yHat=xCopy*ws
ax.plot(xCopy[:,1],yHat)
plt.show()
def test2():
xArr,yArr=loadDataSet('ex0.txt')
ws = standRegres(xArr,yArr)
xMat=mat(xArr)
yMat=mat(yArr)
yHat = xMat*ws
srtInd = xMat[:,1].argsort(0)
xSort=xMat[srtInd][:,0,:]
yHat = lwlrTest(xArr, xArr, yArr,0.002)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(xSort[:,1],yHat[srtInd])
ax.scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0], mat(yArr).T.flatten().A[0] , s=2,c='red')
plt.show()
test2()