Class -- 08 -- Parameter类常用方法解析
这次主要整理下 Java 中 Parameter 类的常用方法
一、Parameter 类的定义
-
Parameter 类位于 java.lang.reflect 包中,主要用于在程序运行状态中,动态地获取参数信息
-
在 JDK8.0 之前,编译器会忽略我们编写代码时设定的参数名,因此会得到像 arg0、arg1 这样无意义的参数名,比如:当我们使用 mybatis 时,我们会用到 @Param 注解来使 mybatis 保留参数名称
-
在 JDK8.0 及之后,Java 在语言层面 (使用反射 API 和 Parameter.getName() 方法) 和字节码层面 (使用新的 javac 编译器以及 -parameters 参数) 提供了支持,不过为了保证向下兼容,在 JDK8.0 及之后的版本中该特性是默认关闭的
-
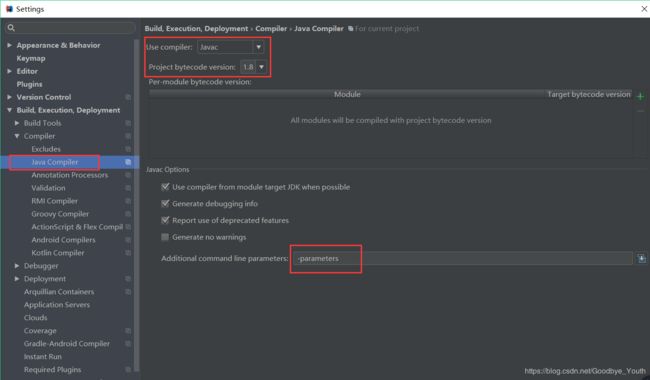
如果使用了 maven,可以配置 maven 的编译插件
<plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-pluginartifactId> <version>3.8.0version> <configuration> <compilerArgument>-parameterscompilerArgument> <source>1.8source> <target>1.8target> configuration> plugin> -
示例如下
public class ParameterTest { public void test(String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); for (Parameter parameter : parameters) { // 正常编译得到: arg0 arg1 // 加入-parameters后编译得到: key value System.out.println(parameter.getName()); } } }
二、Parameter 类常用方法
-
getAnnotatedType()
-
返回一个 AnnotatedType 对象,该对象表示使用类型来指定由该参数对象表示的形式参数的类型
-
通过其 getType() 方法,我们可以获取到对应的形参类型
public class ParameterTest { public void test(String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); for (Parameter parameter : parameters) { AnnotatedType annotatedType = parameter.getAnnotatedType(); // class java.lang.String // class java.lang.String System.out.println(annotatedType.getType()); } } }
-
-
getAnnotation(Class
annotationClass) -
如果该参数对象存在指定类型的注解,则返回该注解,否则返回 null
-
只有类级别的注解会被继承得到,对于其他对象而言,getAnnotation() 方法与 getDeclaredAnnotation() 方法作用相同
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface ParameterAnnotation { String key(); String value(); } public class ParameterTest { public void test(@ParameterAnnotation(key = "key", value = "value") String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); ParameterAnnotation annotation = parameters[0].getAnnotation(ParameterAnnotation.class); // @lang.reflect.Parameter.ParameterAnnotation(key=key, value=value) System.out.println(annotation); } }
-
-
getDeclaredAnnotation(Class
annotationClass) -
如果该参数对象存在指定类型的注解,则返回该注解,否则返回 null
-
只有类级别的注解会被继承得到,对于其他对象而言,getAnnotation() 方法与 getDeclaredAnnotation() 方法作用相同
-
-
getAnnotationsByType(Class
annotationClass) -
如果该参数对象存在指定类型的注解,则返回该注解数组,否则返回 null
-
只有类级别的注解会被继承得到,对于其他对象而言,getAnnotationsByType() 方法与 getDeclaredAnnotationsByType() 方法作用相同
-
getAnnotationsByType() 方法与 getAnnotation() 方法的区别在于:getAnnotationsByType() 方法会检查修饰该参数对象的注解是否为可重复类型注解,如果是则会返回修饰该参数对象的一个或多个注解
-
@Repeatable 用于声明注解为可重复类型注解
-
当声明为可重复类型注解后,如果参数注解仍为一个,则 getAnnotation() 方法会正常返回,如果参数注解为多个,则 getAnnotation() 方法会返回 null
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // @Repeatable: 声明该注解为可重复类型注解 @Repeatable(RepeatableAnnotation.class) public @interface ParameterAnnotation { String key(); String value(); } @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface RepeatableAnnotation { ParameterAnnotation[] value(); } public class ParameterTest { public void test(@ParameterAnnotation(key = "key1", value = "value1") @ParameterAnnotation(key = "key2", value = "value2") String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); ParameterAnnotation annotation = parameters[0].getAnnotation(ParameterAnnotation.class); // null System.out.println(parameters[0].getAnnotation(ParameterAnnotation.class)); ParameterAnnotation[] annotationsByType = parameters[0].getAnnotationsByType(ParameterAnnotation.class); // [@lang.reflect.ParameterAnnotation(key=key1, value=value1), @lang.reflect.ParameterAnnotation(key=key2, value=value2)] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(annotationsByType)); } }
-
-
getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class
annotationClass) -
如果该参数对象存在指定类型的注解,则返回该注解数组,否则返回null
-
只有类级别的注解会被继承得到,对于其他对象而言,getAnnotationsByType() 方法与 getDeclaredAnnotationsByType() 方法作用相同
-
-
getAnnotations()
-
返回该参数对象上的所有注解,如果没有注解,则返回空数组
-
只有类级别的注解会被继承得到,对于其他对象而言,getAnnotations() 方法与 getDeclaredAnnotations() 方法作用相同
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface ParameterAnnotation { String key(); String value(); } @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface TestAnnotation { String key(); String value(); } public class ParameterTest { public void test(@ParameterAnnotation(key = "key1", value = "value1") @TestAnnotation(key = "key2", value = "value2") String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); Annotation[] annotations = parameters[0].getAnnotations(); // [@lang.reflect.ParameterAnnotation(key=key1, value=value1), @lang.reflect.TestAnnotation(key=key2, value=value2)] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(annotations)); } }
-
-
getDeclaredAnnotations()
-
返回该参数对象上的所有注解,如果没有注解,则返回空数组
-
只有类级别的注解会被继承得到,对于其他对象而言,getAnnotations() 方法与 getDeclaredAnnotations() 方法作用相同
-
-
getModifiers()
-
返回修饰该参数对象修饰符的整数形式,使用 Modifier 类对其进行解码
public class ParameterTest { public void test(final String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // final System.out.println(Modifier.toString(parameters[0].getModifiers())); } }
-
-
getName()
-
返回参数对象名称
public class ParameterTest { public void test(String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); for (Parameter parameter : parameters) { // 正常编译得到: arg0 arg1 // 加入-parameters后编译得到: key value System.out.println(parameter.getName()); } } }
-
-
getParameterizedType()
-
返回一个类型对象,该对象表示该参数对象表示的泛型参数的类型 (保留泛型)
public class ParameterTest<T> { public void test(T t, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", Object.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // T System.out.println(parameters[0].getParameterizedType().getTypeName()); } }
-
-
getType()
-
返回一个 Class 对象,该 Class 对象表示该参数对象表示的声明参数的类型 (擦除泛型)
public class ParameterTest<T> { public void test(T t, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", Object.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // class java.lang.Object System.out.println(parameters[0].getType()); } }
-
-
isAnnotationPresent(Class annotationClass)
-
如果该参数对象上有指定类型的注解,则返回 true,否则为 false
public class ParameterTest { public void test(@ParameterAnnotation(key = "key", value = "value") String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // true System.out.println(parameters[0].isAnnotationPresent(ParameterAnnotation.class)); } } -
如果该参数对象上的注解类型为可重复类型注解,则需要标明可重复注解而不是其子注解,才会返回 true,否则为 false
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Repeatable(RepeatableAnnotation.class) public @interface ParameterAnnotation { String key(); String value(); } @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface RepeatableAnnotation { ParameterAnnotation[] value(); } public class ParameterTest { public void test(@ParameterAnnotation(key = "key1", value = "value1") @ParameterAnnotation(key = "key2", value = "value2") final String key, String value) { } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // false System.out.println(parameters[0].isAnnotationPresent(ParameterAnnotation.class)); // true System.out.println(parameters[0].isAnnotationPresent(RepeatableAnnotation.class)); } }
-
-
isVarArgs()
-
如果该参数对象表示 可变参,则返回 true,否则为 false
public class ParameterTest { public void test(String key, String ... values) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String[].class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // false System.out.println(parameters[0].isVarArgs()); // true System.out.println(parameters[1].isVarArgs()); } }
-
-
isNamePresent()
-
如果该参数对象根据类文件能获取到名称,则返回 true,否则为 false
-
当我们带上 -parameters 参数时,该参数对象就有了名称
public class ParameterTest { public void test(String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // 正常编译得到: false arg0 // 加入-parameters 后编译得到: true key System.out.println(parameters[0].isNamePresent() + " " + parameters[0].getName()); } }
-
-
getDeclaringExecutable()
-
返回声明该参数对象的可执行文件
public class ParameterTest { public void test(String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // public void lang.reflect.ParameterTest.test(java.lang.String,java.lang.String) System.out.println(parameters[0].getDeclaringExecutable()); } }
-
-
isImplicit()
-
如果该参数对象为隐式参数,则返回 true,否则为 false
-
Java 编译器会为内部类的构造方法创建一个隐式参数
public class ParameterTest { class InnerClass { public InnerClass(String key) { } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Constructor<InnerClass> declaredConstructor = InnerClass.class.getConstructor(ParameterTest.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = declaredConstructor.getParameters(); for (Parameter parameter : parameters) { // 【final lang.reflect.ParameterTest this$0】 isImplicit() ===> true // 【java.lang.String key】 isImplicit() ===> false System.out.println("【" + parameter + "】 isImplicit() ===> " + parameter.isImplicit()); } } }
-
-
isSynthetic()
-
如果该参数对象为合成参数,则返回 true,否则为 false
public class ParameterTest { public void test(String key, String value) {} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Method method = ParameterTest.class.getMethod("test", String.class, String.class); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // false System.out.println(parameters[0].isSynthetic()); } }
-