《ElasticStack从入门到实践》学习笔记3
三、ElasticSearch的Mapping设置
1、Mapping简介:
1)类似于数据库中的表结构,主要作用如下:
A、定义Index下的Field Name;
B、定义Field的类型,如:数值型、字符串型、布尔型等;
C、定义倒排索引的相关配置,如:是否有索引,记录position等。
2)获取一个mapping,使用endpoint:_mapping,例如:
GET /test_index/_mapping2、自定义Mapping:
1)使用mappings进行自定义mapping,示例:
#创建名为my_index的索引,并自定义mapping
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{ #1.关键字
"doc":{ #2.类型名
"properties":{ #4.字段名称及类型定义
"title":{
"type":"text" #3.字段类型
},
"name":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
}
} #4.截止
}
}
}Mapping中的字段类型一旦设定之后,禁止直接修改。因为Luence事先的倒排索引生成后不能修改。如果一定要改,可以重新建立新的索引,然后对应修改mapping,之后将之前的数据进行reindex操作,导入新的文档。
2)自定义mapping时允许新增字段。通过dynamic参数进行控制字段的新增,dynamic有三种配置:
A、true。默认配置,允许自动新增字段;
B、false。不允许自动新增字段,文档可以正常写入,但不能进行查询等操作;
C、strict。严格模式。文档不能写入,写入会报错。
#使用dynamic参数控制字段的新增
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"dynamic":false, #设置为false,索引不允许新增字段
"properties":{
"title":{
"type":"text"
},
"name":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
}
}
}
}
}如果此时,PUT新的字段,就不会成功,虽然不报错,但是没有内容:
#向名为my_index的索引增加字段
PUT my_index
{
"name":"moumou",
"gender":"male"
}使用head插件可以看到,此时只有name存储成功:
3、copy_to的使用:
功能:将该字段的值复制到目标字段,类似于6.0版本之前的_all的作用。且不会出现在_source,一般只用来进行搜索。
#copy_to的使用
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"properties":{
"first_name":{
"type":"text",
"copy_to":"full_name"
},
"last_name":{
"type":"text",
"copy_to":"full_name"
},
"full_name":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}
}向索引my_index传入数据:
#向索引写入数据
PUT my_index/doc/1
{
"first_name":"John",
"last_name":"Smith"
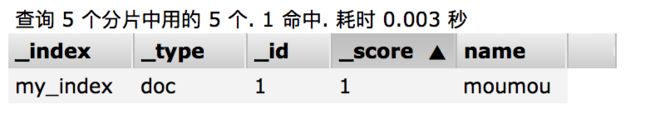
}此时查询结果:
#查询索引my_index中full_name同时包含John 和 Smith的数据
GET my_index/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"full_name":{
"query":"John Smith",
"operator":"and"
}
}
}
}返回结果:
4、index参数的使用:
功能:控制当前字段是否为索引,默认true,当设置为false的时候,不进行记录,此时该字段不能被搜索
#index参数的使用
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"properties":{
"cookie":{
"type":"text",
"index":false #设置为false,该字段不能被搜索
}
}
}
}
}此时在进行数据写入和查询,不能进行该字段搜索。一般用来进行不想被查询的私密信息设置,如身份证号,电话号码等:
#向使用了index参数的字段写入信息
PUT my_index/doc/1
{
"cookie":"name=alfred"
}查询及返回结果:
5、index_options参数的使用:
功能:控制倒排索引记录的内容,有如下四种配置:
1)docs 只记录文档ID
2)freqs 记录文档ID和词频TF
3)positions 记录文档ID、词频TF和分词位置
4)offsets 记录文档ID、词频TF、分词位置和偏移
其中:text类型默认的配置是positions,其他的比如integer等类型默认为docs,目的是为了节省空间。
#index_options参数的使用
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"properties":{
"cookie":{
"type":"text",
"index_options":"offsets" #记录文档ID、词频TF、分词位置和偏移
}
}
}
}
}6、null_value参数的使用:
功能:当字段遇到空值null时的处理策略。默认为null,即跳过。此时ES会忽略该值,可通过修改进行默认值的修改:
#使用null_value修改ES遇到null值时的默认返回值
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"properties":{
"cookie":{
"type":"keyword",
"null_value":"NULL" #当遇到空值null的时候,返回一个字符串形式的NULL
}
}
}
}
}7、Field字段的数据类型:
1)核心数据类型
A、字符串型。 text(分词),keyword(不分词)
B、数值型。 long、integer、short、byte、double、float、half_float、scaled_float
C、日期类型。 date
D、布尔类型。 boolean
E、二进制类型。 binary
F、范围类型。 integer_range、float_range、long_range、double_range、date_range
2)复杂数据类型
A、数组类型。 array
B、对象类型。 object
C、嵌套类型。 nested object
3)地理位置数据类型
A、点。 geo-point
B、形状。 geo-shape
4)专用类型
A、记录ip地址。 ip
B、实现自动补全。 completion
C、记录分词数。 token_count
D、记录字符串hash值。murmur3
E、perclator。
F、join。
5)多字段特性:
ES允许对同一个字段采用不同的配置,如:分词。举例:对一个人名实现拼音搜索,只需要在人名字段中新增一个子字段pinyin即可。
#多字段特性
{
"my_index":{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"properties":{
"username":{
"type":"text",
"field":{ #增加子字段pinyin
"pinyin":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"pinyin"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}8、ES的自动类型识别:
1)Dynamic Mapping:
ES可以自动识别文档字段类型,从而降低用户使用成本。
#ES的自动类型识别
PUT my_index/doc/1
{
"username":"alfred", #username字段自动识别为text类型
"age":20 #age字段自动识别为long类型
}2)ES依靠JSON文档的字段类型实现自动识别字段类型:
| JSON类型 |
ElasticSearch类型 |
| null | 忽略 |
| boolean | boolean |
| 浮点类型 | float |
| 整数类型 | long |
| object | object |
| array | 由第一个非null的值的类型决定 |
| String | 匹配为日期,则为date类型(默认开启); 匹配为数字,则为long类型/float类型(默认关闭); 都未匹配,则设为text类型,并附带keyword子字段 |
3)验证ES的字段类型自动识别:
#验证ES的字段类型自动识别
PUT my_index/doc/1
{
"username":"alfred", #字符串类型text
"age":20, #整数long
"bitrh":"1998-10-10", #默认识别日期date
"married":false, #布尔类型boolean
"year":"18" #默认不识别数字text
"tags":["boy","fashion"], #数组中第一个不为null的元素为字符串类型,所以为text
"money":100.1 #浮点类型float
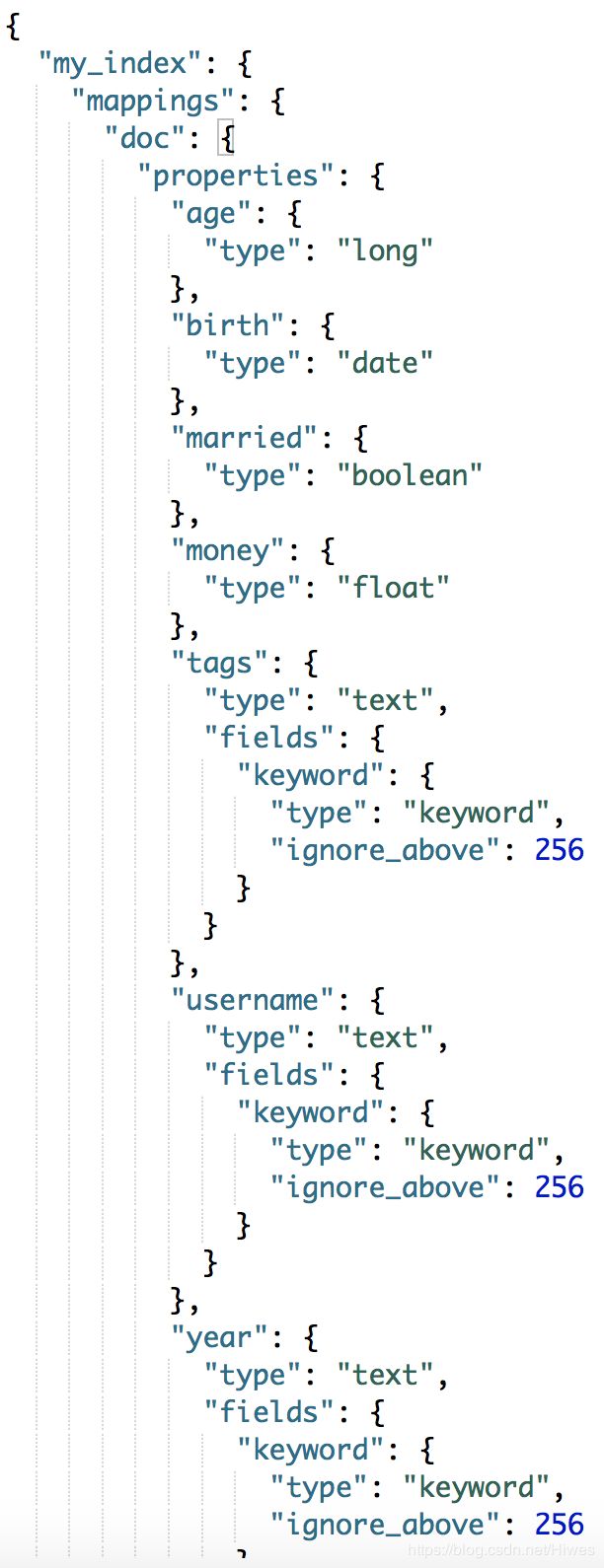
}再对my_index进行mapping查询,就会获得每个字段的类型:
9、ES中日期类型和数字的自动识别:
ES中可自行配置日期的格式,默认:["strict_date_optional_time","yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss Z|| yyyy/MM/dd z"]
1)使用dynamic_date_formats自定义日期格式:
#使用dynamic_date_formats自定义日期格式
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"dynamic_date_formats":["MM/dd/yyyy"]
}
}
}
#写入符合自定义格式的日期数据,可识别为date类型
PUT my_index/doc/1
{
"create_time":"01/01/2018" #create_time字段识别为date类型
}2)使用date_detection可以关闭自动识别日期格式:
#使用date_detection关闭日期的自动识别
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"date_detection":false
}
}
}
PUT my_index/doc/1
{
"create_time":"01/01/2018" #create_time字段是text类型
}ES中可配置数字是否识别,默认关闭:
#ES配置开启数字的自动识别
PUT my_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"numeric_detection":true #开启数字自动识别
}
}
}
#写入数字数据,ES可以自动识别其类型
PUT mu_index/doc/1
{
"year":"18", #year字段自动识别为long类型
"money":"100.1" #money字段自动识别为float类型
}10、ES中根据自动识别的数据类型,动态生成字符类型:
1)(例)所有字符串类型都设为keyword类型(不分词)
2)(例)所有以message开头的字段都设为text类型(分词)
3)(例)所有以long_开头的字段都设为long类型
4)(例)所有自动匹配为double的类型都设为float类型。(为了节省空间)
举例:下面的例子就是讲匹配到的字符串类型都设为keyword类型。
#ES根据自动识别的数据类型、字段名等动态设定字符类型
PUT test_index
{
"mappings":{
"doc":{
"dynamic_template":[
{
"strings":{
"match_mapping_type":"string", #匹配到所有的字符串类型,全部设为keyword类型
"mapping":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}匹配规则一般有如下几个参数:
1)match_mapping_type 匹配ES自动识别的字段类型,如boolean、long、string等;
2)match、unmatch 匹配字段名,比如"match":"message*" ===>以message开头的数据;
3)path_match、path_unmatch 匹配路径
11、一般来说,自定义mapping的操作步骤如下:
1)写入一条文档到ES的临时索引中,获取(复制)ES自动生成的mapping;
2)修改获得的mapping,并在其中自定义相关配置;
3)使用修改后的mapping创建实际所需索引。
这样不但在开发上简便不少,而且还能防止字段遗漏。