C ++ Primer Plus 第六版 第十章编程练习答案
一个类来表示银行账户,数据成员包括储户姓名、账号(使用字符串)和存款。成员函数执行如下操作:
①创建一个对象并将其初始化;
②显示储户姓名、账号和存款;
③存入参数指定的存款;
④取出参数指定的款项。
//bank.h
#include
using namespace std;
#ifndef BANK_H_INCLUDED
#define BANK_H_INCLUDED
class Bank
{
private:
string name;
string id;
double money;
public:
Bank(string n,string i,double m):name(n),id(i),money(m){}
void show();
void deposit(double );
void withdraw(double );
};
#endif // BANK_H_INCLUDED //main.cpp
#include
#include
#include"bank.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
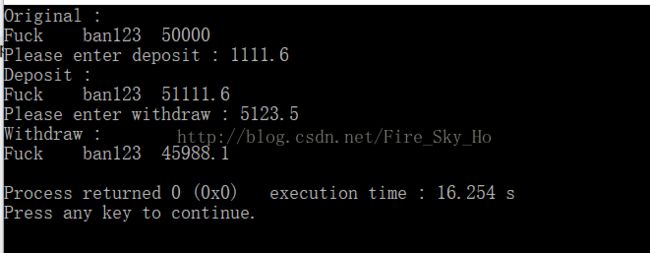
Bank bank{"Fuck", "ban123", 50000};
cout << "Original :" << endl;
bank.show();
cout << "Please enter deposit : ";
double d, w;
cin >> d;
bank.deposit ( d );
cout << "Deposit :" << endl;
bank.show();
cout << "Please enter withdraw : ";
cin >> w;
bank.withdraw ( w );
cout << "Withdraw :" << endl;
bank.show();
return 0;
}
void Bank::show()
{
cout << name << '\t' << id << '\t' << money << endl;
}
void Bank::deposit ( double d )
{
money += d;
}
void Bank::withdraw ( double w )
{
money -= w;
}
2.下面是一个非常简单的类定义:
class Person {
private:
static const LIMIT = 25;
string lname; //Person's last name
char fname[LIMIT]; //Person's first name
public:
Person() {lname = ""; fname[0]='\0'; } //#1
Person(const string & ln, const char* fn = "Heyyou"); //#2
// the following methods display lname and fname
void Show() const; //firstname lastname format
void FormalShow() const; //lastname, firstname format
};
他使用了一个string对象和一个字符数组,让您能够比较他们的用法。请提供未定义的方法的代码,已完成这个类的实现。再编写一个使用这个类的程序,它使用了三种可能的构造函数调用(没有参数、一个参数和两个参数)以及两种显示方法。下面是一个使用这些构造函数和方法的例子:
Person one; //use default constructor
Person two("Smythecraft"); //use #2 with one default argument
Person three("Dimwiddy", "Sam"); //use #2, no defaults
one.Show();
cout<
// etc. for two and three.
#include
#include
#include
#include"Person.h"
int main()
{
Person one;
Person two ( "Smythecratf" );
Person three ( "Dimwiddy", "Sam" );
std::cout<<"one :"< 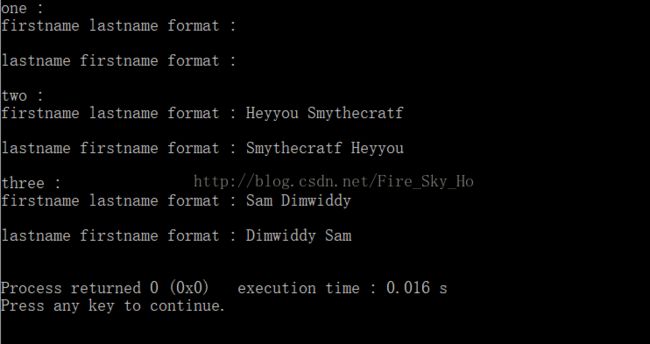
6.下面是一个类声明
class Move
{
private:
double x;
double y;
public:
Move(double a = 0, double b = 0); //set x,y to a,b
showmove()const; //shows current x,y values
Move add(const Move & m) const;
// this function adds x of m to x of invoking object to get new x,
// add y of m to y of invoking object to get new y, creates a new
// move object initialized to new x,y values and returns it
reset(double a = 0, double b = 0); //resets x,y to a,b
};
请提供成员函数的定义和测试这个类的程序。
//main.cpp
#include
#include"Move.h"
int main()
{
Move m[3];
int i;
double x, y;
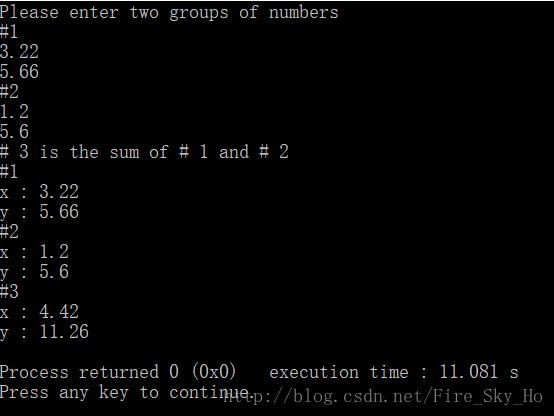
std::cout << "Please enter two groups of numbers" << std::endl;
for ( i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
std::cout << "#" << i + 1 << std::endl;
std::cin >> x >> y;
m[i] = m[i].reset ( x, y );
}
std::cout << "# 3 is the sum of # 1 and # 2 " << std::endl;
std::cout << "#1" << std::endl;
m[0].showmove();
std::cout << "#2" << std::endl;
m[1].showmove();
std::cout << "#3" << std::endl;
m[0].add ( m[1] ).showmove();
return 0;
}
Move Move::add ( const Move & m ) const
{
Move m3;
m3.x = x + m.x;
m3.y = y + m.y ;
return m3;
}
void Move::showmove() const
{
std::cout << "x : " << x << std::endl << "y : " << y << std::endl;
}
Move Move::reset ( double a, double b )
{
Move t;
t.x = a;
t.y = b;
return t;
}
//Move.cpp
#ifndef MOVE_H_INCLUDED
#define MOVE_H_INCLUDED
class Move
{
private:
double x;
double y;
public:
Move ( double a = 0, double b = 0 ):x(a),y(b){}//set x,y to a,b
void showmove() const; //shows current x,y values
Move add ( const Move & m ) const;
// this function adds x of m to x of invoking object to get new x,
// add y of m to y of invoking object to get new y, creates a new
// move object initialized to new x,y values and returns it
Move reset ( double a = 0, double b = 0 ); //resets x,y to a,b
};
#endif // MOVE_H_INCLUDED
7.Betelgeusean plorg有这些特征。
数据:
①plorg的名称不超过19个字符;
②plorg有满意指数(CI),这是一个整数。
操作:
①新的plorg将有名称,其CI值为50;
②plorg的CI可以修改;
③plorg可以报告其名称和CI;
④plorg的默认名称为“Plorga”。
请编写一个Plorg类声明(包括数据成员和成员函数原型)来表示plorg,并编写成员函数的函数定义。然后编写一个小程序,以演示Plorg类的所有特性。
//main.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include"plorg.h"
int main()
{
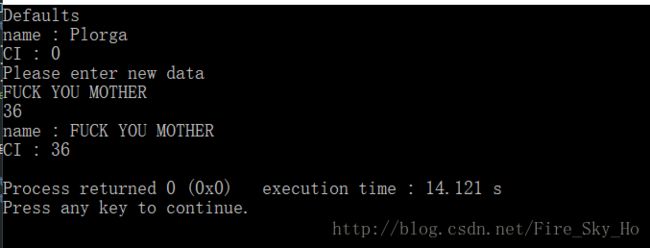
plorg p;
std::cout << "Defaults" << std::endl;
p.show();
p.set();
p.show();
return 0;
}
void plorg::show()
{
std::cout << "name : " << name << std::endl;
std::cout << "CI : " << CI << std::endl;
}
void plorg::set()
{
std::string str;
std::cout << "Please enter new data" << std::endl;
std::cout << "name : ";
getline ( std::cin, str );
while ( str.size() > 19 )
{
std::cerr << "More than 19 characters, please re-enter" << std::endl;
std::cin.clear();
std::cin.sync();
std::cout << "name : ";
getline ( std::cin, str );
}
int n;
std::cout << "CI : ";
std::cin>>n;
name = str;
CI = n;
}
//plorg.h
#include
#ifndef PLORE_H_INCLUDED
#define PLORE_H_INCLUDED
class plorg
{
std::string name;
int CI;
public:
plorg(std::string n="Plorga",int C=0):name(n),CI(C){}
void show();
void set();
};
#endif // PLORE_H_INCLUDED
8.可以将简单列表描述成下面这样:
①可存储0或多个某种类型的列表;
②可创建空列表;
③可在列表中添加数据项;
④可确定列表是否为空;
⑤可确定列表是否为满;
⑥可访问列表中的每一个数据项,并对他执行某种操作。
可以看到,这个列表确实很简单,例如,他不允许插入或删除数据项。
请设计一个List类来表示这种抽象类型,您应提供头文件list.h和实现文件list.cpp,前者包含类定义,后者包含类方法的实现。您还应创建一个简短的程序来使用这个类。
该列表的规范很简单,这主要旨在简化这个编程练习。可以选择使用数据或链表来实现该列表,但公有接口不应依赖于所做的选择。也就是说,公有接口不应有数组索引、节点指针等。应使用某种通用概念来表达创建列表、在列表中添加数据项等操作。对访问数据项以及执行操作,通常应使用函数指针作为参数的函数来处理:
void visit(void (*pf)(Item &));
其中,pf指向一个将Item引用作为参数的函数(不是成员函数),Item是列表中数据项的类型。visit()函数将该函数用于列表中的每个数据项。