Hadoop 之 Avro
从结构上看,Avro和SequenceFile的很相似。schema被序列成Header的一部分,可以是反序列化变的简单。每个block都包含一系列Avro记录,默认情况下,大小为16KB。Avro数据文件支持压缩,并且可切分。
序列化与反序列化
使用程序从数据流中读/写 Avro数据,首先需要一个Avro模式文件。
Avro 模式文件(.avsc):
{
"namespace": "com.hadoop2.data",
"type": "record",
"name": "StringPair",
"doc": "A pair of strings.",
"fields": [
{
"name": "left",
"type": "string"
},
{
"name": "right",
"type": "string"
}
]
}java写:
Schema.Parser parser = new Schema.Parser();
Schema schema = parser.parse(App.class.getResourceAsStream("/StringPair.avsc"));
GenericRecord record = new GenericData.Record(schema);
record.put("left", "L");
record.put("right", "R");
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DatumWriter writer = new GenericDatumWriter<>(schema);
Encoder encoder = EncoderFactory.get().binaryEncoder(out, null);
writer.write(record, encoder);
encoder.flush();
out.close(); DatumWriter 将数据对象翻译成Encoder可以理解的类型。然后有Encoder写入到输出流中。
/** Write data of a schema.
* Implemented for different in-memory data representations.
*/
public interface DatumWriter {
/** Set the schema. */
void setSchema(Schema schema);
/** Write a datum. Traverse the schema, depth first, writing each leaf value
* in the schema from the datum to the output. */
void write(D datum, Encoder out) throws IOException;
} read:
DatumReader reader = new GenericDatumReader<>(schema);
Decoder decoder = DecoderFactory.get().binaryDecoder(out.toByteArray(),null);
record = reader.read(null,decoder);
record.get("left");
record.get("right"); //输出类型是UTF8
System.out.println(record.toString()); 使用maven插件生成Model
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.avrogroupId>
<artifactId>avro-maven-pluginartifactId>
<version>${avro.version}version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>schemasid>
<phase>generate-sourcesphase>
<goals>
<goal>schemagoal>
goals>
<configuration>
<sourceDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resourcessourceDirectory>
<outputDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/java/outputDirectory>
configuration>
execution>
executions>
plugin>在工程目录下运行命令:mvn generate-sources 即可在目录下生成java 代码。当然也可以使用 avro-tools 工具包,不过有些麻烦。
使用StringPair实例代替GenericRecord:
StringPair pair = new StringPair();
pair.setLeft("L");
pair.setRight("R");
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DatumWriter writer = new SpecificDatumWriter<>(StringPair.class);
Encoder encoder = EncoderFactory.get().binaryEncoder(byteArrayOutputStream,null);
writer.write(pair,encoder);
encoder.flush();
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
DatumReader reader = new SpecificDatumReader<>(StringPair.class);
Decoder decoder = DecoderFactory.get().binaryDecoder(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(),null);
StringPair result = reader.read(null,decoder);
System.out.println(result); Avro Datafiles
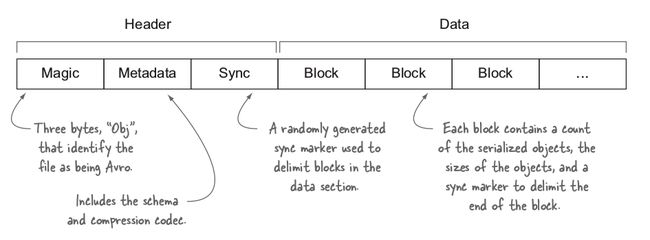
从文章开头的图看到了,数据文件的Header包含元数据(Avro schema 和 sync marker),紧接着是一系列包含序列化Avro对象的数据块。数据块由sync marker来分隔,它对于该文件是唯一的,并且可以像HDFS block一样,允许在文件中搜索到任意位置之后通过 block边界快速地重新进行同步。因此,Avro数据文件是可切分的。
数据文件的扩展名一般为 .avro
换个例子:
DataFileWriter writer = new DataFileWriter<>(new SpecificDatumWriter<>());
System.out.println(App.class.getResource("/"));
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("/data/workspace/hadoop/target/stocks.avro");
writer.setCodec(CodecFactory.snappyCodec());
writer.create(Stock.SCHEMA$,outputStream);
AvroStockUtils.fromCsvStream(App.class.getResourceAsStream("/stocks.txt"))
.stream().forEach(s -> {
try {
writer.append(s);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
IOUtils.closeStream(writer);
IOUtils.closeStream(outputStream);
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("/data/workspace/hadoop/target/stocks.avro");
DataFileStream stream = new DataFileStream<>(inputStream,new SpecificDatumReader(Stock.class));
stream.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
IOUtils.closeStream(stream);
IOUtils.closeStream(inputStream); scheme文件:
{
"namespace":"com.hadoop2.data",
"name": "Stock",
"type": "record",
"fields":[
{"name": "symbol", "type":"string"},
{"name": "date", "type":"string"},
{"name": "open", "type":"double"},
{"name": "high", "type":"double"},
{"name": "low", "type":"double"},
{"name": "close", "type":"double"},
{"name": "volume", "type":"int"},
{"name": "adjClose", "type":"double"}
]
}输出:
{"symbol": "MSFT", "date": "2002-01-02", "open": 66.65, "high": 67.11, "low": 65.51, "close": 67.04, "volume": 48124000, "adjClose": 27.4}
{"symbol": "MSFT", "date": "2001-01-02", "open": 44.13, "high": 45.0, "low": 42.88, "close": 43.38, "volume": 82413200, "adjClose": 17.73}
{"symbol": "MSFT", "date": "2000-01-03", "open": 117.37, "high": 118.62, "low": 112.0, "close": 116.56, "volume": 53228400, "adjClose": 47.64}
{"symbol": "YHOO", "date": "2009-01-02", "open": 12.17, "high": 12.85, "low": 12.12, "close": 12.85, "volume": 9514600, "adjClose": 12.85}
{"symbol": "YHOO", "date": "2008-01-02", "open": 23.8, "high": 24.15, "low": 23.6, "close": 23.72, "volume": 25671700, "adjClose": 23.72}
{"symbol": "YHOO", "date": "2007-01-03", "open": 25.85, "high": 26.26, "low": 25.26, "close": 25.61, "volume": 26352700, "adjClose": 25.61}
{"symbol": "YHOO", "date": "2006-01-03", "open": 39.69, "high": 41.22, "low": 38.79, "close": 40.91, "volume": 24227700, "adjClose": 40.91}上面是以java对象的方式读取,换种方法,使用GenericRecord,比较啰嗦
Schema schema = new Schema.Parser().parse(new File("/data/workspace/hadoop/src/main/resources/Stock.avsc"));
File file = new File("/data/workspace/hadoop/src/main/resources/stocks.avro");
DatumWriter writer = new GenericDatumWriter<>(schema);
DataFileWriter dataFileWriter = new DataFileWriter<>(writer);
dataFileWriter.setCodec(CodecFactory.snappyCodec());
dataFileWriter.create(schema,file);
List list = Files.lines(new File("/data/workspace/hadoop/src/main/resources/stocks.txt").toPath()).collect(Collectors.toList());
list.stream().forEach(s -> {
String[] arrays = s.split(",");
GenericRecord record = new GenericData.Record(schema);
record.put("symbol",arrays[0]);
record.put("date",arrays[1]);
record.put("open",Double.valueOf(arrays[2]));
record.put("high",Double.valueOf(arrays[3]));
record.put("low",Double.valueOf(arrays[4]));
record.put("close",Double.valueOf(arrays[5]));
record.put("volume",Integer.valueOf(arrays[6]));
record.put("adjClose",Double.valueOf(arrays[7]));
try {
dataFileWriter.append(record);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
IOUtils.closeStream(dataFileWriter);
DatumReader reader = new GenericDatumReader<>();
DataFileReader dataFileReader = new DataFileReader(file,reader);
GenericRecord record;
while (dataFileReader.hasNext()){
record = dataFileReader.next();
System.out.println(record);
} 如果需要随机访问数据文件,使用seek() and sync()方法。
avro mapreduce
还是拿最大气温举例:
public class AvroGenricMaxTemperature extends Configured implements Tool {
private static final Schema SCHEMA = new Schema.Parser().parse("{" +
" \"type\": \"record\"," +
" \"name\": \"WeatherRecord\"," +
" \"doc\": \"A weather reading.\"," +
" \"fields\": [" +
"{\"name\": \"year\", \"type\": \"int\"}," +
"{\"name\": \"temperature\", \"type\": \"int\"}," +
"{\"name\": \"stationId\", \"type\": \"string\"}" +
" ]" +
"}");
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int code = ToolRunner.run(new AvroGenricMaxTemperature(),args);
System.exit(code);
}
@Override
public int run(String[] strings) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(getConf(),"AvroGenricMaxTemperature");
job.setJarByClass(getClass());
//使用用户avro版本
job.getConfiguration().setBoolean(Job.MAPREDUCE_JOB_USER_CLASSPATH_FIRST,true);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("hdfs://hadoop:9000/user/madong/input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("hdfs://hadoop:9000/user/madong/avro-out"));
AvroJob.setMapOutputKeySchema(job,Schema.create(Schema.Type.INT));
AvroJob.setMapOutputValueSchema(job,SCHEMA);
AvroJob.setOutputKeySchema(job,SCHEMA);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(AvroKeyOutputFormat.class);
job.setMapperClass(MaxTemperatureMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(MaxTemperatureReducer.class);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
static class MaxTemperatureMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,AvroKey<Integer>,AvroValue<GenericRecord>>{
private NcdcRecordParser parser = new NcdcRecordParser();
private GenericRecord record = new GenericData.Record(SCHEMA);
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
parser.parse(value);
if (parser.isValidTemperature()){
record.put("year",parser.getYearInt());
record.put("temperature",parser.getAirTemperature());
record.put("stationId",parser.getStationId());
context.write(new AvroKey<>(parser.getYearInt()),new AvroValue<>(record));
}
}
}
static class MaxTemperatureReducer extends Reducer<AvroKey<Integer>,AvroValue<GenericRecord>,AvroKey<GenericRecord>,NullWritable>{
@Override
protected void reduce(AvroKey key, Iterable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
GenericRecord max = null;
for (AvroValue value : values){
GenericRecord record = value.datum();
if (max == null || (Integer)record.get("temperature") > (Integer)max.get("temperature")){
max = newWeatherRecord(record);
}
}
context.write(new AvroKey<>(max),NullWritable.get());
}
private GenericRecord newWeatherRecord(GenericRecord value) {
GenericRecord record = new GenericData.Record(SCHEMA);
record.put("year", value.get("year"));
record.put("temperature", value.get("temperature"));
record.put("stationId", value.get("stationId"));
return record;
}
}
} Avro与常规的Hadoop MapReduce 有两处不同:
第一,使用Avro java类型的包装类。在这个程序中,key是year,value是气象记录,用GenericRecord表示。在map输出,reduce输入时,使用AvroKey,AvroValue包装。
第二, 使用AvroJob配置job。AvroJob 主要用于配置 map输入、输出,以及最后数据输出的schema。在上面的程序中,因为读取的是text,没有设置输入schema。
sort
Avro自身定义了对象的排列顺序,不过至于三种方式: ascending(默认)、descending、ignore。
下面代码示例结合Avro的mapreduce排序:
public class AvroSort extends Configured implements Tool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new AvroSort(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
@Override
public int run(String[] strings) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(getConf(),"AvroSort");
job.setJarByClass(getClass());
//使用用户avro版本
job.getConfiguration().setBoolean(Job.MAPREDUCE_JOB_USER_CLASSPATH_FIRST,true);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("hdfs://hadoop:9000/user/madong/avro/pairs.avro"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("hdfs://hadoop:9000/user/madong/avro-out"));
AvroJob.setDataModelClass(job, GenericData.class);
Schema schema = new Schema.Parser().parse(new File("/data/workspace/hadoop/src/main/resources/SortedStringPair.avsc"));
AvroJob.setInputKeySchema(job,schema);
// AvroKey,AvroValue
AvroJob.setMapOutputKeySchema(job,schema);
AvroJob.setMapOutputValueSchema(job,schema);
//AvroKey,NullWritable
AvroJob.setOutputKeySchema(job,schema);
job.setInputFormatClass(AvroKeyInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(AvroKeyOutputFormat.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(AvroKey.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class);
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
static class SortMapper<K> extends Mapper<AvroKey<K>,NullWritable,AvroKey<K>,AvroValue<K>>{
@Override
protected void map(AvroKey key, NullWritable value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key,new AvroValue(key.datum()));
}
}
static class SortReducer<K> extends Reducer<AvroKey<K>,AvroValue<K>,AvroKey<K>,NullWritable>{
@Override
protected void reduce(AvroKey key, Iterable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (AvroValue value : values){
context.write(new AvroKey(value.datum()),NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
} 排序发生在 mapreduce的shuffle期间,并且排序函数有Avro schema确定并传入程序中。