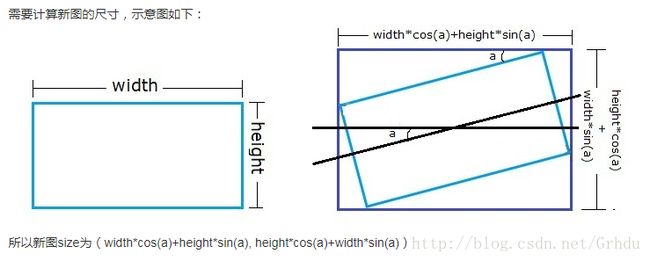
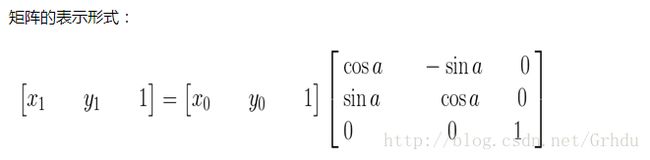图像的仿射变换
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
Mat srcImage, dstImage;
srcImage = imread("1.jpg");
if (!srcImage.data)
{
cout << "读入图片有误!" << endl;
return -1;
}
imshow("原图像", srcImage);//读入原图
//dstImage.create(srcImage.size(), srcImage.type());
double degree=50;//旋转角度可修改或者自行输入
//cout << "请输入旋转角度:";
//cin >> degree;
double a = sin(degree * CV_PI / 180);//sin(弧度)的值
double b = cos(degree * CV_PI / 180);//cos(弧度)的值
int width = srcImage.cols;
int height = srcImage.rows;
//旋转之后新图像的大小
int rotate_width = int(height * fabs(a) + width * fabs(b));
int rotate_height = int(width * fabs(a) + height * fabs(b));
Point center = Point(srcImage.cols / 2, srcImage.rows / 2);//旋转中心不变
//求旋转矩阵如下
Mat map_matrix = getRotationMatrix2D(center, degree, 1.0);
//旋转数组map_matrix
// [ m0 m1 m2 ] ===> [ A11 A12 b1 ]
// [ m3 m4 m5 ] ===> [ A21 A22 b2 ]
//在旋转中坐标原点是左上角的点,X轴沿着水平方向向右,Y轴沿着竖直方向向下,旋转后坐标原点也应该偏移改变
map_matrix.at<double>(0, 2) += (rotate_width - width) / 2; // 修改坐标偏移,修改m2
map_matrix.at<double>(1, 2) += (rotate_height - height) / 2; // 修改坐标偏移,修改m5
warpAffine(srcImage, dstImage, map_matrix, Size(rotate_width, rotate_height), CV_INTER_CUBIC);
Mat resizeimage;
resize(dstImage, resizeimage, Size(600, 600), (0, 0), (0, 0), INTER_LINEAR);//图像缩放便于查看
imshow("rotateimage", resizeimage);
waitKey();
return 0;
}(1)函数 getRotationMatrix2D(Point2fcenter, double angle,
double scale)
第一个參数,Point2f类型的center。表示源图像的旋转中心。
第二个參数,double类型的angle。旋转角度。角度为正值表示向逆时针旋转(坐标原点是左上角)。
第三个參数,double类型的scale,缩放系数。
(2)函数 warpAffine(InputArray src,OutputArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags=INTER_LINEAR,
intborderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar())
第一个參数,InputArray类型的src。输入图像。即源图像。填Mat类的对象就可以。
第二个參数,OutputArray类型的dst,函数调用后的运算结果存在这里,需和源图片有一样的尺寸和类型。
第三个參数,InputArray类型的M。2×3的变换矩阵。
第四个參数,Size类型的dsize,表示输出图像的尺寸。
第五个參数,int类型的flags,插值方法的标识符。
此參数有默认值INTER_LINEAR(线性插值),可选的插值方式例如以下:
INTER_NEAREST - 近期邻插值
INTER_LINEAR - 线性插值(默认值)
INTER_AREA - 区域插值
INTER_CUBIC –三次样条插值
INTER_LANCZOS4 -Lanczos插值
CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS - 填充全部输出图像的象素。假设部分象素落在输入图像的边界外,那么它们的值设定为 fillval.
CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP –表示M为输出图像到输入图像的反变换。即 。因此能够直接用来做象素插值。否则, warpAffine函数从M矩阵得到反变换。
第六个參数。int类型的borderMode,边界像素模式,默认值为BORDER_CONSTANT。
第七个參数,const Scalar&类型的borderValue,在恒定的边界情况下取的值,默认值为Scalar(),即0。
注:另外提一点,我们的WarpAffine函数与一个叫做cvGetQuadrangleSubPix( )的函数类似,可是不全然同样。 WarpAffine要求输入和输出图像具有同样的数据类型,有更大的资源开销(因此对小图像不太合适)并且输出图像的部分能够保留不变。
2、旋转(不再继续维持原图大小,保持窗口大小不变,可能会存在图像不能完全显现)
#include3、透视变换
#include