boost智能指针
一.安装boost
1.首先去下载最新的boost代码包,网址www.boost.org
2.进入到自己的目录,解压:
bzip2 -d boost_1_64_0.tar.bz2
tar -zxvf boost_1_64_0.tar.gz
3.之后进入boost目录
cd boost_1_64_0/
./bootstrap.sh之后会产生bjam和b2两个工具
sudo ./b2 install(确定已经安装了g++与gcc,此过程会花费一些时间)
这个时候你的/usr/local/include下会产生boost的头文件,
/usr/local/lib下面会产生boost库
4.切换到cd /etc/profile.d目录下,使用超级用户创建文件boost.sh
里面添加如下内容
#!/bin/sh
BOOST_ROOT=/home/liuqi/boost_1_64_0(boost的解压路径)
BOOST_INCLUDE=/usr/local/include/boost
BOOST_LIB=/usr/local/lib
export BOOST_INCLUDE BOOST_LIB BOOST_ROOT
修改boost.sh的权限 sudo chmod +x boost.sh,执行./boost.sh
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/lib
可以在 ~/.bashrc 或者 ~/.bash_profile 中加入 export 语句
5.至此,安装完毕,测试代码
二.智能指针
1.智能指针是利用RAII(Resource Acquistion Is Initialization:资源获取即初始化)来管理资源
2.智能指针本质思想:
(1)将堆对象的生存期用栈对象(智能指针)来管理,当new一个堆对象的时候,立刻用智能指针来接管,具体做法是在构造函数进行初始化(用一个指针指向堆对象),在析构 函数中调用delete来释放堆对象;(2)由于智能指针本身是一个栈对象,它的作用域结束的时候,自动调用析构函数,从而调用delete释放了堆对象。
三.shared_ptr
1.shared_ptr内部维护一个引用计数器来判断此指针是不是需要被释放,线程安全https://blog.csdn.net/INGNIGHT/article/details/99881762=
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class X {
public:
X() {
cout << "X" << endl;
}
~X() {
cout << "~X" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
boost::shared_ptr p1(new X);
cout << p1.use_count() << endl; //1
boost::shared_ptr p2(p1);
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; //2
p1.reset();
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; //1
p2.reset();
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; //0
boost::shared_ptr p3;
p3 = p2;
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; //0
cout << p3.use_count() << endl; //0
return 0;
}
2.避免使用匿名的临时shared_ptr
void f(shared_ptr, int);
int g();
void ok()
{
shared_ptr p(new int(2));
f(p,g());
}
void bad)()
{
f(shared_ptr(new int(2)),g());
} 3.shared_ptr可以作为容器成员
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class X {
public:
X() {
cout << "X" << endl;
}
~X() {
cout << "~X" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
//auto_ptr不能作为容器成员
//vector> v;
//auto_ptr p(new X);
//v.push_back(p); //Error
vector> v2;
boost::shared_ptr p2 = boost::shared_ptr(new X);
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; //1
v2.push_back(p2);
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; //2
return 0;
}
4.仿写shared_ptr 见地址 http://blog.csdn.net/ingnight/article/details/50651441
四.weak_ptr
1.(1)强引用,只要有一个引用存在,对象就不能释放
(2)弱引用,并不增加的引用计数,但它能知道对象是否存在
【1】如果存在,提升shared_ptr(强调用)成功
【2】如果不存在,提升失败
(3)通过weak_ptr访问对象的成员时候,要提升为shared_ptr
(4)weak_ptr
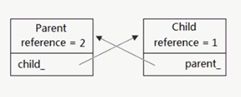
2.解决循环引用
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Parent;
class Child;
typedef boost::shared_ptr parent_ptr;
typedef boost::shared_ptr child_ptr;
class Parent {
public:
Parent() {
cout << "Parent()" << endl;
}
~Parent() {
cout << "~Parent()" << endl;
}
public:
boost::weak_ptr child_;
};
class Child {
public:
Child() {
cout << "Child()" << endl;
}
~Child() {
cout << "~Child()" << endl;
}
public:
parent_ptr parent_;
};
int main() {
parent_ptr parent(new Parent);
child_ptr child(new Child);
parent->child_ = child;
child->parent_ = parent;
//parent->child_.reset();
return 0;
}
3.
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class X{
public:
X() {
cout << "X..." << endl;
}
~X() {
cout << "~X..." << endl;
}
public:
void Fun() {
cout << "X::Fun()" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
boost::weak_ptr p;
{
boost::shared_ptr p2(new X);
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; // 1
p = p2;
cout << p2.use_count() << endl; // 1
boost::shared_ptr p3 = p.lock();
cout << p3.use_count() << endl; // 2
if(!p3) {
cout << "objec is destoryed" << endl;
}
else {
p3->Fun();
}
}
boost::shared_ptr p4 = p.lock();
if(!p4) {
cout << "objec is destoryed" << endl;
}
else {
p4->Fun();
}
boost::scoped_array xx(new X[3]);
return 0;
}
五.shared_array/scoped_array
shared_array